Chemistry:Tert-Butyl nitrite
From HandWiki
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
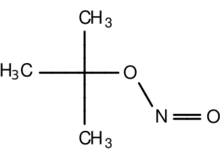
| C4H9NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 103.121 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Boiling point | 61–63 °C (142–145 °F; 334–336 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H225, H302, H332 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P330, P370+378, P403+235, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
tert-Butyl nitrite is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CONO. A colorless liquid, it is the tert-butyl ester of nitrous acid. It is typically employed as a solution with tert-butyl alcohol.
Use
The compound is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.[2] It reacts with secondary amides to give N-nitroso amides:[3]
- RC(O)N(H)R + (CH3)3CONO → RC(O)N(NO)R + (CH3)3COH
See also
References
- ↑ "tert-Butyl nitrite" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/10906#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Di Qiu, He Meng, Liang Jin, Shengbo Tang, Shuai Wang, Fangyang Mo, Yan Zhang, Jianbo Wang (2014). "Synthesis of Arylboronic Pinacol Esters from Corresponding Arylamines". Organic Syntheses 91: 106. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.091.0106.
- ↑ Yedage, Subhash L.; Bhanage, Bhalchandra M. (2017). "Tert-Butyl Nitrite-Mediated Synthesis of N-Nitrosoamides, Carboxylic Acids, Benzocoumarins, and Isocoumarins from Amides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 82 (11): 5769–5781. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.7b00570. PMID 28472882.
 |