Snub dodecadodecahedron
| Snub dodecadodecahedron | |
|---|---|
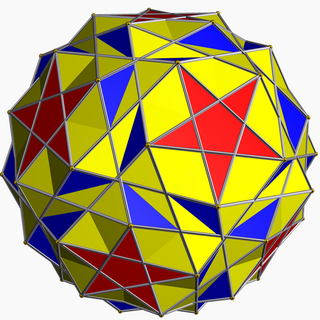
| |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 84, E = 150 V = 60 (χ = −6) |
| Faces by sides | 60{3}+12{5}+12{5/2} |
| Wythoff symbol | | 2 5/2 5 |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | U40, C49, W111 |
| Dual polyhedron | Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron |
| Vertex figure | 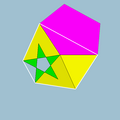 3.3.5/2.3.5 |
| Bowers acronym | Siddid |
File:Snub dodecadodecahedron.stl
In geometry, the snub dodecadodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U40. It has 84 faces (60 triangles, 12 pentagons, and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices.[1] It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄2,5}, as a snub great dodecahedron.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of an inverted snub dodecadodecahedron are all the even permutations of
with an even number of plus signs, where is the golden ratio, and α is the positive real root of Taking the odd permutations of the above coordinates with an odd number of plus signs gives another form, the enantiomorph of the other one. Taking α to be the negative root gives the inverted snub dodecadodecahedron.
Related polyhedra
Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron
| Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron | |
|---|---|
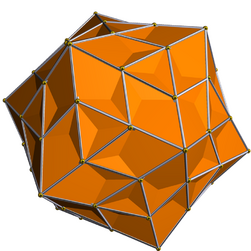
| |
| Type | Star polyhedron |
| Face | 
|
| Elements | F = 60, E = 150 V = 84 (χ = −6) |
| Symmetry group | I, [5,3]+, 532 |
| Index references | DU40 |
| dual polyhedron | Snub dodecadodecahedron |
File:Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron.stl The medial pentagonal hexecontahedron is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the snub dodecadodecahedron. It has 60 intersecting irregular pentagonal faces.
See also
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511569371, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/MedialPentagonalHexecontahedron.html.
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Snub dodecadodecahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SnubDodecadodecahedron.html.
 |
