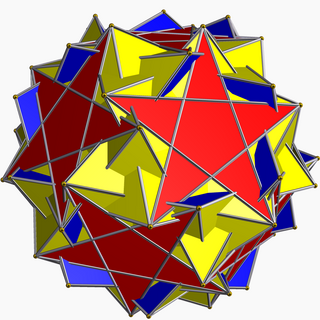
Inverted snub dodecadodecahedron
| Inverted snub dodecadodecahedron | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 84, E = 150 V = 60 (χ = −6) |
| Faces by sides | 60{3}+12{5}+12{5/2} |
| Wythoff symbol | | 5/3 2 5 |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | U60, C76, W114 |
| Dual polyhedron | Medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron |
| Vertex figure | 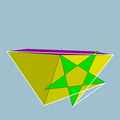 3.3.5.3.5/3 |
| Bowers acronym | Isdid |
File:Inverted snub dodecadodecahedron.stl In geometry, the inverted snub dodecadodecahedron (or vertisnub dodecadodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U60.[1] It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5/3,5}.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of an inverted snub dodecadodecahedron are all the even permutations of [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{array}{crrrc} \Bigl(& \pm\,2\alpha\ ,& \pm\,2\ ,& \pm\,2\beta\ & \Bigr), \\[2pt] \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[\alpha+\frac{\beta}{\varphi} + \varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[-\alpha\varphi + \beta + \frac{1}{\varphi}\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\frac{\alpha}{\varphi} + \beta\varphi - 1\bigr] & \Bigr), \\[2pt] \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[-\frac{\alpha}{\varphi} + \beta\varphi + 1\bigr],& \pm \bigl[-\alpha + \frac{\beta}{\varphi} - \varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha\varphi + \beta - \frac{1}{\varphi}\bigr] & \Bigr), \\[2pt] \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[-\frac{\alpha}{\varphi} + \beta\varphi - 1\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha - \frac{\beta}{\varphi} - \varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha\varphi + \beta + \frac{1}{\varphi}\bigr] & \Bigr), \\[2pt] \Bigl(& \pm \bigl[\alpha + \frac{\beta}{\varphi} - \varphi\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\alpha\varphi - \beta + \frac{1}{\varphi}\bigr],& \pm \bigl[\frac{\alpha}{\varphi} + \beta\varphi + 1\bigr] & \Bigr), \end{array} }[/math]
with an even number of plus signs, where [math]\displaystyle{ \beta = \frac{\ \ \frac{\alpha^2}{\varphi} + \varphi \ \ }{\ \alpha\varphi - \frac{1}{\varphi}}\ , }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi = \tfrac{1+\sqrt 5}{2} }[/math] is the golden ratio, and α is the negative real root of [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi\alpha^4 - \alpha^3 + 2\alpha^2 - \alpha - \frac{1}{\varphi} \quad \implies \quad \alpha \approx -0.3352090. }[/math] Taking the odd permutations of the above coordinates with an odd number of plus signs gives another form, the enantiomorph of the other one. Taking α to be the positive root gives the snub dodecadodecahedron.
Related polyhedra
Medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron
| Medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron | |
|---|---|

| |
| Type | Star polyhedron |
| Face | 
|
| Elements | F = 60, E = 150 V = 84 (χ = −6) |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | DU60 |
| dual polyhedron | Inverted snub dodecadodecahedron |
File:Medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron.stl The medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron (or midly petaloid ditriacontahedron) is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform inverted snub dodecadodecahedron. Its faces are irregular nonconvex pentagons, with one very acute angle.
Proportions
Denote the golden ratio by [math]\displaystyle{ \phi }[/math], and let [math]\displaystyle{ \xi\approx -0.236\,993\,843\,45 }[/math] be the largest (least negative) real zero of the polynomial [math]\displaystyle{ P=8x^4-12x^3+5x+1 }[/math]. Then each face has three equal angles of [math]\displaystyle{ \arccos(\xi)\approx 103.709\,182\,219\,53^{\circ} }[/math], one of [math]\displaystyle{ \arccos(\phi^2\xi+\phi)\approx 3.990\,130\,423\,41^{\circ} }[/math] and one of [math]\displaystyle{ 360^{\circ}-\arccos(\phi^{-2}\xi-\phi^{-1})\approx 224.882\,322\,917\,99^{\circ} }[/math]. Each face has one medium length edge, two short and two long ones. If the medium length is [math]\displaystyle{ 2 }[/math], then the short edges have length [math]\displaystyle{ 1-\sqrt{\frac{1-\xi}{\phi^3-\xi}}\approx 0.474\,126\,460\,54, }[/math] and the long edges have length [math]\displaystyle{ 1+\sqrt{\frac{1-\xi}{\phi^{-3}-\xi}} \approx 37.551\,879\,448\,54. }[/math] The dihedral angle equals [math]\displaystyle{ \arccos(\xi/(\xi+1))\approx 108.095\,719\,352\,34^{\circ} }[/math]. The other real zero of the polynomial [math]\displaystyle{ P }[/math] plays a similar role for the medial pentagonal hexecontahedron.
See also
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5 p. 124
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/MedialInvertedPentagonalHexecontahedron.html.
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Inverted snub dodecadodecahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/InvertedSnubDodecadodecahedron.html.
 |

