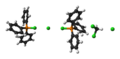Chemistry:Triphenylphosphine dichloride
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dichlorotri(phenyl)-λ5-phosphane | |||
| Other names
Dichlorotriphenylphosphorane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| (C 6H 5) 3PCl 2 | |||
| Molar mass | 333.19 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless solid | ||
| Melting point | 176 °C (349 °F; 449 K),[1] 85-100 °C,[2] 85 °C (decomposes)[3] | ||
| Reacts | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | May cause severe skin and eye injury and cancer. If the chemical is let to enter the drains, there is a risk of explosion.[3] | ||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| HH228Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH314Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, HH350Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |||
| PP210Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP240Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP241Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP260Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP264Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP280Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP301+P330+P331Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP302+P361+P354Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP304+P340Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP305+P354+P338Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP321Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP363Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP370+P378Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP405Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP501Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Triphenylphosphine dichloride is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula (C
6H
5)
3PCl
2, often abbreviated as Ph
3PCl
2, where Ph is phenyl. It is a chlorinating agent widely used in organic chemistry. Applications include the conversion of alcohols and ethers to alkyl chlorides, the cleavage of epoxides to vicinal dichlorides and the chlorination of carboxylic acids to acyl chlorides.[2]
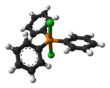
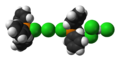
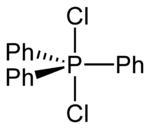
Structure
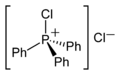
In polar solvents such as acetonitrile, Ph
3PCl
2 adopts an ionic phosphonium salt structure, [Ph
3PCl]+
Cl−
(chlorotriphenylphosphonium chloride),[4] whereas in non-polar solvents like diethyl ether it exists as a non-solvated trigonal bipyramidal molecule.[5] Two [Ph
3PCl]+
species can also adopt an unusual dinuclear ionic structure—both interacting with a Cl−
via long Cl–Cl contacts.[4]
Synthesis
Triphenylphosphine dichloride is usually prepared fresh by the addition of chlorine to triphenylphosphine.
- Ph
3P + Cl
2 → Ph
3PCl
2
Both reagents are typically used in solution to ensure the correct stoichiometry.[2]
Ph
3PCl
2 can also be obtained by the reaction of iodobenzene dichloride (PhICl
2) and triphenylphosphine.[6]
Alternatively, Ph
3PCl
2 can be obtained by chlorination of triphenylphosphine oxide with, for example, phosphorus trichloride, as in Grignard's original 1931 synthesis.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Victor Grignard, J. Savard (1931). Comptes rendus de l'Académie des sciences 192: 592–5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt371
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/GB/en/sds/aldrich/378755?userType=anonymous
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 S. M. Godfrey; C. A. McAuliffe; R. G. Pritchard; J. M. Sheffield (1996). "An X-ray crystallorgraphic study of the reagent Ph3PCl2; not charge-transfer, R3P–Cl–Cl, trigonal bipyramidal or [R3PCl]Cl but an unusual dinuclear ionic species, [Ph3PCl+⋯Cl–⋯+CIPPH3]Cl containing long Cl–Cl contacts". Chemical Communications (22): 2521–2522. doi:10.1039/CC9960002521.
- ↑ S. M. Godfrey; C. A. McAuliffe; J. M. Sheffield (1998). "Structural dependence of the reagent Ph3PCl2 on the nature of the solvent, both in the solid state and in solution; X-ray crystal structure of trigonal bipyramidal Ph3PCl2, the first structurally characterised five-coordinate R3PCl2 compound". Chem. Commun. (8): 921–922. doi:10.1039/a800820e.
- ↑ Carle, M. S., Shimokura, G. K. and Murphy, G. K. (2016), Iodobenzene Dichloride in the Esterification and Amidation of Carboxylic Acids: In-Situ Synthesis of Ph3PCl2. Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2016: 3930–3933. {{DOI:10.1002/ejoc.201600714}}
 |