Chemistry:R13 (drug)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
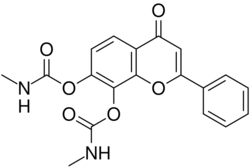
| Other names | 4-Oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromene-7,8-diyl bis(methylcarbamate) |
| Routes of administration | By mouth[1] |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolites | Tropoflavin[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H16N2O6 |
| Molar mass | 368.345 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
R13 is a small-molecule flavonoid and orally active, potent, and selective agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) – the main signaling receptor for the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) – which is under development for the potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease.[1][2] It is a structural modification and prodrug of tropoflavin (7,8-DHF) with improved potency and pharmacokinetics, namely oral bioavailability and duration.[1] The compound is a replacement for the earlier tropoflavin prodrug R7 and has similar properties to it.[1][3] It was developed because while R7 displayed a good drug profile in animal studies, it showed almost no conversion into tropoflavin in human liver microsomes.[1] In contrast to R7, R13 is readily hydrolyzed into tropoflavin in human liver microsomes.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "The prodrug of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone development and therapeutic efficacy for treating Alzheimer's disease". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115 (3): 578–583. January 2018. doi:10.1073/pnas.1718683115. PMID 29295929. Bibcode: 2018PNAS..115..578C.
- ↑ "7,8-Dihydoxyflavone and 7,8-substituted flavone derivatives, compositions, and methods related thereto" US patent application 20150274692, published 2015-10-01, assigned to Emory University
- ↑ "7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a small molecular TrkB agonist, is useful for treating various BDNF-implicated human disorders". Transl Neurodegener 5: 2. 2016. doi:10.1186/s40035-015-0048-7. PMID 26740873.
External links
 |

