Chemistry:Ritalinic acid
From HandWiki
Short description: Major metabolite of the psychostimulant drug methylphenidate
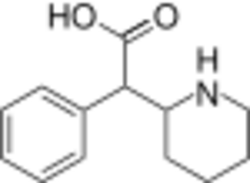 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 219.284 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ritalinic acid is a substituted phenethylamine and an inactive major metabolite of the psychostimulant drugs methylphenidate, dexmethylphenidate and ethylphenidate.[1][2] When administered orally, methylphenidate is extensively metabolized in the liver by hydrolysis of the ester group yielding ritalinic acid.[1] The hydrolysis was found to be catalyzed by carboxylesterase 1 (CES1).[3]
Etymologically, ritalinic acid shares its roots with Ritalin, a common brand name for methylphenidate.
Uses
Ritalinic acid is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of methylphenidate and its analogues, such as ethylphenidate and isopropylphenidate.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Metabolism and disposition of methylphenidate-14C: studies in man and animals". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 191 (3): 535–47. December 1974. PMID 4473537.
- ↑ "Identification of in vitro metabolites of ethylphenidate by liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 117 (5): 474–84. January 2016. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2015.09.029. PMID 26454340.
- ↑ "Methylphenidate is stereoselectively hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase CES1A1". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 310 (2): 469–76. August 2004. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.067116. PMID 15082749.
External links
 |

