Biology:RICTOR
 Generic protein structure example |
Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mammalian target of rapamycin (RICTOR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RICTOR gene.[1][2]
RICTOR and mTOR are components of a protein complex that integrates nutrient- and growth factor-derived signals to regulate cell growth.[2]
Structure
The gene RICTOR is located on chromosome 5 at 5p13.1 with a sequence length of 5440 bp, oriented on the minus strand.[3][4] The translated RICTOR protein contains 1709 amino acids and is present in the cytosol. RICTOR contains few conserved regions and function domains of RICTOR have yet to be observed.[5] However, using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis, 21 phosphorylation sites were identified on RICTOR. Of these sites, T1135 has been shown to undergo growth factor-responsive phosphorylation via S6K1.[6]
Function
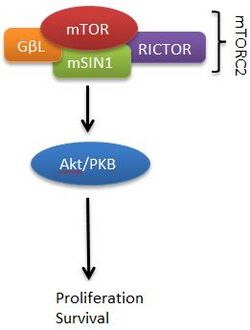
RICTOR is a subunit of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) which contains mTOR, GβL, RICTOR (this protein) and mSIN1.[7]
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a highly conserved Ser/Thr kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation.[8]
mTOR may exist as mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) or mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2). RICTOR is a key component of mTORC2, which, unlike mTORC1, is not directly inhibited by rapamycin. mTORC2, and RICTOR, specifically, has been shown to phosphorylate Akt/protein kinase B (PKB) on SER473. This phosphorylation activates Akt/PKB, where deregulation of Akt/PKB has been implicated in cancer and diabetes.[9]
RICTOR and mTORC2 have been shown to play an essential role in embryonic growth and development, perhaps due to the control that mTORC2 exerts on actin cytoskeleton organization.[10]
Regulation
FoxO transcription factors can activate expression of RICTOR. FoxO has been shown to inhibit mTORC1, while activating Akt through RICTOR elevation.[11]
Degradation
Perifosine has been shown to interfere with mTOR activity by degrading its components, such as RICTOR.[12]
Interactions
RICTOR has been shown to interact with and play a role in:
| * KIAA1303,[13] | * MTOR[7][13][14][15][16][17][18] |
| *EGFR | *Fibroblast growth factor |
| *Nerve growth factor receptor | *Peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation |
| *TOR | *Protein kinase B |
| *Phosphoinositide-mediated signaling [19] | *T cell costimulation [19] |
| *Cell migration[19] | *actin cytoskeleton organization [19] |
Clinical relevance
Diseases associated with mutation in the RICTOR gene include foramen magnum meningioma and syringomyelia. Akt/PMB activation is also involved in glucose metabolism and activation of Akt by RICTOR has been shown to mediate glucose and lipid metabolism.[20] Therefore, the influence of RICTOR and mTORC2 on Akt signaling has been associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Cancer
Akt/PMB activation leads to proliferation and survival, therefore over-activation of the Akt/PMB pathway by mTORC2 (including RICTOR) is implicated in cancerous growth.
In human colorectal carcinoma, RICTOR has been shown to association with FBXW7 (outside of mTORC2) to mediate the ubiquitination of growth-promoting factors cyclin E and c-Myc. Furthermore, elevated growth factor signaling may suppress the ubiquitinating action of RICTOR-FBXW7, resulting in accumulation of cyclin E and c-Myc and subsequent progression through the cell cycle.[21]
In glioblastoma (GBM), RICTOR(along with EGFR) may serve as an effective therapeutic target for silencing RNA, leading to decreased cell proliferation. Co-silencing of RICTOR and EGFR lead to increased sensitivity to alkaloids and alkylating agents. For one particular PTEN-mutant cell line, co-silencing resulted in tumor eradication.[22]
RICTOR has been shown to be significantly overexpressed in well-differentiated leiomyosarcomas. Due to the influence of RICTOR on actin polymerization, RICTOR could play a role in allowing transcription and subsequent differentiation in these muscle cells.[23]
mTOR subunits RICTOR and RAPTOR both showed increased expression, which increased with pituitary adenoma tumor staging. Therefore, mTOR, RPTOR and RICTOR were significantly correlated with the growth and invasion of pituitary adenomas and may have an important predictive and prognostic value in such patients.[24]
See also
References
- ↑ "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99 (26): 16899–903. Dec 2002. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Entrez Gene: RICTOR rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=253260.
- ↑ "Gene & protein Summary: RICTOR". EMBL-EBI. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/s4/summary/molecular?term=RICTOR&classification=9606.
- ↑ "Homo sapiens rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR, mRNA (cDNA clone IMAGE:5787163), partial cds". UniGene. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/seq.cgi?ORG=Hs&SID=15630523.
- ↑ "Targeting mTOR: prospects for mTOR complex 2 inhibitors in cancer therapy". Oncogene 29 (26): 3733–44. 2010. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.139. PMID 20418915.
- ↑ "Characterization of RICTOR phosphorylation sites reveals direct regulation of mTOR complex 2 by S6K1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 29 (21): 5657–70. 2009. doi:10.1128/MCB.00735-09. PMID 19720745.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "RICTOR, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton". Curr. Biol. 14 (14): 1296–302. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.06.054. PMID 15268862.
- ↑ "TOR signaling". Sci. STKE 2003 (212): re15. 2003. doi:10.1126/stke.2122003re15. PMID 14668532.
- ↑ "Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the RICTOR-mTOR complex". Science 307 (5712): 1098–101. 2005. doi:10.1126/science.1106148. PMID 15718470. Bibcode: 2005Sci...307.1098S.
- ↑ "Multiallelic disruption of the gene RICTOR in mice reveals that mTOR complex 2 is essential for fetal growth and viability". Dev. Cell 11 (4): 583–9. 2006. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2006.08.013. PMID 16962829.
- ↑ "FoxOs inhibit mTORC1 and activate Akt by inducing the expression of Sestrin3 and RICTOR". Dev. Cell 18 (4): 592–604. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.03.008. PMID 20412774.
- ↑ "Perifosine inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin signaling through facilitating degradation of major components in the mTOR axis and induces autophagy". Cancer Res. 69 (23): 8967–76. 2009. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2190. PMID 19920197.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "SIN1/MIP1 maintains RICTOR-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity". Cell 127 (1): 125–37. Oct 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.033. PMID 16962653.
- ↑ "Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (11): 1122–8. Nov 2004. doi:10.1038/ncb1183. PMID 15467718.
- ↑ "mSin1 is necessary for Akt/PKB phosphorylation, and its isoforms define three distinct mTORC2s". Curr. Biol. 16 (18): 1865–70. Sep 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.08.001. PMID 16919458.
- ↑ "Identification of Sin1 as an essential TORC2 component required for complex formation and kinase activity". Genes Dev. 20 (20): 2820–32. Oct 2006. doi:10.1101/gad.1461206. PMID 17043309.
- ↑ "Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB". Mol. Cell 22 (2): 159–68. Apr 2006. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.029. PMID 16603397.
- ↑ "Redox regulation of the nutrient-sensitive raptor-mTOR pathway and complex". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (47): 39505–9. Nov 2005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506096200. PMID 16183647.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 "PhosphoSite Message". http://www.phosphosite.org/proteinAction.do?id.
- ↑ "Fat cell-specific ablation of rictor in mice impairs insulin-regulated fat cell and whole-body glucose and lipid metabolism". Diabetes 59 (6): 1397–406. 2010. doi:10.2337/db09-1061. PMID 20332342.
- ↑ "RICTOR regulates FBXW7-dependent c-Myc and cyclin E degradation in colorectal cancer cells". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 418 (2): 426–32. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.054. PMID 22285861.
- ↑ "Combined RNAi-mediated suppression of RICTOR and EGFR resulted in complete tumor regression in an orthotopic glioblastoma tumor model". PLOS ONE 8 (3): e59597. 2013. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059597. PMID 23555046. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...859597V.
- ↑ "From PTEN loss of expression to RICTOR role in smooth muscle differentiation: complex involvement of the mTOR pathway in leiomyosarcomas and pleomorphic sarcomas". Mod. Pathol. 25 (2): 197–211. 2012. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.163. PMID 22080063.
- ↑ "Expression of the mTOR pathway regulators in human pituitary adenomas indicates the clinical course". Anticancer Res. 33 (8): 3123–31. August 2013. PMID 23898069.
Further reading
- "The potential role of custody facilities in controlling sexually transmitted diseases". American Journal of Public Health 82 (4): 552–6. 1992. doi:10.2105/AJPH.82.4.552. PMID 1546771.
- "Characterization of size-fractionated cDNA libraries generated by the in vitro recombination-assisted method". DNA Res. 9 (2): 47–57. 2003. doi:10.1093/dnares/9.2.47. PMID 12056414.
- "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. 2004. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- "Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton". Curr. Biol. 14 (14): 1296–302. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.06.054. PMID 15268862.
- "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. 2004. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMID 15302935. Bibcode: 2004PNAS..10112130B.
- "Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (11): 1122–8. 2004. doi:10.1038/ncb1183. PMID 15467718.
- "Human cytomegalovirus infection alters the substrate specificities and rapamycin sensitivities of raptor- and rictor-containing complexes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (38): 14182–7. 2006. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605825103. PMID 16959881. Bibcode: 2006PNAS..10314182K.
- "SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity". Cell 127 (1): 125–37. 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.033. PMID 16962653.
- "Identification of Sin1 as an essential TORC2 component required for complex formation and kinase activity". Genes Dev. 20 (20): 2820–32. 2006. doi:10.1101/gad.1461206. PMID 17043309.
- "ASCT2 silencing regulates mammalian target-of-rapamycin growth and survival signaling in human hepatoma cells". Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. 293 (1): C55–63. 2007. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00330.2006. PMID 17329400.
- "Identification of Protor as a novel Rictor-binding component of mTOR complex-2". Biochem. J. 405 (3): 513–22. 2007. doi:10.1042/BJ20070540. PMID 17461779.
 |