Biology:Mandarin rat snake
| Mandarin rat snake | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Colubridae |
| Genus: | Euprepiophis |
| Species: | E. mandarinus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Euprepiophis mandarinus (Cantor, 1842)
| |
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
The Mandarin rat snake (Euprepiophis mandarinus) is a species of nonvenomous colubrid snake endemic to Asia. It is closely related to Euprepiophis conspicillata, the Japanese forest rat snake. Mandarin rat snakes are one of the most popular rat snakes found in the pet trade.
Description
It is a relatively small rat snake; adult size is no more than 1.4 m (4 ft 7 in) in total length (body + tail).[3]
Distribution
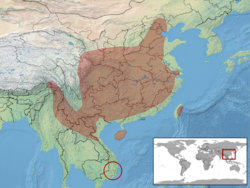
India (Arunachal Pradesh), Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, Taiwan, China (Anhui, Beijing, Chongqing, Fujian, Gansu, Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hainan, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Liaoning, Shaanxi, Shanghai, Shanxi, Sichuan, Tianjin, Tibet, Yunnan, Zhejiang)[1]
Type locality: China: Chekiang, Chusan island (modern transliteration: Zhejiang, Zhoushan) (Cantor, 1842).[2]
Taxonomy
In recent years there has been some taxonomic controversy over the genera of rat snakes. Based on mitochondrial DNA, Utiger et al. (2002)[4] argued for a splintering of the genus Elaphe and suggested a reworking of the genera.[5]
Natural history
The Mandarin rat snake is a secretive species, often using rodent burrows for shelter. It feeds primarily on small rodents, prefers cooler temperatures, and is predominantly crepuscular. It occurs from sea level to at least 3,000 m (9,800 ft).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ji, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P. (2012). "Euprepiophis mandarinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012: e.T192138A2045703. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012-1.RLTS.T192138A2045703.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/192138/2045703. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Euprepiophis mandarinus at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 21 October 2012.
- ↑ Hans Breuer; William Christopher Murphy (2009–2010). "Euprepiophis mandarina Mandarin Ratsnake". Snakes of Taiwan. https://www.snakesoftaiwan.com/euprepiophis-mandarina.html.
- ↑ Utiger, Urs; Notker Helfenberger; Beat Schätti; Catherine Schmidt; Markus Ruf; Vincent Ziswiler (2002). "Molecular systematics and phylogeny of Old World and New World ratsnakes, Elaphe Auct., and related genera (Reptilia, Squamata, Colubridae)". Russian Journal of Herpetology 9 (2): 105–124. http://vipersgarden.at/PDF_files/PDf-352.pdf.
- ↑ Elaphe obsoleta at The Center for North American Herpetology. Accessed 20 June 2008.
Further reading
- Boulenger, G. A. 1894. Catalogue of the Snakes in the British Museum (Natural History). Volume II., Containing the Conclusion of the Colubridæ Aglyphæ. London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis, printers.) xi + 382 pp. + Plates I.- XX. (Coluber mandarinus, pp. 42–43.)
- Cantor, T. 1842. General Features of Chusan, with remarks on the Flora and Fauna of that Island. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. [Series 1] 9: 265-278, 361-370, 481-493. (Coluber mandarinus, p. 483.)
- Gumprecht, A. 2002. Elaphe mandarina (Cantor). Sauria (Suppl.) 24 (3): 565-568.
- Gumprecht, A. 2003. Anmerkungen zu den Chinesischen Kletternattern der Gattung Elaphe (sensu lato) Fitzinger 1833. Reptilia (Münster) 8 (6): 37-41.
- Lenk, P.; Joger, U. & Wink, M. 2001. Phylogenetic relationships among European ratsnakes of the genus Elaphe Fitzinger based on mitochondrial DNA sequence comparisons. Amphibia-Reptilia 22 (3): 329-339.
- Purser, P.A. 2003. Elaphe mandarinus. Reptilia (GB) (31): 30-33.
- Schulz, K.D. 1996. Eine Monographie der Schlangengattung Elaphe Fitzinger. Bushmaster, Berg (CH): 1-460.
- Schulz, Klaus-Dieter 1996. A monograph of the colubrid snakes of the genus Elaphe Fitzinger. Koeltz Scientific Books, 439 pp.
- Smith, M.A. 1943. The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma, Including the Whole of the Indo-Chinese Sub-region. Reptilia and Amphibia. Vol. III.—Serpentes. London: Secretary of State for India. (Taylor and Francis, printers.) xii + 583 pp. (Elaphe mandarina, pp. 157–158.)
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q2569583 entry


