Chemistry:Reed reaction
The Reed reaction is a chemical reaction that utilizes light to oxidize hydrocarbons to alkylsulfonyl chlorides. This reaction is employed in modifying polyethylene to give chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE), which is noted for its toughness.[1]
Commercial implementations
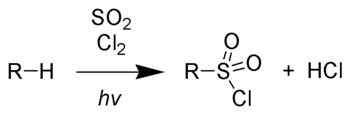
Polyethylene is treated with a mixture of chlorine and sulfur dioxide under UV-radiation. Vinylsulfonic acid can also be prepared beginning with the sulfochlorination of chloroethane. Dehydrohalogenation of the product gives vinylsulfonyl chloride, which subsequently is hydrolyzed to give vinylsulfonic acid:
- ClCH
2CH
3 + SO
2 + Cl
2 → ClCH
2CH
2SO
2Cl + HCl
- ClCH
- ClCH
2CH
2SO
2Cl → H
2C=CHSO
2Cl + HCl
- ClCH
- CH
2=CHSO
2Cl + H
2O → H
2C=CHSO
3H + HCl
- CH
Mechanism
The reaction occurs via a free radical mechanism. UV-light initiates homolysis of chlorine, producing a pair of chlorine atoms:
Chain initiation:
Thereafter a chlorine atom attacks the hydrocarbon chain, freeing hydrogen to form hydrogen chloride and an alkyl free radical. The resulting radical then captures SO2. The resulting sulfonyl radical attacks another chlorine molecule to produce the desired sulfonyl chloride and a new chlorine atom, which continues the reaction chain. Chain propagation steps:
See also
Historical readings
- Reed, C. F. U.S. Patent 2,046,090; U.S. Patent 2,174,110; U.S. Patent 2,174,492.
- Asinger, Friedrich; Schmidt, Walter; Ebeneder, Franz (1942). "Zur Kenntnis der Produkte der gemeinsamen Einwirkung von Schwefeldioxyd und Chlor auf aliphatische Kohlenwasserstoffe im ultravioletten Licht, I. Mitteil.: Die Produkte der gemeinsamen Einwirkung von Schwefeldioxyd und Chlor auf Propan in Tetrachlorkohlen". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) 75: 34–41. doi:10.1002/cber.19420750105.
- Asinger, Friedrich; Ebeneder, Franz; Böck, Erich (1942). "Zur Kenntnis der Produkte der gemeinsamen Einwirkung von Schwefeldioxyd und Chlor auf aliphatische Kohlenwasserstoffe im ultravioletten Licht, II. Mitteil.: Die Produkte der gemeinsamen Einwirkung von Schwefeldioxyd und Chlor auf n-Butan in Tetrachlorkohl". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) 75: 42–48. doi:10.1002/cber.19420750106.
- Asinger, Friedrich; Ebeneder, Franz (1942). "Zur Kenntnis der Produkte der gemeinsamen Einwirkung von Schwefeldioxyd und Chlor auf aliphatische Kohlenwasserstoffe im ultravioletten Licht, III. Mitteilung† : Über die Sulfochlorierung von Isobutan und die Isomerenbildung bei der Sulfochlorierung und Chlorierung gasförmiger Kohlenwasserstoffe". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) 75 (4): 344–349. doi:10.1002/cber.19420750408. ISSN 1099-0682. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cber.19420750408. Retrieved 2023-02-22.
- Helberger, J. H.; Manecka, G.; Fischer, H. M. (1949). "Zur Kenntnis organischer Sulfonsäuren. II. Mitt.: Die Sulfochlorierung des 1-Chlorbutans und anderer Halogenalkyle; Synthese von Sultonen und eines Sultams". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie 562: 23–35. doi:10.1002/jlac.19495620104.
References
- ↑ Happ, Michael; Duffy, John; Wilson, G. J.; Pask, Stephen D.; Buding, Hartmuth; Ostrowicki, Andreas (2011). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.o23_o05.
 |
