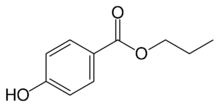
Chemistry:Propylparaben
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12O3 | |
| Molar mass | 180.203 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.0630 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 96 to 99 °C (205 to 210 °F; 369 to 372 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Paraben Butylparaben Ethylparaben Methylparaben |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Propylparaben is the n-propyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. It occurs as a natural substance found in many plants and some insects. Additionally, it can be manufactured synthetically for use in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and foods.[1] It is a member of the class of parabens and can be used as a preservative in many water-based cosmetics, such as creams, lotions, shampoos, and bath products.[2] As a food additive, it has an E number, which is E216.
Sodium propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, the sodium salt of Propyl Paraben, a compound with formula Na(C3H7(C6H4COO)O), is used similarly as a food additive and as an anti-fungal preservation agent. Its E number is E217.
In 2010, the European Union Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety stated that the use of butylparaben and Propyl Paraben as preservatives in finished cosmetic products as safe to the consumer, as long as the sum of their concentrations does not exceed 0.19%.[3]
Applications
Food
Under FDA regulations, Propyl paraben is safe to use with a maximum of 0.1% of the weight of the finished food or 200 - 450 ppm for a variety of foods like coffee extracts, juices, jams, baked goods, dairy products, etc.[4] It’s even found naturally in a plant called Stocksia brahuica.[5] It is often used as a food and cosmetic preservative as it has no odor or taste, and does not change the texture.[4] The compound has some medicinal application as well as it has been used in pills, syrups, eyewashes, weight gain drinks, and recently has been discovered to have anticonvulsant activities suggesting it may be useful in the development of anticonvulsant medicine.[4][6]
Recently, a study of combining Plasma-Activated Water (PAW) with Propyl paraben show increased antimicrobial efficacy of PAW for fresh produce sanitation. PAW is used for fresh produce sanitation. However when used in food applications, its effectiveness decreased due to interfering substances like polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids. With propyl paraben and PAW, bacteria's undergo more oxidative stress and cell damage, increasing preservation of produce. For now, The potential health risk and residue level of propyl paraben with this new method is still unknown.
Propyl Paraben is also used as a food additive, and is designated with the E number E216. Propyl Paraben is commonly used as a preservative in packaged baked goods, particularly pastries and tortillas.[7] Propyl Paraben is also a Standardized Chemical Allergen and is used in allergenic testing.[8][9]
Cosmetic
Propyl paraben is one of the most commonly used paraben in cosmetic formulation.[4] It can be found in moisturizers, shampoos, conditioners, makeups, shaving products, and many more.[10] In cosmetic products, Propyl paraben is typically combined with other parabens (i.e Methyl paraben) or other preservatives to protect against a broader range of microorganisms.[4] The chemical stability in room temperature and wide pH range (4.5-7.5) is advantageous to prolong a product shelf-life. Under FDA regulations, the maximum use of concentration for Propyl paraben is 25%.[10] However, cosmetics don't require testing by the FDA before selling.[10] While there's no conclusive evidence of harm to human health from propyl paraben, more cosmetic companies are creating Paraben-free lines, specifically in shampoos. Since paraben can easily absorb through your skin, daily use is believed to cause toxic accumulation in the body that might be harmful. Some people may also experience allergic reaction to parabens including redness, irritation, itchiness, flaking, and hives.[11]
Pharmaceutical
Used since mid 1920s as a preservative, parabens are present in our eyewashes, pills, cough syrups, injectable solutions, contraceptives, even weight-gain drinks.[4] Unlike cosmetics where propyl paraben is mostly used in the surface, propyl paraben is ingested and absorbed. According to the law made by EEC (European Economic Community) , the maximum level of parabens in pharmaceutical products is 1% (w/w),[12] much stricter and defined than cosmetics. Propyl paraben also can't be used alone in ophthalmic products, such as eyewash because it may cause irritation at the effective concentration level to have antimicrobial activities.[4]
A MES (Maximal Electroshock) test also shows anticonvulsant activity in Propyl paraben. Since Propyl paraben has minimum to no toxicity and well absorbed in the GI tract, it can potentially be develop to new anticonvulsant medicine to control seizures.[6]
Chemical Properties
Propyl paraben is a stable and non-volatile compound with antimicrobial properties and has been used as preservatives in food for over 50 years.[4] It is typically used in a variety of water-based cosmetics and personal-care products.[13] it is a white crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 202.18 amu.[14] Humans most often absorb the chemical through their skin or ingestion as it is in many cosmetic and food products as an antifungal preservative.[15][14] It is metabolized in two major pathways leading to the production of either conjugated metabolites or hydrolysates (PHBA, PHHA).[15] These products are excreted from the body in urine.[15] Propyl Paraben is an effective antimicrobial, especially against green and blue molds on citrus fruits.[14] Its high solubility in water allows it to be applied to the fruits easily.[14]
Synthesis
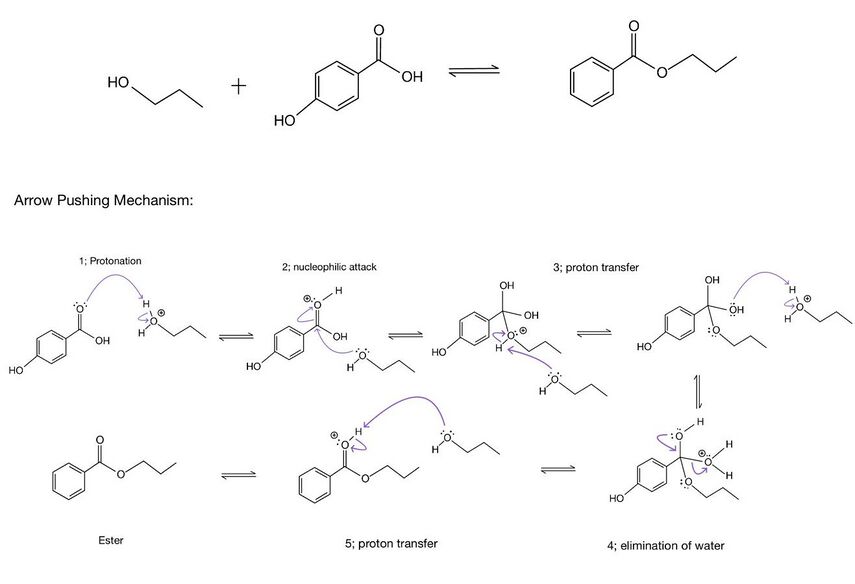
One of the simplest ways to produce Propyl Paraben is through the esterification of 4-hydroxy benzoic acid with propanol using an acidic catalyst.[16] The first major step includes the protonation of the carbonyl due to the acidic conditions. This protonation results in a positive charge on the carbonyl which will offset the electron density from the ester carbon atom, this allows the propanol to preform a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl.[17] The proton of the nucleophilic propanol is then transferred by the solvent to the esters hydroxyl group. The hydroxyl can then act as a good leaving group and be expelled from the tetrahedral intermediate as water, allowing the ester carbonyl group to reform. Finally, deprotonation of the reformed carbonyl group will produce the final ester product, Propyl Paraben.[17]
Health Considerations
Propyl paraben, among other parabens, has been raising concerns on its possible interaction and disruption of estrogen in the endocrine system[18] Exposure to high levels of propyl parabens has been correlated to lower sperm and testosterone production in males in animal studies.[1][18] Studies showcase that propyl paraben can even act as an effective spermicide.[19] Animal studies of propyl paraben in the body showcases that propyl paraben is metabolized from the GI tract and excreted rapidly through urine with no accumulation in the body. Despite parabens interaction with the endocrine system it has not been shown to be significantly correlated with breast cancer.[18] With broken or damaged skins the use of propyl paraben in cosmetics or skincare can result in skin sensitization, however for normal skin it is considered safe.[5]
As of May 2023, New York began considering banning the use of Propyl Paraben because studies in humans and animals indicate that it acts as an endocrine disruptor and affects male and female reproductive health.[1][7]
In October 2023, the Governor of California signed a bill into law outlawing the use of Propyl Paraben in foods by 2027.[20][21] The new law bans the manufacture, sale, and distribution of Propyl Paraben and three other additives (brominated vegetable oil, potassium bromate, and Red 3). This is the first law in the U.S. to ban it and will possibly have nationwide effects.[22]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Oishi (December 2002). "Effects of propyl paraben on the male reproductive system". Food and Chemical Toxicology 40 (12): 1807–1013. doi:10.1016/s0278-6915(02)00204-1. PMID 12419695.
- ↑ PubChem. "Propylparaben" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7175.
- ↑ Directorate-General for Consumer Safety, European Union (2011). "Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety Opinion on Parabens COLIPA n° P82". http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_041.pdf.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Soni, M. G.; Burdock, G. A.; Taylor, S. L.; Greenberg, N. A. (June 2001). "Safety assessment of propyl paraben: a review of the published literature". Food and Chemical Toxicology 39 (6): 513–532. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(00)00162-9. ISSN 0278-6915.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Soni, M.G.; Carabin, I.G.; Burdock, G.A. (July 2005). "Safety assessment of esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (parabens)" (in en). Food and Chemical Toxicology 43 (7): 985–1015. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2005.01.020.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Talevi, Alan; Bellera, Carolina L.; Castro, Eduardo A.; Bruno-Blanch, Luis E. (2007-10-25). "A successful virtual screening application: prediction of anticonvulsant activity in MES test of widely used pharmaceutical and food preservatives methylparaben and propylparaben" (in en). Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design 21 (9): 527–538. doi:10.1007/s10822-007-9136-9. ISSN 0920-654X.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Dana G. Smith (April 13, 2023). "Two States Have Proposed Bans on Common Food Additives Linked to Health Concerns". New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/04/13/well/eat/food-additive-ban.html.
- ↑ "DailyMed - Browse Drug Classes". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/browse-drug-classes.cfm.
- ↑ "Propylparaben". https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB14177.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (2022-03-03). "Parabens in Cosmetics" (in en). FDA. https://www.fda.gov/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredients/parabens-cosmetics.
- ↑ Jones, Oliver A. H. (2023-03-27). "What is a paraben and why are so many products advertised as 'paraben-free'?" (in en-US). http://theconversation.com/what-is-a-paraben-and-why-are-so-many-products-advertised-as-paraben-free-198994.
- ↑ "EUR-Lex - l21191 - EN - EUR-Lex" (in en). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/EN/legal-content/summary/cosmetic-products-until-2013.html.
- ↑ "propylparaben (CHEBI:32063)". https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:32063.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Moscoso-Ramírez, Pedro A.; Montesinos-Herrero, Clara; Palou, Lluís (September 2014). "Antifungal activity of sodium propylparaben alone or in combination with low doses of imazalil against Penicillium decay on citrus fruit" (in en). European Journal of Plant Pathology 140 (1): 145–157. doi:10.1007/s10658-014-0450-5. ISSN 0929-1873.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Shin, Mi-Yeon; Shin, Chorong; Choi, Jeong Weon; Lee, Jangwoo; Lee, Seungho; Kim, Sungkyoon (September 2019). "Pharmacokinetic profile of propyl paraben in humans after oral administration". Environment International 130: 104917. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2019.104917. ISSN 0160-4120.
- ↑ Hazarika, Mridul; Parajuli, Raghab; Phukan, Prodeep (January 2007). "Synthesis of parabens using montmorillonite K10 clay as catalyst: A green protocol". Indian Journal of Chemical Technology 14: 104–106. https://nopr.niscpr.res.in/bitstream/123456789/1070/1/IJCT%2014(1)%20(2007)%20104-106.pdf.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "21.6: Chemistry of Esters" (in en). 2015-08-26. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Organic_Chemistry_(Morsch_et_al.)/21%3A_Carboxylic_Acid_Derivatives-_Nucleophilic_Acyl_Substitution_Reactions/21.06%3A_Chemistry_of_Esters.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Boberg, Julie; Taxvig, Camilla; Christiansen, Sofie; Hass, Ulla (September 2010). "Possible endocrine disrupting effects of parabens and their metabolites" (in en). Reproductive Toxicology 30 (2): 301–312. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.03.011.
- ↑ Bao-Liang, Song; Hai-Ying, Li; Dun-Ren, Peng (March 1989). "In vitro spermicidal activity of parabens against human spermatozoa" (in en). Contraception 39 (3): 331–335. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(89)90065-6. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0010782489900656.
- ↑ "AB-418 The California Food Safety Act." (in en). ca.gov. https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billCompareClient.xhtml?bill_id=202320240AB418&showamends=false.
- ↑ Chuck, Elizabeth (2023-09-12). "California Legislature passes first bill in U.S. to ban food additives, including red dye No. 3" (in en). https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/california-legislature-passes-first-bill-us-banning-food-additives-red-rcna104644.
- ↑ Cimons, Marlene (Oct 11, 2023). "California isn’t banning Skittles, but four additives will be removed". Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/wellness/2023/10/11/california-skittles-ban-chemicals-food/. The article notes that Red dye No. 3, bromated vegetable oil, potassium bromate and propyl paraben all have been linked to risk of cancer and hyperactivity in children.
ja:プロピルパラベン
 |