Earth:Eumeralla Formation
| Eumeralla Formation Stratigraphic range: Aptian–Albian | |
|---|---|
 Eric the Red West fossil locality, with AS and ES representing Anchor Sandstone and ETRW Sandstone, respectively | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Otway Group |
| Sub-units | Windermere Sandstone Member, Heathfield Sandstone Member |
| Underlies | Sherbrook Group |
| Overlies | Katnook Sandstone, Laira Formation (Crayfish Subgroup) |
| Thickness | Up to 3,000 m (9,800 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Volcanilithic sandstone, siltstone, mudstone, conglomerate |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 38°48′S 143°18′E / 38.8°S 143.3°E |
| Paleocoordinates | [ ⚑ ] 74°48′S 115°48′E / 74.8°S 115.8°E |
| Region | Victoria |
| Country | Australia |
| Extent | Otway Basin |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Eumeralla River |
| Named by | Reynolds, M.A |
| Year defined | 1971 |
The Eumeralla Formation is a geological formation in Victoria, Australia whose strata date back to the Early Cretaceous. It is Aptian to Albian in age. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, particularly from the Dinosaur Cove locality.[1]
Geology
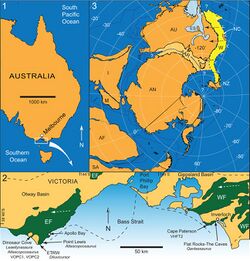
The Eumeralla Formation was deposited within the Otway Basin, which at the time of deposition was part of an extensional rift valley system formed between Australia and Antarctica. The lithology primarily consists of fluvially deposited siliciclastics derived from volcanic material. The strata of the Eumeralla Formation are folded as a result of northwest–southeast crustal compression during the Neogene, which also reactivated some Cretaceous aged normal faults.[2] It is one of three major fossiliferous deposits in Victoria dating to the Early Cretaceous, including the older Wonthaggi Formation and the Koonwarra fossil bed (which some authors have considered part of the Eumeralla Formation).[3]
Paleoclimate
Paleosol facies in the Eumeralla Formation record climate fluctuations between warm and cool intervals. Warm, temperate periods are represented by Ultisols while cooler intervals at the Cape Paton locality record associated thin, gleyed Inceptisols and Entisols, which are characteristic of modern boreal forests.[4]
Paleobiota
Invertebrate traces named as Skolithos sp. and Arenicolites sp.,[5] as well as indeterminate ornithischian tracks are present in Victoria, Australia.[1] Indeterminate ornithopod remains are present at Eric the Red West locality and Elliot River, including material that possibly belongs to a new taxon.[6] Indeterminate theropod and possible indeterminate dromaeosaurid remains are present in Victoria, Australia.[1] An indeterminate unenlagiine is known from the formation.[7]
Dinosaurs
Ornithischians
| Ornithischians of the Eumeralla Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Ankylosauria[8] | Indeterminate | Dinosaur Cove | Dorsal vertebra | ||
|
A. loadsi[1] |
|
"Maxilla [and] teeth."[9] |
Elasmarian ornithopod |  | |
| D. pickeringi[2] | Eric the Red West locality | Partial postcranial skeleton.[2] | Elasmarian ornithopod |  | |
| cf.Galleonosaurus | G. dorisae[6] | Eric the Red West locality | Maxillae | Elasmarian ornithopod | |
| Leaellynasaura[1] | L. amicagraphica[1] |
|
Skull fragments, teeth, maxillae. Postcranial remains associated with the taxon cannot be confidently referred to it | Elasmarian ornithopod |  |
Theropods
| Dinosaurs of the Eumeralla Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| cf. Australovenator[10] | cf. A. wintonensis | Eric the Red West locality | "two teeth, two manual unguals, and a right astragalus" | Megaraptoran theropod |  |
| Indeterminate | Footprints belonging to a crane-sized bird, determined to be an ornithurine or enantiornithe. | Possibly from a species also found at the Wonthaggi Formation (single furcula). | |||
| Carcharodontosauria[12] | Indeterminate | "Isolated, distal end of a right tibia" | First probable record of carcharodontosaurian theropod in Australia | ||
| Elaphrosaurinae[13] | Indeterminate | Eric the Red West locality | Single cervical vertebra | ||
| Indeterminate | Dinosaur Cove |
Known from a left ulna. |
Probably a megaraptorid. Previously referred to Megaraptor.[16] | ||
| Megaraptoridae[10] |
Indeterminate |
Eric the Red West locality | Known from a single cervical vertebra. | Previously thought to be a Baryonyx-related spinosaurid.[7] |  |
| Timimus[1] | T. hermani[1] | Dinosaur Cove | Femur | Possible tyrannosauroid theropod | |
| Unenlagiinae[7] | Indeterminate | Proximal portion of right femur | Probable record of unenlagiine theropod in Australia | ||
Fish
| Fish of the Eumeralla Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Ceratodus | C. nargun | A lungfish |
 | ||
Mammals
| Mammals of the Eumeralla Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Kryoryctes | K. cadburyi | Dinosaur Cove | A monotreme | ||
| Sundrius | S. ziegleri | A monotreme | |||
Reptiles
| Reptiles of the Eumeralla Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Otwayemys | O. cunicularius | Dinosaur Cove | A meiolaniform turtle | ||
| Pterosauria | Indeterminate | Dinosaur Cove | |||
| Plesiosauria | Indeterminate | Dinosaur Cove | |||
| Mesoeucrocodylia[17] | Indeterminate | Dinosaur Cove | Distinct from other known Australian crocodilians | ||
See also
- List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations
- South Polar region of the Cretaceous
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Cretaceous, Australasia)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 573-574. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Herne, M. C.; Tait, A. M.; Weisbecker, V.; Hall, M.; Nair, J. P.; Cleeland, M.; Salisbury, S. W. (2018-01-11). "A new small-bodied ornithopod (Dinosauria, Ornithischia) from a deep, high-energy Early Cretaceous river of the Australian–Antarctic rift system". PeerJ 5. doi:10.7717/peerj.4113. PMID 29340228.
- ↑ McLoughlin, Stephen; Pott, Christian (February 2019). "Plant mobility in the Mesozoic: Disseminule dispersal strategies of Chinese and Australian Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous plants" (in en). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 515: 47–69. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.12.036. Bibcode: 2019PPP...515...47M. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0031018217307320.
- ↑ Retallack, G. J. (2023-08-18). "Dinosaur and tree-line invasion of southeastern Australia during Cretaceous greenhouse spikes". Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 70 (6): 840–858. doi:10.1080/08120099.2023.2212026. ISSN 0812-0099.
- ↑ Milanesia Beach tracksite at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Duncan, Ruairidh J.; Evans, Alistair R.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Rich, Thomas H.; Poropat, Stephen F. (2021-05-04). "Ornithopod jaws from the Lower Cretaceous Eumeralla Formation, Victoria, Australia, and their implications for polar neornithischian dinosaur diversity". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 41 (3). doi:10.1080/02724634.2021.1946551. ISSN 0272-4634. Bibcode: 2021JVPal..41E6551D. https://research.monash.edu/en/publications/1deae4e9-3b35-401d-b608-8d48016cca27.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Benson, Roger B. J.; Rich, Thomas H.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Hall, Mike (2012-05-16). "Theropod Fauna from Southern Australia Indicates High Polar Diversity and Climate-Driven Dinosaur Provinciality" (in en). PLOS ONE 7 (5). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037122. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 22615916. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...737122B.
- ↑ Barrett, Paul M.; Rich, Thomas H.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Tumanova, Tat'yana A.; Inglis, Matthew; Pickering, David; Kool, Lesley; Kear, Benjamin P. (September 2010). "Ankylosaurian dinosaur remains from the Lower Cretaceous of southeastern Australia" (in en). Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology 34 (3): 205–217. doi:10.1080/03115511003655430. ISSN 0311-5518. Bibcode: 2010Alch...34..205B.
- ↑ "Table 18.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 394.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Poropat, Stephen F.; White, Matt A.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Rich, Thomas H. (2019-07-04). "New megaraptorid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) remains from the Lower Cretaceous Eumeralla Formation of Cape Otway, Victoria, Australia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 39 (4). doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1666273. ISSN 0272-4634. Bibcode: 2019JVPal..39E6273P.
- ↑ Martin, Anthony J.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Rich, Thomas H.; Hall, Michael (2013). "Oldest known avian footprints from Australia: Eumeralla Formation (Albian), Dinosaur Cove, Victoria". Palaeontology 57: 7–19. doi:10.1111/pala.12082.
- ↑ Kotevski, J.; Duncan, R.J.; Ziegler, T.; Bevitt, J.J.; Vickers-Rich, P.; Rich, T.H.; Evans, A.R.; Poropat, S.F. (2025). "Evolutionary and paleobiogeographic implications of new carcharodontosaurian, megaraptorid, and unenlagiine theropod remains from the upper Lower Cretaceous of Victoria, southeast Australia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 44 (4): e2441903. doi:10.1080/02724634.2024.2441903.
- ↑ Poropat, Stephen F.; Pentland, Adele H.; Duncan, Ruairidh J.; Bevitt, Joseph J.; Vickers-Rich, Patricia; Rich, Thomas H. (2020-08-01). "First elaphrosaurine theropod dinosaur (Ceratosauria: Noasauridae) from Australia — A cervical vertebra from the Early Cretaceous of Victoria" (in en). Gondwana Research 84: 284–295. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2020.03.009. ISSN 1342-937X. Bibcode: 2020GondR..84..284P. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X20301234.
- ↑ Smith, Nathan D; Makovicky, Peter J; Agnolin, Federico L; Ezcurra, Martín D; Pais, Diego F; Salisbury, Steven W (2008-06-10). "A Megaraptor-like theropod (Dinosauria: Tetanurae) in Australia: support for faunal exchange across eastern and western Gondwana in the Mid-Cretaceous". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 275 (1647): 2085–2093. doi:10.1098/rspb.2008.0504. ISSN 0962-8452. PMID 18544511.
- ↑ Benson, Roger B. J.; Carrano, Matthew T.; Brusatte, Stephen L. (2009-10-14). "A new clade of archaic large-bodied predatory dinosaurs (Theropoda: Allosauroidea) that survived to the latest Mesozoic" (in en). Naturwissenschaften 97 (1): 71–8. doi:10.1007/s00114-009-0614-x. ISSN 1432-1904. PMID 19826771.
- ↑ Smith, Nathan D; Makovicky, Peter J; Agnolin, Federico L; Ezcurra, Martín D; Pais, Diego F; Salisbury, Steven W (2008-09-22). "A Megaraptor-like theropod (Dinosauria: Tetanurae) in Australia: support for faunal exchange across eastern and western Gondwana in the Mid-Cretaceous". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 275 (1647): 2085–2093. doi:10.1098/rspb.2008.0504. ISSN 0962-8452. PMID 18544511.
- ↑ Ristevski, J.; Willis, P.M.A.; Yates, A.M.; White, M.A.; Hart, L.J.; Stein, M.D.; Price, G.J.; Salisbury, S.W. (2023). "Migrations, diversifications and extinctions: the evolutionary history of crocodyliforms in Australasia". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology 47 (4): 370–415. doi:10.1080/03115518.2023.2201319. Bibcode: 2023Alch...47..370R.
 |