Chemistry:Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid
From HandWiki
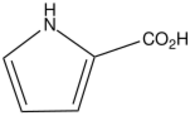
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-Mialine, 2-Minaline, Minalin, Minaline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 80825 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| 101562 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 111.100 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 206 °C (403 °F; 479 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HNC4H3CO2H. It is one of two monocarboxylic acids of pyrrole. It is a white solid. It arises in nature by dehydrogenation of the amino acid proline.[1] It also arises by carboxylation of pyrrole.[2] The ethyl ester of this acid is readily prepared from pyrrole.[3]
References
- ↑ Thomas, Michael G.; Burkart, Michael D.; Walsh, Christopher T. (2002). "Conversion of L-Proline to Pyrrolyl-2-Carboxyl-S-PCP during Undecylprodigiosin and Pyoluteorin Biosynthesis". Chemistry & Biology 9 (2): 171–184. doi:10.1016/S1074-5521(02)00100-X. PMID 11880032.
- ↑ Wieser, Marco; Yoshida, Toyokazu; Nagasawa, Toru (2001). "Carbon dioxide fixation by reversible pyrrole-2-carboxylate decarboxylase and its application". Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic 11 (4–6): 179–184. doi:10.1016/S1381-1177(00)00038-2.
- ↑ Denis M. Bailey, Robert E. Johnson, and Noel F. Albertson (1971). "Ethyl Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate". Organic Syntheses 51: 100. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.051.0100.
 |

