Chemistry:Succinylacetone
From HandWiki
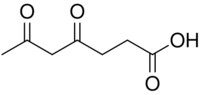
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4,6-Dioxoheptanoic acid | |
| Other names
Succinyl acetone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 158.153 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Succinylacetone is a chemical compound that is formed by the oxidation of glycine and is a precursor of methylglyoxal. It is a pathognomonic compound found in the urine of patients with tyrosinemia type 1,[1] which is due to congenital deficiency of an enzyme, fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase. This enzyme is involved in the catabolism of tyrosine, and if deficient, leads to accumulation of fumarylacetoacetate which is subsequently converted to succinylacetone which can be detected in the urine by GCMS. Succinylacetone also inhibits ALA dehydratase (PBG synthase) which increases ALA and precipitates acute neuropathic symptoms, similar to porphyria.
References
- ↑ "Recommendations for the management of tyrosinaemia type 1". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 8: 8. January 2013. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-8. PMID 23311542.
 |

