Chemistry:Tesamorelin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Egrifta SV |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a611035 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ≤4%[1] |
| Metabolism | Proteolysis |
| Elimination half-life | 26–38 min |
| Excretion | Renal/proteolysis |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C221H366N72O67S |
| Molar mass | 5135.86 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
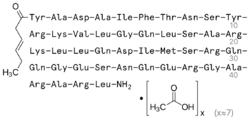
Tesamorelin (INN) (trade name Egrifta SV) is a synthetic form of growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) which is used in the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy, approved initially in 2010. It is produced and developed by Theratechnologies, Inc. of Canada. The drug is a synthetic peptide consisting of all 44 amino acids of human GHRH with the addition of a trans-3-hexenoic acid group.[2]
Mechanism of action
Tesamorelin is the N-terminally modified compound based on 44 amino acids sequence of human GHRH.[3] This modified synthetic form is more potent and stable than the natural peptide. It is also more resistant to cleavage by the dipeptidyl aminopeptidase than human GHRH.[4] It stimulates the synthesis and release of endogenous GH, with an increase in level of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1). The released GH then binds with the receptors present on various body organs and regulates the body composition. This regulation is mainly because of the combination of anabolic and lipolytic mechanisms. However, it has been found that the main mechanisms by which Tesamorelin reduces body fat mass are lipolysis followed by reduction in triglycerides level.[5]
Contraindication
Tesamorelin therapy may cause glucose intolerance and increase the risk of type 2-diabetes, so it is contraindicated in pregnancy.[6] It is also contraindicated in pregnancy (category X) because it may cause harm to fetus. It is also contraindicated in patients affected by hypothalamic-pituitary axis disruption due to pituitary gland tumor, head irradiation and hypopituitarism.[7]
Adverse effects
Injection site erythema, peripheral edema, injection site pruritus and diarrhea.[8]
See also
- List of growth hormone secretagogues
References
- ↑ "Egrifta (tesamorelin for injection) for Subcutaneous Use. U.S. Full Prescribing Information". EMD Serono, Inc.. http://www.egrifta.com/Pdfs/Prescribing_Information.pdf.
- ↑ "FDA Application Chemistry Review". http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2010/022505Orig1s000ChemR.pdf.
- ↑ "Tesamorelin: a review of its use in the management of HIV-associated lipodystrophy". Drugs 71 (8): 1071–1091. May 2011. doi:10.2165/11202240-000000000-00000. PMID 21668043.
- ↑ "Non-clinical pharmacology and safety evaluation of TH9507, a human growth hormone-releasing factor analogue". Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 100 (1): 49–58. January 2007. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00008.x. PMID 17214611.
- ↑ "Recombinant human growth hormone: rationale for use in the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy". BioDrugs 22 (2): 101–112. 2008. doi:10.2165/00063030-200822020-00003. PMID 18345707.
- ↑ "Tesamorelin: A hope for ART-induced lipodystrophy". Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences 3 (2): 319–320. April 2011. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.80763. PMID 21687371.
- ↑ "Review of Selected NMEs 2011" (in en). Auburn: Health Information Designs, Inc. https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/review-of-selected-nmes-2011.
- ↑ "Effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor, in HIV-infected patients with abdominal fat accumulation: a randomized placebo-controlled trial with a safety extension". Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 53 (3): 311–322. March 2010. doi:10.1097/qai.0b013e3181cbdaff. PMID 20101189.
 |

