Chemistry:Rumenic acid
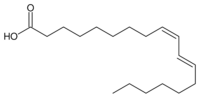
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(9Z,11E)-Octadeca-9,11-dienoic acid | |
| Other names
Bovinic acid; C9-T11 acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 280.452 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rumenic acid, also known as bovinic acid, is a conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) found in the fat of ruminants and in dairy products. It is an omega-7 trans fatty acid. Its lipid shorthand name is cis-9, trans-11 18:2 acid. The name was proposed by Kramer et al. in 1998.[1] It can be considered as the principal dietary form, accounting for as much as 85-90% of the total CLA content in dairy products.[2]
Biosynthesis and biotransformations
Rumenic acid is produced from vaccenic acid by the action of unsaturase enzymes.[3] Rumenic acid is converted back to vaccenic acid en route to stearic acid
Further reading
F. Destaillats; E. Buyukpamukcu; P.-A. Golay; F. Dionisi; F. Giuffrida (2005). "Letter to the Editor: Vaccenic and Rumenic Acids, A Distinct Feature of Ruminant Fats". Journal of Dairy Science 88 (449): 449. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72705-3. PMID 15653508.
References
- ↑ "Rumenic acid: a proposed common name for the major conjugated linoleic acid isomer found in natural products". Lipids 33 (8): 835. 1998. doi:10.1007/s11745-998-0279-6. PMID 9727617.
- ↑ Cyberlipid. "Polyenoic Fatty Acids". http://www.cyberlipid.org/fa/acid0003.htm. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- ↑ Turpeinen, Anu M.; Mutanen, Marja; Aro, Antti; Salminen, Irma; Basu, Samar; Palmquist, Donald L.; Griinari, J Mikko (2002). "Bioconversion of vaccenic acid to conjugated linoleic acid in humans". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 76 (3): 504–510. doi:10.1093/ajcn/76.3.504. PMID 12197992.
 |

