Physics:Eckhaus equation
From HandWiki
In mathematical physics, the Eckhaus equation – or the Kundu–Eckhaus equation – is a nonlinear partial differential equation within the nonlinear Schrödinger class:[1]
- [math]\displaystyle{ i \psi_t + \psi_{xx} +2 \left( |\psi|^2 \right)_x\, \psi + |\psi|^4\, \psi = 0. }[/math]
The equation was independently introduced by Wiktor Eckhaus and by Anjan Kundu to model the propagation of waves in dispersive media.[2][3]
Linearization
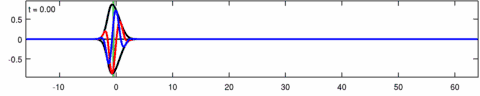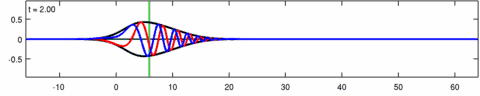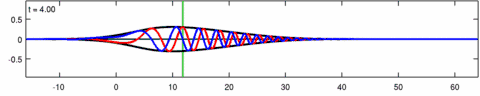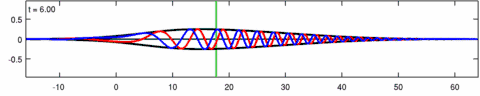
Animation of a wave-packet solution of the Eckhaus equation. The blue line is the real part of the solution, the red line is the imaginary part and the black line is the wave envelope (absolute value). Note the asymmetry in the envelope [math]\displaystyle{ |\psi(x,t)| }[/math] for the Eckhaus equation, while the envelope [math]\displaystyle{ |\varphi(x,t)| }[/math] – of the corresponding solution to the linear Schrödinger equation – is symmetric (in [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]). The short waves in the packet propagate faster than the long waves.
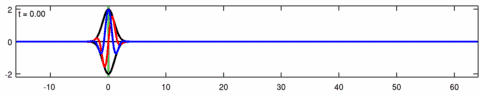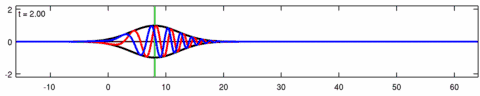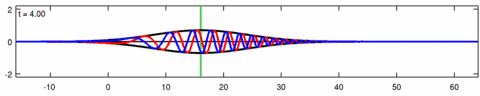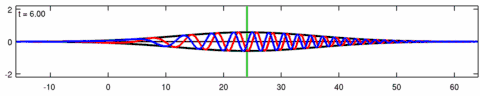
Animation of the wave-packet solution of the linear Schrödinger equation – corresponding with the above animation for the Eckhaus equation. The blue line is the real part of the solution, the red line is the imaginary part, the black line is the wave envelope (absolute value) and the green line is the centroid of the wave packet envelope.
The Eckhaus equation can be linearized to the linear Schrödinger equation:[4]
- [math]\displaystyle{ i \varphi_t + \varphi_{xx} =0, }[/math]
through the non-linear transformation:[5]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi(x,t) = \psi(x,t)\, \exp\left( \int_{-\infty}^x |\psi(x^\prime,t)|^2\; \text{d}x^\prime \right). }[/math]
The inverse transformation is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \psi(x,t) = \frac{\varphi(x,t)}{\displaystyle \left( 1 + 2\, \int_{-\infty}^x |\varphi(x^\prime,t)|^2\; \text{d}x^\prime \right)^{1/2}}. }[/math]
This linearization also implies that the Eckhaus equation is integrable.
Notes
References
- Ablowitz, M.J.; Ahrens, C.D.; De Lillo, S. (2005), "On a "quasi" integrable discrete Eckhaus equation", Journal of Nonlinear Mathematical Physics 12 (Supplement 1): 1–12, doi:10.2991/jnmp.2005.12.s1.1, Bibcode: 2005JNMP...12S...1A
- Calogero, F.; De Lillo, S. (1987), "The Eckhaus PDE iψt + ψxx+ 2(|ψ|2)x ψ + |ψ|4 ψ = 0", Inverse Problems 3 (4): 633–682, doi:10.1088/0266-5611/3/4/012, Bibcode: 1987InvPr...3..633C
- Eckhaus, W. (1985), The long-time behaviour for perturbed wave-equations and related problems, Department of Mathematics, University of Utrecht, Preprint no. 404.
Published in part in: Eckhaus, W. (1986), "The long-time behaviour for perturbed wave-equations and related problems", in Kröner, E.; Kirchgässner, K., Trends in applications of pure mathematics to mechanics, Lecture Notes in Physics, 249, Berlin: Springer, pp. 168–194, doi:10.1007/BFb0016391, ISBN 978-3-540-16467-8 - Kundu, A. (1984), "Landau–Lifshitz and higher-order nonlinear systems gauge generated from nonlinear Schrödinger-type equations", Journal of Mathematical Physics 25 (12): 3433–3438, doi:10.1063/1.526113, Bibcode: 1984JMP....25.3433K
- Taghizadeh, N.; Mirzazadeh, M.; Tascan, F. (2012), "The first-integral method applied to the Eckhaus equation", Applied Mathematics Letters 25 (5): 798–802, doi:10.1016/j.aml.2011.10.021
- Zwillinger, D. (1998), Handbook of differential equations (3rd ed.), Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-12-784396-4
 |

