Chemistry:Ibogaline
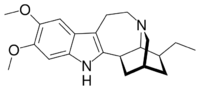
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R,17S)-17-Ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-3,13-diazapentacyclo[13.3.1.02,10.04,9.013,18]nonadeca-2(10),4,6,8-tetraene
| |
| Other names
12,13-Dimethoxyibogamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H28N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 340.467 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ibogaline is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga along with the related chemical compounds ibogaine, ibogamine, and other minor alkaloids. It is a relatively smaller component of Tabernanthe iboga root bark total alkaloids (TA) content. It is also present in Tabernaemontana species such as Tabernaemontana australis[1] which shares similar ibogan-biosynthetic pathways. The percentage of ibogaline in T. iboga root bark is up to 15% TA with ibogaine constituting 80% of the alkaloids and ibogamine up to 5%.[2][3]
Chemistry
Derivatives
Kisantine and Gabonine are thought to be ibogaline's oxidation byproducts.[4]
Adverse effect
In rodents, ibogaline induces more body tremor and ataxia compared to ibogaine and ibogamine.[5] Among a series of iboga and harmala alkaloids evaluated in rats, the study authors found the following order of potency in causing tremors:[5]
- ED50 (μmol/kg, sc): tabernanthine (4.5) > ibogaline (7.6) > harmaline (12.8) > harmine (13.7) > ibogaine (34.8) > noribogaine (176.0)
A subsequent study confirmed these findings.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Indole alkaloids from Tabernaemontana australis (Muell. Arg) Miers that inhibit acetylcholinesterase enzyme". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 13 (12): 4092–5. June 2005. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.03.045. PMID 15911323.
- ↑ Piotr Popik, Phil Skolnick (1998). Pharmacology of Ibogaine and Ibogaine-Related Alkaloids. 52. San Diego.
- ↑ Norbert Neuss (1959). "Notes- Alkaloids from Apocynaceae II. Ibogaline, A New Alkaloid From Tabernanthe Iboga Baill". J. Org. Chem. 24 (12): 2047–2048. doi:10.1021/jo01094a622.
- ↑ Taylor, W. I. (2002). "The Alkaloids of Tabernanthe iboga. IX.1 The Structures of the Ibogaline Derivatives, Kisantine and Gabonine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 30 (1): 309–310. doi:10.1021/jo01012a515. ISSN 0022-3263.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Cerebral Phamacokinetics of Tremor-producing Harmala and Iboga Alkaloids". Pharmacology 7 (4): 237–248. 1972. doi:10.1159/000136294. PMID 5077309.
- ↑ "Effects of iboga alkaloids on morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats: relationship to tremorigenic effects and to effects on dopamine release in nucleus accumbens and striatum". Brain Res. 657 (1–2): 14–22. 1994. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)90948-2. PMID 7820611.
 |

