Engineering:Exploration Flight Test-1
 Launch of EFT-1 on December 5, 2014 | |
| Names | Orion Flight Test-1 (OFT-1) |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Technology demonstration |
| Operator | NASA |
| Mission duration | 4 hours, 24 minutes |
| Orbits completed | 2 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Orion CM-001 |
| Spacecraft type | Orion |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Martin |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | December 5, 2014, 12:05 UTC (7:05 am EST)[1][2] |
| Rocket | Delta IV Heavy |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral, SLC-37B |
| Contractor | United Launch Alliance |
| End of mission | |
| Recovered by | missing name |
| Landing date | December 5, 2014, 16:29 UTC (8:29 am PST) |
| Landing site | Pacific Ocean, 640 mi (1,030 km) SSE of San Diego ( [ ⚑ ] 23°37′N 114°28′W / 23.61°N 114.46°W) |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Apogee altitude | 5,800 km (3,604 mi) |
 Mission insignia Orion program | |
Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1 (previously known as Orion Flight Test 1 or OFT-1) was a technology demonstration mission and the first flight test of the crew module portion of the Orion spacecraft. Without a crew, it was launched on December 5, 2014 at 12:05 UTC (7:05 am EST, local time at the launch site) by a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.[3]
The mission was a four-hour, two-orbit test of the Orion crew module featuring a high apogee on the second orbit and concluding with a high-energy reentry at around 8.9 kilometers per second (20,000 mph).[4] This mission design corresponds to the Apollo 2/3 missions of 1966, which validated the Apollo flight control system and heat shield at re-entry conditions planned for the return from lunar missions.
Objectives

EFT-1 tested several systems of the crew module portion of the Orion spacecraft, including separation events, avionics, heat shield performance, parachutes, and recovery operations. The uncrewed test flight served as a precursor to Orion’s first mission aboard the Space Launch System (SLS) on Artemis I. Because the European Service Module was not yet available, Orion flew with a structural representation. It also carried only a partial launch abort system, limited to the motor used to jettison the system at the end of launch, along with an Orion-to-stage adapter designed for future use with the SLS.[5]
For the mission, Orion remained attached to the dummy service module, which itself was connected to the Delta IV Heavy’s upper stage. This stage was nearly identical to the Interim Cryogenic Upper Stage planned for the Block 1 version of the SLS. Unlike future flights, Orion relied on internal batteries for power rather than photovoltaic arrays.[6]
Data returned from EFT-1 informed Orion’s design and were incorporated into its critical design review (CDR) in April 2015.[7] These results helped pave the way for the Artemis I mission, which launched on November 16, 2022,[8] more than seven years after EFT-1.
Vehicle assembly
Orion CM-001 used on the EFT-1 mission was built by Lockheed Martin.[9] On June 22, 2012, the final welds of the EFT-1 Orion were completed at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana.[9] It was then transported to Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Checkout Building, where the remainder of the spacecraft was completed.[10] The Delta IV rocket was put in a vertical position on October 1, 2014, and Orion was mated with the vehicle on November 11.[11][12][13]
Flight
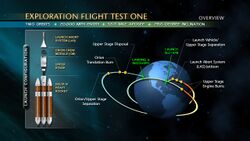
The four-and-a-half-hour flight took the Orion spacecraft on two orbits of Earth. Peak apogee was approximately 5,800 kilometres (3,600 mi). The distance allowed the spacecraft to reach reentry speeds of up to 8.9 km/s (20,000 mph), which exposed the heat shield to temperatures up to around 2,200 °C (4,000 °F).[4][5]
| Time | Event |
|---|---|
| L‑6:00:00 | Orion powered on, mobile service tower retracts, fueling of Delta IV Heavy begins |
| 0:00:00 | Launch (7:05 a.m. EST, 12:05 UTC) |
| 0:01:23 | Max q |
| 0:01:23 | Vehicle is supersonic |
| 0:03:56 | Booster separation |
| 0:05:30 | First stage MECO (main engine cut-off) |
| 0:05:33 | First stage separation |
| 0:05:49 | Second stage ignition No. 1 |
| 0:06:15 | Service module fairing jettison |
| 0:06:20 | Launch Abort System jettison |
| 0:17:39 | SECO No. 1 (second engine cut-off), Orion begins first orbit |
| 1:55:26 | Orion completes first orbit, second stage ignition No. 2 |
| 2:00:09 | SECO No. 2 |
| 2:05:00 | Enter first high radiation period |
| 2:20:00 | Leave first high radiation period |
| 2:40:00 | Reaction control system (RCS) activation |
| 3:05:00 | Reach peak apogee: 5,800 km (3,600 mi) |
| 3:23:41 | Orion separates from combined service module/second stage, second stage performs disposal burn |
| 3:57:00 | Orion positions for reentry |
| 4:13:41 | Entry interface |
| 4:20:22 | Forward bay cover jettisons, parachute deployment begins (two drogues, three mains) |
| 4:24:46 | Splashdown and recovery by the USS Anchorage crew |
After splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, crews from the USS Anchorage recovered the EFT-1 Orion crew vehicle. Plans were later made to outfit the capsule for an ascent abort test in 2017.[15]
Launch attempts
| Attempt | Planned | Result | Turnaround | Reason | Decision point | Weather go (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2014-12-04 07:05:00 AM 4 Dec 2014, 7:05:00 am | Scrubbed | — | Weather | 2014-12-04 09:44:00 AM 4 Dec 2014, 9:44 am (T−00:03:09) | A boat entered the launch range, wind gusts in excess of speed limit (21 kn or 24 mph or 39 km/h), and a fuel fill and drain valve did not close. 24-hour recycle. | |
| 2 | 2014-12-05 07:05:00 AM 5 Dec 2014, 7:05:00 am | Success | 1 day, 0 hours, 0 minutes |
Public outreach
NASA heavily promoted the mission, collaborating with Sesame Street and its characters to educate children about the flight test and the Orion spacecraft.[16]
The Orion capsule used for EFT-1 is now on display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, in the "NASA Now" exhibit.[17]
Gallery
-
First weld on the EFT-1 Orion structure, September 2011
-
Orion structure after final weld, June 2012, at the Michoud Assembly Facility
-
Orion's Service Module prior to encapsulation, December 2013, in the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C)
-
EFT-1 Orion Weight and Center of Gravity Test, June 2014
-
EFT-1 Orion back shell tile installation, September 2014
-
Completed EFT-1 Orion, September 2014
-
EFT-1 Orion in fairing and with LES, October 2014
-
EFT-1 Orion on its Delta IV Heavy
-
EFT-1 Orion on its Delta IV Heavy
-
Earth seen from the EFT-1 Orion spacecraft
-
The EFT-1 Orion before splashdown, 5 December 2014
-
Recovery of the EFT-1 Orion by the USS Anchorage, 5 December 2014
-
Recovery of Orion capsule
-
Recovery of Orion capsule
References
- ↑ Rhian, Jason (March 14, 2014). "NASA's EFT-1 Mission Slips to December". http://www.spaceflightinsider.com/missions/nasas-eft-1-mission-slips-december/.
- ↑ Siceloff, Steven (December 5, 2014). "LIFTOFF! Orion Begins New Era in Space Exploration!". NASA. https://blogs.nasa.gov/orion/2014/12/05/liftoff-orion-begins-new-era-in-space-exploration/.
- ↑ Foust, Jeff (December 5, 2014). "Delta 4 Heavy Launches Orion on Second Attempt". SpaceNews. https://spacenews.com/delta-4-heavy-launches-orion-second-attempt/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bergin, Chris (November 14, 2011). "EFT-1 Orion Receives Hatch Door—Denver Orion Ready for Modal Testing". http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2011/11/eft-1-orion-hatch-door-orion-modal-testing.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Orion First Flight Test – NASA Facts". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/fs-2014-08-005-jsc-orion-eft-final.pdf.
- ↑ "OFT-1: NASA gearing up for Orion's 2013 debut via Delta IV Heavy". August 8, 2011. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2011/08/oft-1-nasa-orions-2013-debut-via-delta-iv-heavy/.
- ↑ "EFT-1 September, 2014 launch date "paced" by the Delta IV-H". November 7, 2012. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2012/11/eft-1-september-2014-launch-paced-delta-ivh.
- ↑ "NASA: Artemis I". https://www.nasa.gov/specials/artemis-i/index.html.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Clark, Stephen (June 26, 2012). "Space-bound Orion capsule to arrive in Florida next week". SpaceFlightNow. http://spaceflightnow.com/news/n1206/26orion/.
- ↑ "NASA Unveils Orion During Ceremony". NASA. July 2, 2012. http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/orion_arrival.html.
- ↑ "NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, Rocket Move Closer to First Flight" NASA. Retrieved: October 5, 2014.
- ↑ "Orion Spacecraft Complete" NASA. Retrieved: October 30, 2014.
- ↑ "Orion Arrives at Launch Pad" NASA. Retrieved: November 12, 2014.
- ↑ NASA. "Orion Exploration Flight Test-1". https://www.nasa.gov/pdf/663703main_flighttest1_fs_051812.pdf.
- ↑ Stephen Clark (November 23, 2011). "Cracks discovered in Orion capsule's pressure shell". Spaceflightnow.com. http://www.spaceflightnow.com/news/n1211/23eft1cracks/.
- ↑ NASA (November 24, 2014). "Sesame Street Characters 'On Board' as NASA Counts Down to Orion's Test Flight". http://www.nasa.gov/content/sesame-street-characters-on-board-with-orion/#.VIN40THF-4k.
- ↑ "Orion EFT-1 flown spacecraft joins display in 'NASA Now' exhibit | collectSPACE". http://www.collectspace.com/news/news-041317a-orion-eft1-kennedy-display.html.
External links
- Orion MPCV homepage (NASA)
- EFT-1 Fact sheet (NASA)
- EFT-1 Press kit (NASA)
- Animation of the EFT-1 mission (NASA)
- Video of the launch of EFT-1 – 5 December 2014 (NASA)
- Video of the landing of the EFT-1 Orion – 5 December 2014 (NASA/U.S. Navy)
 |















