Software:RawTherapee
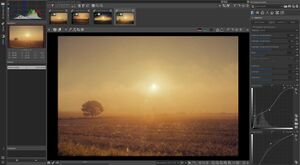 Screenshot of RawTherapee pre-5.0 editing a raw photo | |
| Initial release | 2005[1][2] |
|---|---|
| Written in | C++ gtkmm |
| Operating system | Linux, Microsoft Windows, and macOS[3] |
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Type | Post-production tool for photography |
| License | Since 3.0: GPL-3.0-or-later Until 2.4.1: Proprietary |
| Website | {{{1}}} |
RawTherapee is a free and open source application for processing photographs in raw image formats such as those created by many digital cameras.[4] It comprises a subset of image editing operations specifically aimed at non-destructive post-production of raw photos and is primarily focused on improving a photographer's workflow by facilitating the handling of large numbers of images. It is notable for the advanced control it gives the user over the demosaicing and developing process. It is cross-platform, with versions for Microsoft Windows, macOS and Linux.
RawTherapee was originally written by Gábor Horváth of Budapest, Hungary, and was re-licensed as free and open-source software under the GNU General Public License Version 3 in January 2010.[5] It is written in C++, using a GTK+ front-end and a patched version of dcraw for reading raw files. The name "Therapee" was originally an acronym derived from "The Experimental Raw Photo Editor".[6]
Features
RawTherapee involves the concept of non-destructive editing, similar to that of some other raw conversion software. Adjustments made by the user are immediately reflected in the preview image, though they are not physically applied to the opened image but the parameters are saved to a separate sidecar file.[7] These adjustments are then applied during the export process. All the internal processing is done in a high precision 32-bit floating point engine.[8]
Input file formats
RawTherapee supports most raw formats, including Pentax Pixel Shift, Canon Dual-Pixel, and those from Foveon and X-Trans sensors. It also supports common non-raw image formats like JPEG, PNG and TIFF[9][10] as well as high dynamic range, 16/24/32-bit raw DNG images.
RawTherapee uses a patched version of dcraw code to read and parse raw formats, with additional tweaks and constraints to parameters such as white levels and the raw crop area based on in-house measurements.[11] Thus, RawTherapee supports all the formats supported by dcraw.
User interface
RawTherapee provides the user with a file browser, a queue, a panel for batch image adjustments, a 1:1 preview of the embedded JPEG image in the case of raw files, and an image editing tab.
The file browser shows photo thumbnails along with a caption of the shooting information metadata. The browser includes 5-star rating, flagging, and an Exif-based filter. It can be used to apply a profile, or parts of a profile, to a whole selection of photos in one operation.
A toolbox alongside the file browser allows for batch image adjustments.
Adjustment tools and processing
- Bayer demosaicing algorithms: AMaZE, IGV, LMMSE, EAHD, HPHD, VNG4, DCB, AHD, fast or mono, as well as none.[12]
- Raw files from X-Trans sensors have the 3-pass, 1-pass and fast demosaicing methods at their disposal.
- Processing profiles support via sidecar files with the ability to fully and partially load, save and copy profiles between images
- Processing parameters can be generated dynamically based on image metadata using the Dynamic Profile Builder.
- Exposure control and curves in the L*a*b* and RGB color spaces
- CIECAM02 mode
- Advanced highlight reconstruction algorithms and shadow/highlight controls
- Tone mapping using edge-preserving decomposition
- Pre-crop vignetting correction and post-crop vignetting for artistic effect
- Graduated filter
- Various methods of sharpening
- Various methods of noise reduction
- Detail recovery
- Removal of purple fringing
- Manual and automatic pre- and post-demosaic chromatic aberration correction
- Advanced wavelet processing
- Retinex processing
- White balance (presets, color temperature, spot white balance and auto white balance)
- Channel mixer
- Black-and-white conversion
- Color boost and vibrance (saturation control with the option of preserving natural skin tones)
- Hue, saturation and value adjustments using curves
- Various methods of color toning
- Lockable color picker
- Wide gamut preview support on Microsoft Windows and Linux (the macOS preview is limited to sRGB)
- Soft-proofing support
- Color-managed workflow
- ICC color profiles (input, working and output)
- DCP color profiles (input)
- Adobe Lens Correction Profiles (LCP)
- Cropping, resizing, post-resize sharpening
- Rotation with visual straightening tool
- Distortion correction
- Perspective adjustment
- Dark frame subtraction
- Flat field removal (hue shifts, dust removal, vignetting correction)
- Hot and dead pixel filters
- Metadata (Exif and IPTC) editor
- A processing queue to free up the CPU during editing where instant feedback is important and to make maximal use of it afterwards
Output formats
The output format can be selected from:[13]
- TIFF (8-bit, 16-bit, 16-bit float, 32-bit float)
- JPEG (8-bit)
- PNG (8-bit and 16-bit)
See also
References
- ↑ "Getting Started". 21 July 2021. https://rawpedia.pixls.us/Getting_Started.
- ↑ "RawTherapee as a Free Lightroom Alternative". 27 June 2022. https://havecamerawilltravel.com/rawtherapee-raw-image-processing/.
- ↑ "Downloads". 2020. https://www.rawtherapee.com/downloads/.
- ↑ Schroder, Carla (25 August 2014). "Raw Sharpening And NoiseReduction with Raw Therapee On Linux". http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/785383-raw-sharpening-and-noise-reduction-with-raw-therapee-on-linux/.
- ↑ Hilzinger, Marcel (7 January 2010). "Free Therapy: RawTherapee as of Version 3.0 Under GPLv3". http://www.linux-magazine.com/Online/News/Free-Therapy-RawTherapee-as-of-Version-3.0-Under-GPLv3.
- ↑ "RawTherapee - issue #885". 3 August 2011. https://code.google.com/archive/p/rawtherapee/issues/885.
- ↑ "Sidecar Files - Processing Profiles - RawPedia". https://rawpedia.rawtherapee.com/Sidecar_Files_-_Processing_Profiles.
- ↑ "The Floating Point Engine". http://rawpedia.rawtherapee.com/The_Floating_Point_Engine.
- ↑ Leichtenstern, Thomas (October 2008). "Digital Darkroom". http://www.linux-magazine.com/Issues/2008/95/RawTherapee.
- ↑ "RawTherapee 4.0.11". 6 September 2013. https://www.photoreview.com.au/rawtherapee-40112/rawtherapee-4011/.
- ↑ "Adding Support for New Raw Formats - RawPedia". https://rawpedia.rawtherapee.com/Adding_Support_for_New_Raw_Formats.
- ↑ Williams, Mike (23 April 2019). "Raw Therapee 5.6". https://www.techadvisor.co.uk/download/audio-video-photo/raw-therapee-56-3328476/.
- ↑ "Raw Therapee". http://www.majorgeeks.com/files/details/rawtherapee.html.
External links
- No URL found. Please specify a URL here or add one to Wikidata.
 |
