Kaniadakis distribution
In statistics, a Kaniadakis distribution (also known as κ-distribution) is a statistical distribution that emerges from the Kaniadakis statistics.[1] There are several families of Kaniadakis distributions related to different constraints used in the maximization of the Kaniadakis entropy, such as the κ-Exponential distribution, κ-Gaussian distribution, Kaniadakis κ-Gamma distribution and κ-Weibull distribution. The κ-distributions have been applied for modeling a vast phenomenology of experimental statistical distributions in natural or artificial complex systems, such as, in epidemiology,[2] quantum statistics,[3][4][5] in astrophysics and cosmology,[6][7][8] in geophysics,[9][10][11] in economy,[12][13][14] in machine learning.[15]
The κ-distributions are written as function of the κ-deformed exponential, taking the form
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_i=\exp_{\kappa}(-\beta E_i+\beta \mu) }[/math]
enables the power-law description of complex systems following the consistent κ-generalized statistical theory.,[16][17] where [math]\displaystyle{ \exp_{\kappa}(x)=(\sqrt{1+ \kappa^2 x^2}+\kappa x)^{1/\kappa} }[/math] is the Kaniadakis κ-exponential function.
The κ-distribution becomes the common Boltzmann distribution at low energies, while it has a power-law tail at high energies, the feature of high interest of many researchers.
List of κ-statistical distributions
Supported on the whole real line
- The Kaniadakis Gaussian distribution, also called the κ-Gaussian distribution. The normal distribution is a particular case when [math]\displaystyle{ \kappa \rightarrow 0. }[/math]
- The Kaniadakis double exponential distribution, as known as Kaniadakis κ-double exponential distribution or κ-Laplace distribution. The Laplace distribution is a particular case when [math]\displaystyle{ \kappa \rightarrow 0. }[/math][18]
Supported on semi-infinite intervals, usually [0,∞)
- The Kaniadakis Exponential distribution, also called the κ-Exponential distribution. The exponential distribution is a particular case when [math]\displaystyle{ \kappa \rightarrow 0. }[/math]
- The Kaniadakis Gamma distribution, also called the κ-Gamma distribution, which is a four-parameter ([math]\displaystyle{ \kappa, \alpha, \beta, \nu }[/math]) deformation of the generalized Gamma distribution.
- The κ-Gamma distribution becomes a ...
- κ-Exponential distribution of Type I when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = \nu = 1 }[/math].
- κ-Erlang distribution when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = n = }[/math] positive integer.
- κ-Half-Normal distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 1/2 }[/math].
- Generalized Gamma distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 1 }[/math];
- In the limit [math]\displaystyle{ \kappa \rightarrow 0 }[/math], the κ-Gamma distribution becomes a ...
- Erlang distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = n = }[/math] positive integer;
- Chi-Squared distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = }[/math] half integer;
- Nakagami distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu \gt 0 }[/math];
- Rayleigh distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 1 }[/math];
- Chi distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = }[/math] half integer;
- Maxwell distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 3/2 }[/math];
- Half-Normal distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 1/2 }[/math];
- Weibull distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \gt 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 1 }[/math];
- Stretched Exponential distribution, when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \gt 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 1/\alpha }[/math];
- The κ-Gamma distribution becomes a ...
Common Kaniadakis distributions
κ-Exponential distribution
κ-Gaussian distribution
κ-Gamma distribution
κ-Weibull distribution
κ-Logistic distribution
κ-Erlang distribution
κ-Distribution Type IV
|
Probability density function  Plot of the κ-Distribution Type IV for typical κ-values, and [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = \beta = 1 }[/math]. | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 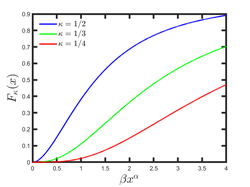 | |||
| Parameters |
[math]\displaystyle{ 0 \leq \kappa \lt 1 }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \gt 0 }[/math] shape (real) [math]\displaystyle{ \beta\gt 0 }[/math] rate (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | [math]\displaystyle{ x \in [0, +\infty) }[/math] | ||
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\alpha}{\kappa} (2\kappa \beta )^{1/\kappa } \left(1 - \frac{\kappa \beta x^\alpha}{\sqrt{1+\kappa^2\beta^2x^{2\alpha} } } \right) x^{ -1 + \alpha / \kappa} \exp_\kappa(-\beta x^\alpha) }[/math] | |||
| CDF | [math]\displaystyle{ (2\kappa \beta )^{1/\kappa} x^{\alpha / \kappa} \exp_\kappa(-\beta x^\alpha) }[/math] | ||
The Kaniadakis distribution of Type IV (or κ-Distribution Type IV) is a three-parameter family of continuous statistical distributions.[1]
The κ-Distribution Type IV distribution has the following probability density function:
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_{_{\kappa}}(x) = \frac{\alpha}{\kappa} (2\kappa \beta )^{1/\kappa} \left(1 - \frac{\kappa \beta x^\alpha}{\sqrt{1+\kappa^2\beta^2x^{2\alpha} } } \right) x^{ -1 + \alpha / \kappa} \exp_\kappa(-\beta x^\alpha) }[/math]
valid for [math]\displaystyle{ x \geq 0 }[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \leq |\kappa| \lt 1 }[/math] is the entropic index associated with the Kaniadakis entropy, [math]\displaystyle{ \beta \gt 0 }[/math] is the scale parameter, and [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \gt 0 }[/math] is the shape parameter.
The cumulative distribution function of κ-Distribution Type IV assumes the form:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_\kappa(x) = (2\kappa \beta )^{1/\kappa} x^{\alpha / \kappa} \exp_\kappa(-\beta x^\alpha) }[/math]
The κ-Distribution Type IV does not admit a classical version, since the probability function and its cumulative reduces to zero in the classical limit [math]\displaystyle{ \kappa \rightarrow 0 }[/math].
Its moment of order [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{E}[X^m] = \frac{(2 \kappa \beta)^{-m/\alpha} }{ 1 + \kappa \frac{ m }{ 2\alpha } } \frac{\Gamma\Big(\frac{1}{\kappa} + \frac{m}{\alpha}\Big) \Gamma\Big(1 - \frac{m}{2\alpha}\Big)}{\Gamma\Big(\frac{1}{\kappa} + \frac{m}{2\alpha}\Big)} }[/math]
The moment of order [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] of the κ-Distribution Type IV is finite for [math]\displaystyle{ m \lt 2\alpha }[/math].
See also
- Giorgio Kaniadakis
- Kaniadakis statistics
- Kaniadakis κ-Exponential distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Gaussian distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Gamma distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Weibull distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Logistic distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Erlang distribution
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Kaniadakis, G. (2021-01-01). "New power-law tailed distributions emerging in κ-statistics (a)". Europhysics Letters 133 (1): 10002. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/133/10002. ISSN 0295-5075. Bibcode: 2021EL....13310002K. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1209/0295-5075/133/10002.
- ↑ Kaniadakis, Giorgio; Baldi, Mauro M.; Deisboeck, Thomas S.; Grisolia, Giulia; Hristopulos, Dionissios T.; Scarfone, Antonio M.; Sparavigna, Amelia; Wada, Tatsuaki et al. (2020). "The κ-statistics approach to epidemiology" (in en). Scientific Reports 10 (1): 19949. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-76673-3. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 33203913. Bibcode: 2020NatSR..1019949K.
- ↑ Santos, A.P.; Silva, R.; Alcaniz, J.S.; Anselmo, D.H.A.L. (2011). "Generalized quantum entropies" (in en). Physics Letters A 375 (35): 3119–3123. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2011.07.001. Bibcode: 2011PhLA..375.3119S. https://repositorio.ufrn.br/jspui/handle/123456789/29118.
- ↑ Ourabah, Kamel; Tribeche, Mouloud (2014-06-24). "Planck radiation law and Einstein coefficients reexamined in Kaniadakis κ statistics" (in en). Physical Review E 89 (6): 062130. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.89.062130. ISSN 1539-3755. PMID 25019747. Bibcode: 2014PhRvE..89f2130O. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.89.062130.
- ↑ Lourek, Imene; Tribeche, Mouloud (2017). "Thermodynamic properties of the blackbody radiation: A Kaniadakis approach" (in en). Physics Letters A 381 (5): 452–456. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2016.12.019. Bibcode: 2017PhLA..381..452L.
- ↑ Carvalho, J. C.; do Nascimento, J. D.; Silva, R.; De Medeiros, J. R. (2009-05-01). "Non-Gaussian Statistics and Stellar Rotational Velocities of Main-Sequence Field Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 696 (1): L48–L51. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/696/1/L48. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2009ApJ...696L..48C. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0004-637X/696/1/L48.
- ↑ Abreu, Everton M.C.; Ananias Neto, Jorge; Mendes, Albert C.R.; de Paula, Rodrigo M. (2019). "Loop quantum gravity Immirzi parameter and the Kaniadakis statistics" (in en). Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 118: 307–310. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2018.11.033. Bibcode: 2019CSF...118..307A.
- ↑ Soares, Bráulio B.; Barboza, Edésio M.; Abreu, Everton M.C.; Neto, Jorge Ananias (2019). "Non-Gaussian thermostatistical considerations upon the Saha equation" (in en). Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications 532: 121590. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2019.121590. Bibcode: 2019PhyA..53221590S.
- ↑ Hristopulos, Dionissios T.; Petrakis, Manolis P.; Kaniadakis, Giorgio (2014-05-28). "Finite-size effects on return interval distributions for weakest-link-scaling systems" (in en). Physical Review E 89 (5): 052142. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.89.052142. ISSN 1539-3755. PMID 25353774. Bibcode: 2014PhRvE..89e2142H. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.89.052142.
- ↑ da Silva, Sérgio Luiz E.F. (2021). "κ -generalised Gutenberg–Richter law and the self-similarity of earthquakes" (in en). Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 143: 110622. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110622. Bibcode: 2021CSF...14310622D.
- ↑ da Silva, Sérgio Luiz E. F.; Carvalho, Pedro Tiago C.; de Araújo, João M.; Corso, Gilberto (2020-05-27). "Full-waveform inversion based on Kaniadakis statistics" (in en). Physical Review E 101 (5): 053311. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.101.053311. ISSN 2470-0045. PMID 32575242. Bibcode: 2020PhRvE.101e3311D. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.101.053311.
- ↑ Clementi, Fabio; Gallegati, Mauro; Kaniadakis, Giorgio; Landini, Simone (2016). "κ-generalized models of income and wealth distributions: A survey" (in en). The European Physical Journal Special Topics 225 (10): 1959–1984. doi:10.1140/epjst/e2016-60014-2. ISSN 1951-6355. Bibcode: 2016EPJST.225.1959C. http://link.springer.com/10.1140/epjst/e2016-60014-2.
- ↑ Clementi, Fabio; Gallegati, Mauro; Kaniadakis, Giorgio (2012). "A new model of income distribution: the κ-generalized distribution" (in en). Journal of Economics 105 (1): 63–91. doi:10.1007/s00712-011-0221-0. ISSN 0931-8658. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00712-011-0221-0.
- ↑ Trivellato, Barbara (2013-09-02). "Deformed Exponentials and Applications to Finance" (in en). Entropy 15 (12): 3471–3489. doi:10.3390/e15093471. ISSN 1099-4300. Bibcode: 2013Entrp..15.3471T. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/18ab/6d30fe656eaac3f9510d9d58b7f70fe6b76f.pdf.
- ↑ Passos, Leandro Aparecido; Cleison Santana, Marcos; Moreira, Thierry; Papa, Joao Paulo (2019). "κ-Entropy Based Restricted Boltzmann Machines". 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Budapest, Hungary: IEEE. pp. 1–8. doi:10.1109/IJCNN.2019.8851714. ISBN 978-1-7281-1985-4. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8851714.
- ↑ Kaniadakis, Giorgio (2013-09-25). "Theoretical Foundations and Mathematical Formalism of the Power-Law Tailed Statistical Distributions" (in en). Entropy 15 (12): 3983–4010. doi:10.3390/e15103983. ISSN 1099-4300. Bibcode: 2013Entrp..15.3983K.
- ↑ Kaniadakis, G. (2001). "Non-linear kinetics underlying generalized statistics" (in en). Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications 296 (3–4): 405–425. doi:10.1016/S0378-4371(01)00184-4. Bibcode: 2001PhyA..296..405K.
- ↑ da Silva, Sérgio Luiz E. F.; dos Santos Lima, Gustavo Z.; Volpe, Ernani V.; de Araújo, João M.; Corso, Gilberto (2021). "Robust approaches for inverse problems based on Tsallis and Kaniadakis generalised statistics" (in en). The European Physical Journal Plus 136 (5): 518. doi:10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01521-w. ISSN 2190-5444. Bibcode: 2021EPJP..136..518D. https://link.springer.com/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01521-w.
External links
This article needs additional or more specific categories. (August 2022) |
 |



