Medicine:Adducted thumb syndrome
| Adducted thumb syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Christian syndrome, craniostenosis arthrogryposis cleft palate |
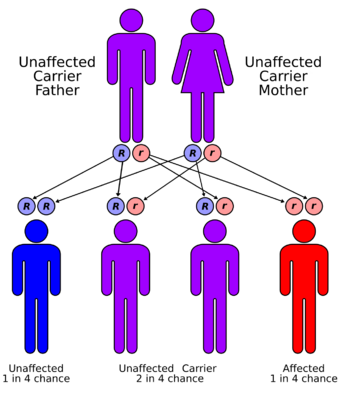 | |
| Adducted thumb syndrome has a lysosomal recessive pattern of inheritance | |
| Causes | mutation in the CHST14 gene |
Adducted thumb syndrome recessive form is a rare disease affecting multiple systems causing malformations of the palate, thumbs, and upper limbs. The name Christian syndrome derives from Joe. C. Christian, the first person to describe the condition. Inheritance is believed to be autosomal recessive,[1] caused by mutation in the CHST14 (carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14) gene.[2]
Signs and symptoms
This syndrome is characterised by typical facial appearance, slight build, thin and translucent skin, severely adducted thumbs, arachnodactyly, club feet, joint instability, facial clefting and bleeding disorders, as well as heart, kidney or intestinal defects. Severe psychomotor and developmental delay and decreased muscle tone may also be present during infancy. Cognitive development during childhood is normal.[3]
Cause
Diagnosis
The syndrome is associated with microcephaly, arthrogryposis and cleft palate and various craniofacial, respiratory, neurological and limb abnormalities, including bone and joint defects of the upper limbs, adducted thumbs, camptodactyly and talipes equinovarus or calcaneovalgus. It is characterized by craniosynostosis, and myopathy in association with congenital generalized hypertrichosis.[4] Patients with the disease are considered intellectually disabled. Most die in childhood. Patients often have respiratory difficulties such as pneumonia, and from seizures due to dysmyelination in the brain's white matter.[5] It has been hypothesized that the Moro reflex (startle reflex in infants) may be a tool in detecting the congenital clasped thumb early in infancy.[6] The thumb normally extends as a result of this reflex.[citation needed]
Treatment
See also
- Adams–Oliver syndrome
- List of cutaneous conditions
- Tetrasomy 18p
References
- ↑ "Adducted thumb syndromes". Clin. Genet. 8 (3): 190–8. 1975. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb01493.x. PMID 1175322.
- ↑ "CHST14". National Center for Biotechnology Information database. NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=113189.
- ↑ "Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, musculocontractural type – Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/QnASelected.aspx?diseaseID=8486.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 1008. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ "Adducted thumb syndrome. Report of a new case and a diagnostic approach". Eur. J. Pediatr. 141 (2): 122–6. 1983. doi:10.1007/BF00496805. PMID 6662143.
- ↑ "Congenital clasped thumb and the Moro reflex. (Letter)". The Journal of Pediatrics 99: 664–665. 1981. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80293-4.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
 |

