Medicine:Posterior circulation infarct
From HandWiki
| Posterior circulation infarct | |
|---|---|
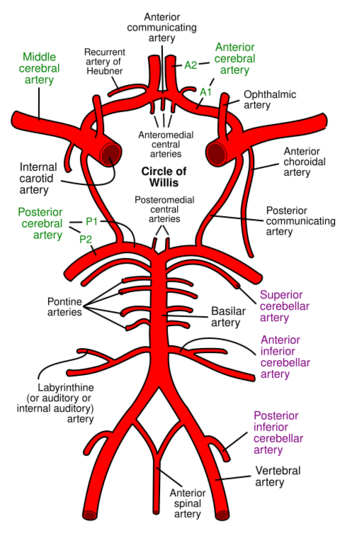 | |
| Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain (inferior view). Posterior circulation represented by bottom half of diagram. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Posterior circulation infarct (POCI) is a type of cerebral infarction affecting the posterior circulation supplying one side of the brain.
Posterior circulation stroke syndrome (POCS) refers to the symptoms of a patient who clinically appears to have had a posterior circulation infarct, but who has not yet had any diagnostic imaging (e.g. CT Scan) to confirm the diagnosis.
It can cause the following symptoms:
- Cranial nerve palsy AND contralateral motor/sensory defect
- Bilateral motor or sensory defect
- Eye movement problems (e.g.nystagmus)
- Cerebellar dysfunction
- Isolated homonymous hemianopia
- Vertigo
It has also been associated with deafness.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Lee H (2008). "Sudden deafness related to posterior circulation infarction in the territory of the nonanterior inferior cerebellar artery: frequency, origin, and vascular topographical pattern". Eur. Neurol. 59 (6): 302–6. doi:10.1159/000121421. PMID 18408371. https://www.karger.com/Article/PDF/000121421.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
 |

