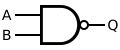
Engineering:NAND gate
| NAND gate truth table | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | A NAND B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
In digital electronics, a NAND gate (NOT-AND) is a logic gate which produces an output which is false only if all its inputs are true; thus its output is complement to that of an AND gate. A LOW (0) output results only if all the inputs to the gate are HIGH (1); if any input is LOW (0), a HIGH (1) output results. A NAND gate is made using transistors and junction diodes. By De Morgan's laws, a two-input NAND gate's logic may be expressed as [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{A} \lor \overline{B} = \overline{A \cdot B} }[/math], making a NAND gate equivalent to inverters followed by an OR gate.
The NAND gate is significant because any Boolean function can be implemented by using a combination of NAND gates. This property is called "functional completeness". It shares this property with the NOR gate. Digital systems employing certain logic circuits take advantage of NAND's functional completeness.
NAND gates with two or more inputs are available as integrated circuits in transistor-transistor logic, CMOS, and other logic families.
Symbols
There are three symbols for NAND gates: the MIL/ANSI symbol, the IEC symbol and the deprecated DIN symbol sometimes found on old schematics. The ANSI symbol for the NAND gate is a standard AND gate with an inversion bubble connected.
|

|
file:NAND DIN.svg |
| MIL/ANSI Symbol | IEC Symbol | DIN Symbol |
Logic
The function NAND(a1, a2, ..., an) is logically equivalent to NOT(a1 AND a2 AND ... AND an).
One way of expressing A NAND B is [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{A \land B} }[/math], where the symbol [math]\displaystyle{ {\land} }[/math] signifies AND and the bar signifies the negation of the expression under it: in essence, simply [math]\displaystyle{ {\displaystyle \lnot (A \land B)} }[/math].
Hardware design and pinout
NAND gates are basic logic gates, and as such they are recognised in TTL and CMOS ICs.
The standard, 4000 series, CMOS IC is the 4011, which includes four independent, two-input, NAND gates. These devices are available from many semiconductor manufacturers. These are usually available in both through-hole DIL and SOIC formats. Datasheets are readily available in most datasheet databases.
The standard two-, three-, four- and eight-input NAND gates are available:
- CMOS
- 4011: Quad two-input NAND gate
- 4023: Triple three-input NAND gate
- 4012: Dual four-input NAND gate
- 4068: Mono eight-input NAND gate
- TTL
- 7400: Quad two-input NAND gate
- 7410: Triple three-input NAND gate
- 7420: Dual four-input NAND gate
- 7430: Mono eight-input NAND gate
Functional completeness
thumb|construction of a NAND gate from NOR gates
The NAND gate has the property of functional completeness, which it shares with the NOR gate. That is, any other logic function (AND, OR, etc.) can be implemented using only NAND gates.[1] An entire processor can be created using NAND gates alone. In TTL ICs using multiple-emitter transistors, it also requires fewer transistors than a NOR gate.
As NOR gates are also functionally complete, if no specific NAND gates are available, one can be made from NOR gates using NOR logic.[1]
See also
References
External links
- TTL NAND and AND gates at All About Circuits
 |