Medicine:Sotos syndrome
| Sotos syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cerebral gigantism or Sotos-Dodge syndrome |
 | |
| Girl with Sotos syndrome | |
Sotos syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by excessive physical growth during the first years of life. Excessive growth often starts in infancy and continues into the early teen years. The disorder may be accompanied by autism,[1] mild intellectual disability, delayed motor, cognitive, and social development, hypotonia (low muscle tone), and speech impairments. Children with Sotos syndrome tend to be large at birth and are often taller, heavier, and have relatively large skulls (macrocephaly) than is normal for their age. Signs of the disorder, which vary among individuals, include a disproportionately large skull with a slightly protrusive forehead, large hands and feet, large mandible, hypertelorism (an abnormally increased distance between the eyes), and downslanting eyes. Clumsiness, an awkward gait, and unusual aggressiveness or irritability may also occur.
Although most cases of Sotos syndrome occur sporadically, familial cases have also been reported. It is similar to Weaver syndrome.
Signs and symptoms

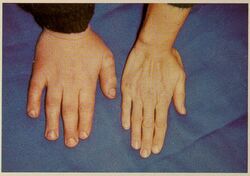
This syndrome is characterized by overgrowth and advanced bone age. Affected individuals have dysmorphic features, with macrodolichocephaly, downslanting palpebral fissures and a pointed chin. The facial appearance is most notable in early childhood. Affected infants and children tend to grow quickly; they are significantly taller than their siblings and peers, and have an unusually large skull and large head. Adult height is usually in the normal range, although Broc Brown has the condition and was named the world's tallest teenager; as of late 2016, he was 2.34 m (7 ft 8 in) tall and still growing.[2]
Individuals with Sotos syndrome often have intellectual impairment,[3][4] and most also display autistic traits.[5] Frequent behavioral impairments include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), phobias, obsessive compulsive disorder, tantrums, and impulsive behaviors (impulse control disorder). Problems with speech and language are also common.[6] Affected individuals may often have stuttering, difficulty with sound production, or a monotone voice. Additionally, weak muscle tone (hypotonia) may delay other aspects of early development, particularly motor skills such as sitting and crawling.[citation needed]
Other signs include scoliosis, seizures, heart or kidney defects, hearing loss, and problems with vision. Some infants with this disorder experience jaundice and poor feeding. A small number of patients with Sotos syndrome have developed cancer, most often in childhood, but no single form of cancer has been associated with this condition. It remains uncertain whether Sotos syndrome increases the risk of specific types of cancer. If persons with this disorder have any increased cancer risk, their risk is only slightly greater than that of the general population.[7]
Genetics
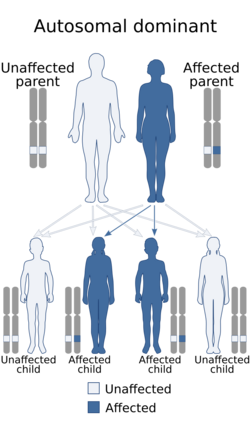
Mutations in the NSD1 gene cause Sotos syndrome.[8][9] The NSD1 gene provides instructions for making a protein (histone methyltransferase) that is involved in normal growth and development. The function of this protein is unknown, however. In the Japanese population, the most common genetic change leading to Sotos syndrome deletes genetic material from the region of chromosome 5 containing the NSD1 gene. In other populations, small mutations within the NSD1 gene occur more frequently. Genetic changes involving the NSD1 gene prevent one copy of the gene from producing any functional protein. It is unclear how a reduced amount of this protein during development leads to learning disabilities, overgrowth, and the other features of Sotos syndrome.[citation needed]
About 95 percent of Sotos syndrome cases occur by spontaneous mutation. Most of these cases result from new mutations involving the NSD1 gene. A few families have been described with more than one affected family member. These inherited cases enabled researchers to determine that Sotos syndrome has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on physical examination, looking for excessive growth among other symptoms. There are no biochemical markers for the disease.[10]
Treatment
Treatment is symptomatic.[10] There is no standard course of treatment for Sotos syndrome.[citation needed]
Prognosis
Sotos syndrome is not a life-threatening disorder and patients may have a normal life expectancy. Developmental delays may improve in the school-age years; however, coordination problems may persist into adulthood, along with any learning disabilities and/or other physical or mental issues.[11]
Epidemiology
Incidence is approximately 1 in 14,000 births.[6]
See also
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Perlman syndrome
- Proteus syndrome
- Gigantism
References
- ↑ "Exploring Autism". http://www.exploringautism.org/autism/evaluation.htm.
- ↑ "7-foot-tall Broc Brown: Facts". Morning News USA. http://www.morningnewsusa.com/7-foot-tall-broc-d-brown-worlds-tallest-teenager-michigan-23106848.html.
- ↑ "Cognition and Behaviour in Sotos Syndrome: A Systematic Review". PLOS ONE 11 (2): e0149189. 2016. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0149189. PMID 26872390. Bibcode: 2016PLoSO..1149189L.
- ↑ "The cognitive profile of Sotos syndrome". J Neuropsychol 13 (2): 240–252. January 2018. doi:10.1111/jnp.12146. PMID 29336120. http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/126341/3/The%20Cognitive%20Profile%20of%20Sotos%20Syndrome%20Final.pdf.
- ↑ "Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Sotos Syndrome". J Autism Dev Disord 47 (1): 135–143. January 2017. doi:10.1007/s10803-016-2941-z. PMID 27771801.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Parent-Reported Communication Abilities of Children with Sotos Syndrome: Evidence from the Children's Communication Checklist-2". J Autism Dev Disord 49 (4): 1475–1483. December 2018. doi:10.1007/s10803-018-3842-0. PMID 30536215.
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home. "Sotos syndrome". https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/sotos-syndrome.
- ↑ "Haploinsufficiency of NSD1 causes Sotos syndrome". Nat. Genet. 30 (4): 365–6. April 2002. doi:10.1038/ng863. PMID 11896389.
- ↑ "dHPLC screening of the NSD1 gene identifies nine novel mutations--summary of the first 100 Sotos syndrome mutations". Ann. Hum. Genet. 69 (Pt 2): 222–6. March 2005. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2004.00150.x. PMID 15720303.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Sotos Syndrome" (in en-US). https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/sotos-syndrome/.
- ↑ Foster, Alison; Zachariou, Anna; Loveday, Chey; Ashraf, Tazeen; Blair, Edward; Clayton‐Smith, Jill; Dorkins, Huw; Fryer, Alan et al. (2019). "The phenotype of Sotos syndrome in adulthood: A review of 44 individuals". Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 181 (4): 502–508. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31738. PMID 31479583.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
 |

