Chemistry:Tricholomic acid
From HandWiki
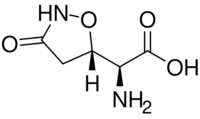
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-2-[(5S)-3-oxo-1,2-oxazolidin-5-yl]acetic acid
| |
| Other names
α-Cycloglutamate; α-Amino-3-oxo-5-isoxazolidineacetic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 160.129 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K)[1] (decomp.) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Tricholomic acid is a non-proteinogenic amino acid found in some mushrooms, including Tricholoma muscarium.[1] It has a chemical structure similar to glutamic acid, hence the synonym cycloglutamate, and it interacts with glutamate receptors.[2] Because glutamate receptors are thought to be responsible for the reception of umami taste, tricholomic acid and close analogs have been investigated as flavor enhancers.[3]
See also
- Ibotenic acid, a related compound found in mushrooms
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Takemoto, Tsunematsu; Nakajima, Tadashi (1964). "Studies on the Constituents of Indigenous Fungi. I". Yakugaku Zasshi 84 (12): 1183. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.84.12_1183.
- ↑ Tamborini, Lucia; Mastronardi, Federica; Lo Presti, Leonardo; Nielsen, Birgitte; De Micheli, Carlo; Conti, Paola; Pinto, Andrea (2017). "Synthesis of L-Tricholomic Acid Analogues and Pharmacological Characterization at Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors". ChemistrySelect 2 (31): 10295. doi:10.1002/slct.201702154.
- ↑ Kuninaka, Akira (1969). "Recent Studies of 5′-Nucleotides as New Flavor Enhancers". Flavor Chemistry. Advances in Chemistry 56: 261–274. doi:10.1021/ba-1966-0056.ch015. ISBN 0-8412-0057-2.
External links
- Tricholomic acid, Human Metabolome Database
 |

