Kaniadakis Weibull distribution
|
Probability density function  | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function  | |||
| Parameters |
rate shape (real) rate (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Quantile | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
The Kaniadakis Weibull distribution (or κ-Weibull distribution) is a probability distribution arising as a generalization of the Weibull distribution.[1][2] It is one example of a Kaniadakis κ-distribution. The κ-Weibull distribution has been adopted successfully for describing a wide variety of complex systems in seismology, economy, epidemiology, among many others.
Definitions
Probability density function
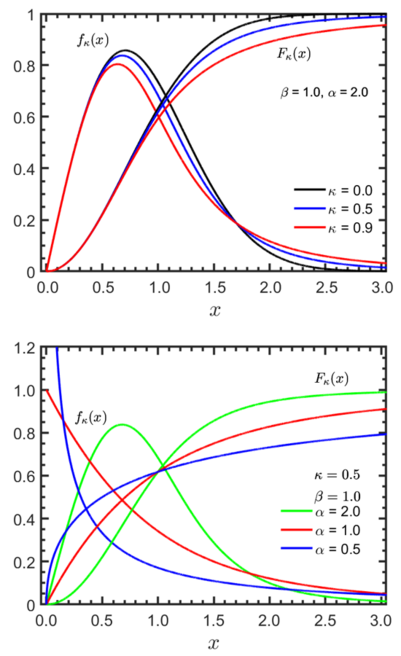
The Kaniadakis κ-Weibull distribution is exhibits power-law right tails, and it has the following probability density function:[3]
valid for , where is the entropic index associated with the Kaniadakis entropy, is the scale parameter, and is the shape parameter or Weibull modulus.
The Weibull distribution is recovered as
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function of κ-Weibull distribution is given by
valid for
. The cumulative Weibull distribution is recovered in the classical limit
.
Survival distribution and hazard functions
The survival distribution function of κ-Weibull distribution is given by
valid for . The survival Weibull distribution is recovered in the classical limit .
The hazard function of the κ-Weibull distribution is obtained through the solution of the κ-rate equation:
with
, where
is the hazard function:
The cumulative κ-Weibull distribution is related to the κ-hazard function by the following expression:
where
is the cumulative κ-hazard function. The cumulative hazard function of the Weibull distribution is recovered in the classical limit : .
Properties
Moments, median and mode
The κ-Weibull distribution has moment of order given by
The median and the mode are:
Quantiles
The quantiles are given by the following expression
with
.
Gini coefficient
The Gini coefficient is:[3]
Asymptotic behavior
The κ-Weibull distribution II behaves asymptotically as follows:[3]
Related distributions
- The κ-Weibull distribution is a generalization of:
- κ-Exponential distribution of type II, when ;
- Exponential distribution when and .
- A κ-Weibull distribution corresponds to a κ-deformed Rayleigh distribution when and a Rayleigh distribution when and .
Applications
The κ-Weibull distribution has been applied in several areas, such as:
- In economy, for analyzing personal income models, in order to accurately describing simultaneously the income distribution among the richest part and the great majority of the population.[1][4][5]
- In seismology, the κ-Weibull represents the statistical distribution of magnitude of the earthquakes distributed across the Earth, generalizing the Gutenberg–Richter law,[6] and the interval distributions of seismic data, modeling extreme-event return intervals.[7][8]
- In epidemiology, the κ-Weibull distribution presents a universal feature for epidemiological analysis.[9]
See also
- Giorgio Kaniadakis
- Kaniadakis statistics
- Kaniadakis distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Exponential distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Gaussian distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Gamma distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Logistic distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Erlang distribution
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Clementi, F.; Gallegati, M.; Kaniadakis, G. (2007). "κ-generalized statistics in personal income distribution" (in en). The European Physical Journal B 57 (2): 187–193. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2007-00120-9. ISSN 1434-6028. Bibcode: 2007EPJB...57..187C. http://link.springer.com/10.1140/epjb/e2007-00120-9.
- ↑ Clementi, F.; Di Matteo, T.; Gallegati, M.; Kaniadakis, G. (2008). "The -generalized distribution: A new descriptive model for the size distribution of incomes" (in en). Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications 387 (13): 3201–3208. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2008.01.109. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0378437108001349.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Kaniadakis, G. (2021-01-01). "New power-law tailed distributions emerging in κ-statistics (a)". Europhysics Letters 133 (1): 10002. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/133/10002. ISSN 0295-5075. Bibcode: 2021EL....13310002K. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1209/0295-5075/133/10002.
- ↑ Clementi, Fabio; Gallegati, Mauro; Kaniadakis, Giorgio (October 2010). "A model of personal income distribution with application to Italian data" (in en). Empirical Economics 39 (2): 559–591. doi:10.1007/s00181-009-0318-2. ISSN 0377-7332. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00181-009-0318-2.
- ↑ Clementi, F; Gallegati, M; Kaniadakis, G (2012-12-06). "A generalized statistical model for the size distribution of wealth". Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2012 (12): P12006. doi:10.1088/1742-5468/2012/12/P12006. ISSN 1742-5468. Bibcode: 2012JSMTE..12..006C. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-5468/2012/12/P12006.
- ↑ da Silva, Sérgio Luiz E.F. (2021). "κ -generalised Gutenberg–Richter law and the self-similarity of earthquakes" (in en). Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 143: 110622. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110622. Bibcode: 2021CSF...14310622D. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0960077920310134.
- ↑ Hristopulos, Dionissios T.; Petrakis, Manolis P.; Kaniadakis, Giorgio (2014-05-28). "Finite-size effects on return interval distributions for weakest-link-scaling systems" (in en). Physical Review E 89 (5): 052142. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.89.052142. ISSN 1539-3755. PMID 25353774. Bibcode: 2014PhRvE..89e2142H. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.89.052142.
- ↑ Hristopulos, Dionissios; Petrakis, Manolis; Kaniadakis, Giorgio (2015-03-09). "Weakest-Link Scaling and Extreme Events in Finite-Sized Systems" (in en). Entropy 17 (3): 1103–1122. doi:10.3390/e17031103. ISSN 1099-4300. Bibcode: 2015Entrp..17.1103H.
- ↑ Kaniadakis, Giorgio; Baldi, Mauro M.; Deisboeck, Thomas S.; Grisolia, Giulia; Hristopulos, Dionissios T.; Scarfone, Antonio M.; Sparavigna, Amelia; Wada, Tatsuaki et al. (2020). "The κ-statistics approach to epidemiology" (in en). Scientific Reports 10 (1): 19949. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-76673-3. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 33203913. Bibcode: 2020NatSR..1019949K.
External links
 |

