Physics:Tithi
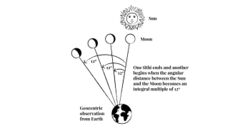
In Vedic timekeeping, a tithi is a "duration of two faces of moon that is observed from earth", known as milа̄lyа̄ (Template:Lang-new) in Nepal Bhasa,[1] or the time it takes for the longitudinal angle between the Moon and the Sun to increase by 12°. In other words, a tithi is a time duration between the consecutive epochs that correspond to when the longitudinal angle between the Sun and the Moon is an integer multiple of 12°. Tithis begin at varying times of day and vary in duration approximately from 19 to 26 hours.[2] Every day of a lunar month is called tithi.
Panchanga
| Part of a series on |
| Hinduism |
|---|
 |
A Hindu muhurta (forty-eight minute duration) can be represented in five attributes of Hindu astronomy namely, vara the weekday, tithi, nakshatra the Moon's asterism, yoga the angular relationship between Sun and Moon and karana half of tithi.
Tithi plays an important role along with nakshatra in Hindus' daily as well as special activities in selecting the muhurta. There are auspicious tithis as well as inauspicious tithis, each considered more propitious for some purposes than for other.
There are 30 tithis in each lunar month, named as:
| Sl.No | Krishna paksha (dark fortnight) |
Shukla paksha (bright fortnight) |
Deity and properties[citation needed] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prathama / Padyami | Prathama / Padyami | The presiding deity of the first lunar day is Agni and it is good for all types of auspicious and religious ceremonies. |
| 2 | Dwitiya / Vidiya | Dwitiya / Vidiya | Vidhatr or Brahma rules this lunar day and is good for the laying of foundations for buildings and other things of a permanent nature. |
| 3 | Tritiya / Thadiya | Tritiya / Thadiya | Gauri is the lord of this day and is good for the cutting of one's hair and nails and shaving. |
| 4 | Chaviti | Chaviti | Yama/Ganapati is lord of the 4th lunar day, which is good for the destruction of one's enemies, the removal of obstacles, and acts of combat. |
| 5 | Panchami | Panchami | The Naaga or Serpents rule this day, which is favourable for administering medicine, the purging of poisons, and surgery. |
| 6 | Shashthi | Shashthi | Karttikeya presides over this day and is favourable for coronations, meeting new friends, festivities, and enjoyment. |
| 7 | Saptami | Saptami | The 7th lunar day is ruled by Surya; one may begin a journey, buy conveyances, and deal with other such things of a movable nature. |
| 8 | Ashtami | Ashtami | The Rudra rule this day, which is good for taking up arms, building of one's defenses, and fortification. |
| 9 | Navami | Navami | The Ambikaa rules this day, which is suitable for killing enemies, acts of destruction, and violence. Inauspicious for ceremonies and journeys. |
| 10 | Dasami | Dashami | The day is ruled by Dharmaraja and is auspicious for acts of virtue, religious functions, spiritual practices, and other pious activities. |
| 11 | Ekadasi | Ekadashi | Rudra rule this day; fasting, devotional activities, and remembrance of the Supreme Lord Vishnu are very favourable. This day has special religious significance in Hinduism and Jainism—usually observed by fasting. |
| 12 | Dvadasi | Dwadashi | The Vishnu or Aditya rules this day, which is auspicious for religious ceremonies, the lighting of the sacred fire, and the performance of one's duties. |
| 13 | Trayodasi | Thrayodashi | The day is ruled by Kamadeva and is good for forming friendships, sensual pleasures, and festivities. |
| 14 | Chaturdashi | Chaturdashi | Kali rules this day, suitable for administering poison and calling of elementals and spirits. |
| 15 | Amavasya (new moon) |
Purnima or Paurnami (full moon) |
The Pitru-devas rule the New Moon, suitable for the propitiation of the Manes and performance of austerities. Purnima is ruled by Moon and is suitable for merry making and fire sacrifice. |
Types of Panchang
The calculations in Panchang are also done according to time and place because the Panchang which is applicable in North India is not applicable in South India, hence the Panchangs differ according to the region. But in any Panchang, there is almost equality at the level of information. In any Panchang, there are five parts like Tithi, Vaar, Nakshatra, Yoga and Karan etc. Because the information of these five parts is contained in it, it is called Panchang. Talking about the types of Panchang, it is of many types depending on the region and religious-cultural basis.[3]
Many types of almanacs are found in India alone. Indian almanacs are made mainly by calculating the time based on the motion of the moon, constellations and the sun. In North India, where the completion of the month is associated with Purnima, in South India Amavasya is considered as the end of the month. To calculate the year, it is calculated from the solar year. According to the constellations, a month is of 27 days, while according to the movement of the moon, it is considered to be of 29+1/2 days.
References
- ↑ Kapali, Rukshana. "नेपाल संवत् - नेपाल सम्बत". https://nepalsambat.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/NBlearning_NSpages.pdf.
- ↑ Defouw, Hart; Svoboda, Robert (2003). Light on Life: An Introduction to the Astrology of India. Lotus Press. p. 186. ISBN 0-940985-69-1. https://archive.org/details/lightonlife00hart. "Shukla paksha -inpublisher:icon."
- ↑ "Aaj Kaun Sa Din Hai" (in en-US). 2023-02-28. https://bzzhive.com/aaj-kaun-sa-din-hai/.
External links
- Ahargana - The Astronomy of the Hindu Calendar: Tithi Explains Tithi by means of astronomical simulations created using Stellarium.
- आज की तिथि क्या है, आज क्या तिथि है और आज की तिथि, आज का त्यौहार और व्रत
- Nepali Panchang
- Panchangam In Telugu With Tithi
- The Vaisnava Calendar
- The Hindu Lunisolar Calendar
- iPhone app for Nepali Panchang
- iPhone app
- Free Hindu Panchang
- Tithi in Indian Hindi Calendar
 |