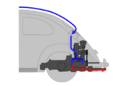
Engineering:Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout

In automotive design, an RR, or rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout places both the engine and drive wheels at the rear of the vehicle. In contrast to the RMR layout, the center of mass of the engine is between the rear axle and the rear bumper. Although very common in transit buses and coaches due to the elimination of the drive shaft with low-floor buses, this layout has become increasingly rare[specify] in passenger cars.[1]
Overview

Most of the traits of the RR configuration are shared with the mid-engine rear-wheel-drive, or MR. Placing the engine near the driven rear wheels allows for a physically smaller, lighter, less complex, and more efficient drivetrain, since there is no need for a driveshaft, and the differential can be integrated with the transmission, commonly referred to as a transaxle. The front-engine front-wheel-drive layout also has this advantage.
Since the engine is typically the heaviest component of the car, putting it near the rear axle usually results in more weight over the rear axle than the front, commonly referred to as a rear weight bias. The farther back the engine, the greater the bias. Typical weight bias for an FF (front engine, front-wheel-drive) is 65/35 front/rear; for FR, 55/45; for MR, 45/55; for RR, 35/65. A static rear weight requires less forward brake bias, as load is more evenly distributed among all four wheels under braking. Similarly, a rear weight bias means that the driven wheels have increased traction when accelerating, allowing them to put more power on the ground and accelerate faster.
The disadvantage to a rear weight bias is that the car can become unstable and tend to oversteer, especially when decelerating (whether braking or lifting off the throttle; see lift-off oversteer). When this happens, rotational inertia dictates that the added weight away from the axis of rotation (generally the steering wheels) will be more likely to maintain the spin, especially under braking. This is an inherent instability in the design, making it easier to induce and more difficult to recover from a slide than in a less rear-weight-biased vehicle.
Under hard acceleration, the decreased weight over the front wheels means less traction, sometimes producing a tendency for rear-engined cars to understeer out of a corner.
In these respects, an RR can be considered to be an exaggeration of MR - harder braking, faster and earlier acceleration, and increased oversteer.
In off-road and low-traction situations, the RR layout has some advantages compared to other 2WD layouts. The weight is biased towards the driven wheels- as with FF vehicles. This both improves drive-wheel traction and reduces the tendency for the undriven wheels to dig in. In addition, the driving and steering requirements are split between front and rear- as with FR vehicles- making it less likely for either to lose traction. Many dune buggies successfully use a Volkswagen beetle as the donor car for this reason. The relative simplicity and light weight compared to 4WD can therefore sometimes outweigh the disadvantage of only having two driven wheels.[2][3]
Where RR differs from MR is in that the engine is located outside the wheelbase. The major advantage of MR - low moment of inertia - is negated somewhat (though still lower than FR), and there is more room for passengers and cargo (though usually less than FR). Furthermore, because both axles are on the same side of the engine, it is technically more straightforward to drive all four wheels, than in a mid-engined configuration (though there have been more high-performance cars with the M4 layout than with R4). Finally, a rear-mounted engine has empty air (often at a lower pressure) behind it when moving, allowing more efficient cooling for air-cooled vehicles (more of which have been RR than liquid-cooled, such as the Volkswagen Beetle, and one of the few production air-cooled turbocharged cars, the Porsche 930).
For liquid-cooled vehicles, however, this layout presents a disadvantage, since it requires either increased coolant piping from a front-mounted radiator (meaning more weight and complexity), or relocating the radiator(s) to the sides or rear, and adding air ducting to compensate for the lower airflow at the rear of the car.
Due to the handling difficulty, the need for more space efficiency, and the near ubiquitous use of liquid-cooled engines in modern cars, most manufacturers have abandoned the RR layout. The major exception is Porsche, who has developed the 911 for over 40 years and has taken advantage of the benefits of RR while mitigating its drawbacks to acceptable levels, lately with the help of electronic aids. [4]
History
One of first RR cars was Tatra 77 of 1934, the first serial-produced aerodynamic car, designed by Hans Ledwinka. Tatra used this layout until end of production of T700 in 1999. In case of T613 and T700 Tatra used layout with engine above rear axle, which reduced some disadvantages of RR layout. Mercedes-Benz also produced several models of RR cars in this period, starting with the 130H (1934). The radical 1930s Tatra format (air-cooled, rear engine and streamlined, teardrop design) was an influence on Ferdinand Porsche's 'People's Car' (Volkswagen) for Adolf Hitler. As well as being the most produced car ever, it set a trend for RR small cars that lasted well into the 1960s. The final form of the RR Volkswagen was the Type 3 of 1961, which flattened the engine (or 'pancake'), allowing for luggage spaces front and rear.
Porsche has continued to develop its 911 model as a rear-engined vehicle, although they have introduced multiple all-wheel-drive models. Most notably, the 911 Turbo has been sold as AWD-only since the release of the 993 model. Race-oriented models such as the GT3 and twin-turbocharged GT2 remain solely RR, however.[5]
Another manufacturer to implement the RR configuration was the DeLorean Motor Company with its DeLorean sports car. To compensate for the uneven (35/65) weight distribution caused by the rear-mounted engine, De Lorean used rear wheels with a diameter slightly greater than the front wheels. Before that was the rear-engined Škoda's from Škoda 1000MB (produced from 1964) to Škoda 130/135/136 (produced until 1990) or the Polski Fiat 126p (produced until October 2000).
A range of sports road cars and racing cars with the RR layout was produced by the French company Alpine. These had bodies made of composite materials and used mechanical components made by Renault. (Alpine was eventually acquired by Renault; the A610 was a Renault product that used the Alpine name.)
Early cars using the RR layout included the Tucker, Volkswagen Beetle, Porsche 356, Chevrolet Corvair, NSU Prinz, ZAZ Zaporozhets and Hino Contessa.
Present day
Examples of modern combustion engine cars using the layout include the Porsche 911, Mitsubishi i, Smart Forfour, and Renault Twingo.[6]
Many modern electric cars use an RR layout for base variants with a single motor due to the low weight and cooling requirements of the electric motor. The Tesla Cybertruck and GMC Hummer EV will also use this layout for their base variants.
Most modern heavy duty buses use an extreme RR layout. In transit buses this can be used to make a very low floor level in the first two-thirds of the bus, thus making disabled access much easier.
Most tour buses and coaches also employ a similar design, however the free space is usually used for luggage, and sometimes airconditioning equipment.
Examples
-
BMW i3, a rear wheel drive, rear motor electric vehicle
-
Tatra 77, one of the first streamlined cars with RR platform
-
Illustration of the Beetle's engine air cooling in a Volkswagen Bug/Beetle (VW Type 1)
-
1962 Volkswagen Beetle Engine
-
Volkswagen Type 4: Volkswagen 411, Volkswagen 412
-
Tatra 603 with RR platform.
-
Porsche 911 with RR platform. Some current models are now all-wheel drive.
-
DMC DeLorean with RR platform.
-
Škoda 110R Coupé with RR platform.
-
The original Fiat 500 was rear-engined.
-
Volkswagen Wasserboxer four-cylinder rear engine in a Volkswagen Type 2 (T3)
-
An Oettinger WBX6, aftermarket six-cylinder rear engine in a Volkswagen Type 2 (T3)
-
Volkswagen Type 2, Single-cab utility pickup
-
The Meyers Manx, a dune buggy, with VW rear engine
-
Baja Bug-style modified Beetle
-
Early US- Porsche 930 with "Turbo Carrera" label
-
A view of the Ruf CTR engine bay of the CTR with Alois Ruf present near the car
-
Ruf CTR Yellowbird rear powerplant.
-
Volkswagen 181 also called the Volkswagen Thing, Safari, Trekker, and Pescaccia
-
ZAZ Zaporozhets Engine
-
1960 Renault 4CV longitudinally-mounted rear engine (750 cc)
-
Tata Nano engine in trunk that is only accessible from inside as a cost reduction feature
-
Front door open and side door in view on a BMW 600
-
Porsche 356 engine layout shows VW ancestry
-
Solaris Urbino 12 bus rear engine
-
Nishitetsu bus rear engine
-
Nishitetsu bus
-
The engine of the Mitsubishi i
References
- ↑ 1965 Chevrolet Corvair
- ↑ Semi Realistic Handling 1974 VW Beetle
- ↑ Technical Anatomy, What is Rear Engine Layout And Know How Is It Beneficial?, January 5,2018
- ↑ Why Is The Chevrolet Corvair Such An Overlooked Classic?, By Andrew Golseth, February 12, 2016
- ↑ arstechnica.com, Porsche 911: 52 years of staying true to its roots, First unveiled in 1963, the Porsche 911 has only ever been fully redesigned twice., Jonathan M. Gitlin, 8/18/2015
- ↑ Specifications of Tata's Nano-India Business-Business-The Times of India
 |