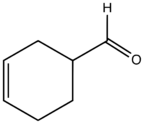
Chemistry:Tetrahydrobenzaldehyde
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclohex-3-ene-1-carbaldehyde | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2498 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10O | |
| Molar mass | 110.156 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.94 g/mL |
| Melting point | 2 °C (36 °F; 275 K) |
| Boiling point | 163–164 °C (325–327 °F; 436–437 K) |
| Solubility | Acetone methanol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H312, H314, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P370+378 | |
| Flash point | 57 °C (135 °F; 330 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
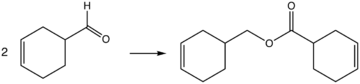
1,2,3,6-Tetrahydrobenzaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula C6H9CHO. This colorless liquid is formally a partially hydrogenated derivative of benzaldehyde. It is produced by the Diels-Alder reaction of acrolein to butadiene. It is of interest as a precursor to 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3′,4′-epoxycyclohexane carboxylate, a useful resin and precursor to industrial coatings. The conversion entails the Tishchenko reaction, i.e., base-catalyzed conversion to the ester followed by double epoxidation.[1]
References
- ↑ Guenter Sienel; Robert Rieth; Kenneth T. Rowbottom. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_531.
 |