Philosophy:Reinforcement

In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is any consequence that increases the likelihood of an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a particular antecedent stimulus.[1] For example, a rat can be trained to push a lever to receive food whenever a light is turned on. In this example, the light is the antecedent stimulus, the lever pushing is the behavior, and the food is the reinforcement. Likewise, a student that receives attention and praise when answering a teacher's question will be more likely to answer future questions in class. The teacher's question is the antecedent, the student's response is the behavior, and the praise and attention are the reinforcements.
Consequences that lead to appetitive behavior such as subjective "wanting" and "liking" (desire and pleasure) function as rewards or positive reinforcement.[2] There is also negative reinforcement, which involves taking away an undesirable stimulus. An example of negative reinforcement would be taking an aspirin to relieve a headache.
Reinforcement is an important component of operant conditioning and behavior modification. The concept has been applied in a variety of practical areas, including parenting, coaching, therapy, self-help, education, and management.
Terminology
| Addiction and dependence glossary[3][4][5][6] | |
|---|---|
| |
In the behavioral sciences, the terms "positive" and "negative" refer when used in their strict technical sense to the nature of the action performed by the conditioner rather than to the responding operant's evaluation of that action and its consequence(s). "Positive" actions are those that add a factor, be it pleasant or unpleasant, to the environment, whereas "negative" actions are those that remove or withhold from the environment a factor of either type. In turn, the strict sense of "reinforcement" refers only to reward-based conditioning; the introduction of unpleasant factors and the removal or withholding of pleasant factors are instead referred to as "punishment", which when used in its strict sense thus stands in contradistinction to "reinforcement". Thus, "positive reinforcement" refers to the addition of a pleasant factor, "positive punishment" refers to the addition of an unpleasant factor, "negative reinforcement" refers to the removal or withholding of an unpleasant factor, and "negative punishment" refers to the removal or withholding of a pleasant factor.
This usage is at odds with some non-technical usages of the four term combinations, especially in the case of the term "negative reinforcement", which is often used to denote what technical parlance would describe as "positive punishment" in that the non-technical usage interprets "reinforcement" as subsuming both reward and punishment and "negative" as referring to the responding operant's evaluation of the factor being introduced. By contrast, technical parlance would use the term "negative reinforcement" to describe encouragement of a given behavior by creating a scenario in which an unpleasant factor is or will be present but engaging in the behavior results in either escaping from that factor or preventing its occurrence, as in Martin Seligman’s experimente involving dogs learning to avoid electric shocks.
Introduction
B.F. Skinner was a well-known and influential researcher who articulated many of the theoretical constructs of reinforcement and behaviorism. Skinner defined reinforcers according to the change in response strength (response rate) rather than to more subjective criteria, such as what is pleasurable or valuable to someone. Accordingly, activities, foods or items considered pleasant or enjoyable may not necessarily be reinforcing (because they produce no increase in the response preceding them). Stimuli, settings, and activities only fit the definition of reinforcers if the behavior that immediately precedes the potential reinforcer increases in similar situations in the future; for example, a child who receives a cookie when he or she asks for one. If the frequency of "cookie-requesting behavior" increases, the cookie can be seen as reinforcing "cookie-requesting behavior". If however, "cookie-requesting behavior" does not increase the cookie cannot be considered reinforcing.
The sole criterion that determines if a stimulus is reinforcing is the change in probability of a behavior after administration of that potential reinforcer. Other theories may focus on additional factors such as whether the person expected a behavior to produce a given outcome, but in the behavioral theory, reinforcement is defined by an increased probability of a response.
The study of reinforcement has produced an enormous body of reproducible experimental results. Reinforcement is the central concept and procedure in special education, applied behavior analysis, and the experimental analysis of behavior and is a core concept in some medical and psychopharmacology models, particularly addiction, dependence, and compulsion.
History
Laboratory research on reinforcement is usually dated from the work of Edward Thorndike, known for his experiments with cats escaping from puzzle boxes.[7] A number of others continued this research, notably B.F. Skinner, who published his seminal work on the topic in The Behavior of Organisms, in 1938, and elaborated this research in many subsequent publications.[8] Notably Skinner argued that positive reinforcement is superior to punishment in shaping behavior.[9] Though punishment may seem just the opposite of reinforcement, Skinner claimed that they differ immensely, saying that positive reinforcement results in lasting behavioral modification (long-term) whereas punishment changes behavior only temporarily (short-term) and has many detrimental side-effects.
A great many researchers subsequently expanded our understanding of reinforcement and challenged some of Skinner's conclusions. For example, Azrin and Holz defined punishment as a “consequence of behavior that reduces the future probability of that behavior,”[10] and some studies have shown that positive reinforcement and punishment are equally effective in modifying behavior.[citation needed] Research on the effects of positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement and punishment continue today as those concepts are fundamental to learning theory and apply to many practical applications of that theory.
Operant conditioning
The term operant conditioning was introduced by B. F. Skinner to indicate that in his experimental paradigm, the organism is free to operate on the environment. In this paradigm, the experimenter cannot trigger the desirable response; the experimenter waits for the response to occur (to be emitted by the organism) and then a potential reinforcer is delivered. In the classical conditioning paradigm, the experimenter triggers (elicits) the desirable response by presenting a reflex eliciting stimulus, the Unconditional Stimulus (UCS), which he pairs (precedes) with a neutral stimulus, the Conditional Stimulus (CS).
Reinforcement is a basic term in operant conditioning. For the punishment aspect of operant conditioning, see punishment (psychology).
Positive reinforcement
Positive reinforcement occurs when a desirable event or stimulus is presented as a consequence of a behavior and the chance that this behavior will manifest in similar environments increases.[11]:253
- Example: A father gives candy to his daughter when she tidies up her toys. If the frequency of picking up the toys increases, the candy is a positive reinforcer (to reinforce the behavior of cleaning up).
- Example: A company enacts a rewards program in which employees earn prizes dependent on the number of items sold. The prizes the employees receive are the positive reinforcement if they increase sales.
- Example: A supervisor attaches a monetary reward for the employee who exceeds expectations the most. The monetary reward is the positive reinforcement of the good behavior: exceeding expectations.
The high probability instruction (HPI) treatment is a behaviorist treatment based on the idea of positive reinforcement.
Negative reinforcement
Negative reinforcement increases the rate of a behavior to avoid or escape an aversive situation or stimulus.[11]:253 Doing something unpleasant to people to prevent or remove a behavior from happening again is punishment, not negative reinforcement. The difference is that reinforcement always increases the likelihood of a behavior whereas punishment always decreases it.
- Example: A child cleans their room, and this behavior is followed by the parent stopping "nagging" or asking the child repeatedly to do so. Here, the nagging serves to negatively reinforce the behavior of cleaning because the child wants to remove that aversive stimulus of nagging.
- Example: A company has a policy that if an employee completes their assigned work by Friday, they can have Saturday off. Working Saturday is the aversive stimulus; the employees have incentive to increase productivity to avoid the aversive stimulus.
- Example: An individual leaves early for work to beat traffic and avoid arriving late. The behavior is leaving early for work, and the aversive stimulus the individual wishes to remove is being late to work.
Extinction
Extinction occurs when a given behavior is ignored (i.e. followed up with no consequence), where it will disappear over time if the behavior continuously receives no reinforcement. Behavior after extinction spikes first and then declines over time.[12] Extinction does not have to be deliberate in order to have an effect on a subject's behavior. The following examples demonstrate scenarios in which it can be intentionally or unintentionally applied:
- Example (Intended): A young child ignores bullies making fun of them. The bullies do not get a reaction from the child and lose interest in bullying them.
- Example (Unintended): A worker does not receive any recognition for their above and beyond hard work. They then stop working as hard.
- Example (Intended): A cat keeps meowing for food in the night. The owners do not feed the cat, so the cat eventually stops meowing.
Reinforcement versus punishment
Reinforcers serve to increase behaviors whereas punishers serve to decrease behaviors; thus, positive reinforcers are stimuli that the subject will work to attain, and negative reinforcers are stimuli that the subject will work to be rid of or to end.[13] The table below illustrates the adding and subtracting of stimuli (pleasant or aversive) in relation to reinforcement vs. punishment.
For example, offering a child candy if he cleans his room is positive reinforcement. Spanking a child if he breaks a window is positive punishment. Taking away a child's toys for misbehaving is negative punishment. Giving a child a break from his chores if he performs well on a test is negative reinforcement. "Positive and negative" do not carry the meaning of "good and bad" in this usage.
Further ideas and concepts
- Distinguishing between positive and negative reinforcement can be difficult and may not always be necessary. Focusing on what is being removed or added and how it affects behavior can be more helpful.
- An event that punishes behavior for some may reinforce behavior for others. Example: A child is repeatedly given detention for acting up in school, but the frequency of bad behavior increases. Thus, the detention may be a reinforcer, through attention or avoidance of unpleasant situations, such as abuse at home.
- Some reinforcement can include both positive and negative features, such as a drug addict taking drugs for the added euphoria (positive reinforcement) and also to eliminate withdrawal symptoms (negative reinforcement).
- Reinforcement in the business world is essential in driving productivity. Employees are constantly motivated by the ability to receive a positive stimulus, such as a promotion or a bonus. Employees are also driven by negative reinforcement, such as by eliminating unpleasant tasks.
- Though negative reinforcement has a positive effect in the short term for a workplace (i.e. encourages a financially beneficial action), over-reliance on a negative reinforcement hinders the ability of workers to act in a creative, engaged way creating growth in the long term.[14]
Primary and secondary reinforcers
A primary reinforcer, sometimes called an unconditioned reinforcer, is a stimulus that does not require pairing with a different stimulus in order to function as a reinforcer and most likely has obtained this function through the evolution and its role in species' survival.[15] Examples of primary reinforcers include food, water, and sex. Some primary reinforcers, such as certain drugs, may mimic the effects of other primary reinforcers. While these primary reinforcers are fairly stable through life and across individuals, the reinforcing value of different primary reinforcers varies due to multiple factors (e.g., genetics, experience). Thus, one person may prefer one type of food while another avoids it. Or one person may eat much food while another eats very little. So even though food is a primary reinforcer for both individuals, the value of food as a reinforcer differs between them.
A secondary reinforcer, sometimes called a conditioned reinforcer, is a stimulus or situation that has acquired its function as a reinforcer after pairing with a stimulus that functions as a reinforcer. This stimulus may be a primary reinforcer or another conditioned reinforcer (such as money). An example of a secondary reinforcer would be the sound from a clicker, as used in clicker training. The sound of the clicker has been associated with praise or treats, and subsequently, the sound of the clicker may function as a reinforcer. Another common example is the sound of people clapping – there is nothing inherently positive about hearing that sound, but we have learned that it is associated with praise and rewards.
When trying to distinguish primary and secondary reinforcers in human examples, use the "caveman test." If the stimulus is something that a caveman would naturally find desirable (e.g. candy) then it is a primary reinforcer. If, on the other hand, the caveman would not react to it (e.g. a dollar bill), it is a secondary reinforcer. As with primary reinforcers, an organism can experience satisfaction and deprivation with secondary reinforcers.
Other reinforcement terms
- A generalized reinforcer is a conditioned reinforcer that has obtained the reinforcing function by pairing with many other reinforcers and functions as a reinforcer under a wide-variety of motivating operations. (One example of this is money because it is paired with many other reinforcers).[16]:83
- In reinforcer sampling, a potentially reinforcing but unfamiliar stimulus is presented to an organism without regard to any prior behavior.
- Socially-mediated reinforcement involves the delivery of reinforcement that requires the behavior of another organism. For example, another person is providing the reinforcement.
- The Premack principle is a special case of reinforcement elaborated by David Premack, which states that a highly preferred activity can be used effectively as a reinforcer for a less-preferred activity.[16]:123
- Reinforcement hierarchy is a list of actions, rank-ordering the most desirable to least desirable consequences that may serve as a reinforcer. A reinforcement hierarchy can be used to determine the relative frequency and desirability of different activities, and is often employed when applying the Premack principle.[citation needed]
- Contingent outcomes are more likely to reinforce behavior than non-contingent responses. Contingent outcomes are those directly linked to a causal behavior, such a light turning on being contingent on flipping a switch. Note that contingent outcomes are not necessary to demonstrate reinforcement, but perceived contingency may increase learning.
- Contiguous stimuli are stimuli closely associated by time and space with specific behaviors. They reduce the amount of time needed to learn a behavior while increasing its resistance to extinction. [citation needed] Giving a dog a piece of food immediately after sitting is more contiguous with (and therefore more likely to reinforce) the behavior than a several minute delay in food delivery following the behavior.
- Noncontingent reinforcement refers to response-independent delivery of stimuli identified as reinforcers for some behaviors of that organism. However, this typically entails time-based delivery of stimuli identified as maintaining aberrant behavior, which decreases the rate of the target behavior.[17] As no measured behavior is identified as being strengthened, there is controversy surrounding the use of the term noncontingent "reinforcement".[18]
Natural and artificial reinforcement
In his 1967 paper, Arbitrary and Natural Reinforcement, Charles Ferster proposed classifying reinforcement into events that increase the frequency of an operant behavior as a natural consequence of the behavior itself, and events that affect frequency by their requirement of human mediation, such as in a token economy where subjects are rewarded for certain behavior by the therapist.
In 1970, Baer and Wolf developed the concept of "behavior traps."[19] A behavior trap requires only a simple response to enter the trap, yet once entered, the trap cannot be resisted in creating general behavior change. It is the use of a behavior trap that increases a person's repertoire, by exposing them to the naturally occurring reinforcement of that behavior. Behavior traps have four characteristics:
- They are "baited" with desirable reinforcers that "lure" the student into the trap.
- Only a low-effort response already in the repertoire is necessary to enter the trap.
- Interrelated contingencies of reinforcement inside the trap motivate the person to acquire, extend, and maintain targeted skills.[20]
- They can remain effective for long periods of time because the person shows few, if any, satiation effects.
Thus, artificial reinforcement can be used to build or develop generalizable skills, eventually transitioning to naturally occurring reinforcement to maintain or increase the behavior. Another example is a social situation that will generally result from a specific behavior once it has met a certain criterion (if you use candy to train a child to say hello and smile at people when they meet them, after that skill has been built up, the natural reinforcer of other people smiling, and having more friendly interactions will naturally reinforce the skill and the edibles can be faded).
Intermittent reinforcement schedules
Behavior is not always reinforced every time it is emitted, and the pattern of reinforcement strongly affects how fast an operant response is learned, what its rate is at any given time, and how long it continues when reinforcement ceases. The simplest rules controlling reinforcement are continuous reinforcement, where every response is reinforced, and extinction, where no response is reinforced. Between these extremes, more complex schedules of reinforcement specify the rules that determine how and when a response will be followed by a reinforcer.
Specific schedules of reinforcement reliably induce specific patterns of response, and these rules apply across many different species. The varying consistency and predictability of reinforcement is an important influence on how the different schedules operate. Many simple and complex schedules were investigated at great length by B.F. Skinner using pigeons.
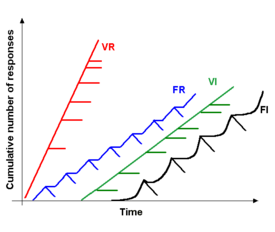
Simple schedules
- Ratio schedule – the reinforcement depends only on the number of responses the organism has performed.
- Continuous reinforcement (CRF) – a schedule of reinforcement in which every occurrence of the instrumental response (desired response) is followed by the reinforcer.[16]:86
- Lab example: each time a rat presses a bar it gets a pellet of food.
- Real-world example: each time a dog defecates outside its owner gives it a treat; each time a person puts $1 in a candy machine and presses the buttons they receive a candy bar.
Simple schedules have a single rule to determine when a single type of reinforcer is delivered for a specific response.
- Fixed ratio (FR) – schedules deliver reinforcement after every nth response.[16]:88 An FR 1 schedule is synonymous with a CRF schedule.
- Example: FR 2 = every second desired response the subject makes is reinforced.
- Lab example: FR 5 = rat's bar-pressing behavior is reinforced with food after every 5 bar-presses in a Skinner box.
- Real-world example: FR 10 = Used car dealer gets a $1000 bonus for each 10 cars sold on the lot.
- Variable ratio schedule (VR) – reinforced on average every nth response, but not always on the nth response.[16]:88
- Lab example: VR 4 = first pellet delivered on 2 bar presses, second pellet delivered on 6 bar presses, third pellet 4 bar presses (2 + 6 + 4 = 12; 12 / 3= 4 bar presses to receive pellet).
- Real-world example: slot machines (because, though the probability of hitting the jackpot is constant, the number of lever presses needed to hit the jackpot is variable).
- Fixed interval (FI) – reinforced after n amount of time.
- Example: FI 1-s = reinforcement provided for the first response after 1 second.
- Lab example: FI 15-s = rat's bar-pressing behavior is reinforced for the first bar press after 15 seconds passes since the last reinforcement.
- Real-world example: FI 30-min = a 30-minute washing machine cycle.
- Variable interval (VI) – reinforced on an average of n amount of time, but not always exactly n amount of time.[16]:89
- Example: VI 4-min = first pellet delivered after 2 minutes, second delivered after 6 minutes, third is delivered after 4 minutes (2 + 6 + 4 = 12; 12 / 3 = 4). Reinforcement is delivered on the average after 4 minutes.
- Lab example: VI 10-s = a rat's bar-pressing behavior is reinforced for the first bar press after an average of 10 seconds passes since the last reinforcement.
- Real-world example: VI 30-min = Going fishing—you might catch a fish after 10 minutes, then have to wait an hour, then have to wait 20 minutes.
- Fixed time (FT) – Provides a reinforcing stimulus at a fixed time since the last reinforcement delivery, regardless of whether the subject has responded or not. In other words, it is a non-contingent schedule.
- Lab example: FT 5-s = rat gets food every 5 seconds regardless of the behavior.
- Real-world example: FT 30-d = a person gets an annuity check every month regardless of behavior between checks
- Variable time (VT) – Provides reinforcement at an average variable time since last reinforcement, regardless of whether the subject has responded or not.
Simple schedules are utilized in many differential reinforcement[21] procedures:
- Differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DRA) - A conditioning procedure in which an undesired response is decreased by placing it on extinction or, less commonly, providing contingent punishment, while simultaneously providing reinforcement contingent on a desirable response. An example would be a teacher attending to a student only when they raise their hand, while ignoring the student when he or she calls out.
- Differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO) – Also known as omission training procedures, an instrumental conditioning procedure in which a positive reinforcer is periodically delivered only if the participant does something other than the target response. An example would be reinforcing any hand action other than nose picking.[16]:338
- Differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI) – Used to reduce a frequent behavior without punishing it by reinforcing an incompatible response. An example would be reinforcing clapping to reduce nose picking
- Differential reinforcement of low response rate (DRL) – Used to encourage low rates of responding. It is like an interval schedule, except that premature responses reset the time required between behavior.
- Lab example: DRL 10-s = a rat is reinforced for the first response after 10 seconds, but if the rat responds earlier than 10 seconds there is no reinforcement and the rat has to wait 10 seconds from that premature response without another response before bar pressing will lead to reinforcement.
- Real-world example: "If you ask me for a potato chip no more than once every 10 minutes, I will give it to you. If you ask more often, I will give you none."
- Differential reinforcement of high rate (DRH) – Used to increase high rates of responding. It is like an interval schedule, except that a minimum number of responses are required in the interval in order to receive reinforcement.
- Lab example: DRH 10-s/FR 15 = a rat must press a bar 15 times within a 10-second increment to get reinforced.
- Real-world example: "If Lance Armstrong is going to win the Tour de France he has to pedal x number of times during the y-hour race."
Effects of different types of simple schedules
- Fixed ratio: activity slows after reinforcer is delivered, then response rates increase until the next reinforcer delivery (post-reinforcement pause).
- Variable ratio: rapid, steady rate of responding; most resistant to extinction.
- Fixed interval: responding increases towards the end of the interval; poor resistance to extinction.
- Variable interval: steady activity results, good resistance to extinction.
- Ratio schedules produce higher rates of responding than interval schedules, when the rates of reinforcement are otherwise similar.
- Variable schedules produce higher rates and greater resistance to extinction than most fixed schedules. This is also known as the Partial Reinforcement Extinction Effect (PREE).
- The variable ratio schedule produces both the highest rate of responding and the greatest resistance to extinction (for example, the behavior of gamblers at slot machines).
- Fixed schedules produce "post-reinforcement pauses" (PRP), where responses will briefly cease immediately following reinforcement, though the pause is a function of the upcoming response requirement rather than the prior reinforcement.[22]
- The PRP of a fixed interval schedule is frequently followed by a "scallop-shaped" accelerating rate of response, while fixed ratio schedules produce a more "angular" response.
- fixed interval scallop: the pattern of responding that develops with fixed interval reinforcement schedule, performance on a fixed interval reflects subject's accuracy in telling time.
- The PRP of a fixed interval schedule is frequently followed by a "scallop-shaped" accelerating rate of response, while fixed ratio schedules produce a more "angular" response.
- Organisms whose schedules of reinforcement are "thinned" (that is, requiring more responses or a greater wait before reinforcement) may experience "ratio strain" if thinned too quickly. This produces behavior similar to that seen during extinction.
- Ratio strain: the disruption of responding that occurs when a fixed ratio response requirement is increased too rapidly.
- Ratio run: high and steady rate of responding that completes each ratio requirement. Usually higher ratio requirement causes longer post-reinforcement pauses to occur.
- Partial reinforcement schedules are more resistant to extinction than continuous reinforcement schedules.
- Ratio schedules are more resistant than interval schedules and variable schedules more resistant than fixed ones.
- Momentary changes in reinforcement value lead to dynamic changes in behavior.[23]
Compound schedules
Compound schedules combine two or more different simple schedules in some way using the same reinforcer for the same behavior. There are many possibilities; among those most often used are:
- Alternative schedules – A type of compound schedule where two or more simple schedules are in effect and whichever schedule is completed first results in reinforcement.[24]
- Conjunctive schedules – A complex schedule of reinforcement where two or more simple schedules are in effect independently of each other, and requirements on all of the simple schedules must be met for reinforcement.
- Multiple schedules – Two or more schedules alternate over time, with a stimulus indicating which is in force. Reinforcement is delivered if the response requirement is met while a schedule is in effect.
- Example: FR4 when given a whistle and FI6 when given a bell ring.
- Mixed schedules – Either of two, or more, schedules may occur with no stimulus indicating which is in force. Reinforcement is delivered if the response requirement is met while a schedule is in effect.
- Example: FI6 and then VR3 without any stimulus warning of the change in schedule.
- Concurrent schedules – A complex reinforcement procedure in which the participant can choose any one of two or more simple reinforcement schedules that are available simultaneously. Organisms are free to change back and forth between the response alternatives at any time.
- Real-world example: changing channels on a television.
- Concurrent-chain schedule of reinforcement – A complex reinforcement procedure in which the participant is permitted to choose during the first link which of several simple reinforcement schedules will be in effect in the second link. Once a choice has been made, the rejected alternatives become unavailable until the start of the next trial.
- Interlocking schedules – A single schedule with two components where progress in one component affects progress in the other component. In an interlocking FR 60 FI 120-s schedule, for example, each response subtracts time from the interval component such that each response is "equal" to removing two seconds from the FI schedule.
- Chained schedules – Reinforcement occurs after two or more successive schedules have been completed, with a stimulus indicating when one schedule has been completed and the next has started
- Example: On an FR 10 schedule in the presence a red light, a pigeon pecks a green disc 10 times; then, a yellow light indicates an FR 3 schedule is active; after the pigeon pecks a yellow disc 3 times, a green light to indicates a VI 6-s schedule is in effect; if this were the final schedule in the chain, the pigeon would be reinforced for pecking a green disc on a VI 6-s schedule; however, all schedule requirements in the chain must be met before a reinforcer is provided.
- Tandem schedules – Reinforcement occurs when two or more successive schedule requirements have been completed, with no stimulus indicating when a schedule has been completed and the next has started.
- Example: VR 10, after it is completed the schedule is changed without warning to FR 10, after that it is changed without warning to FR 16, etc. At the end of the series of schedules, a reinforcer is finally given.
- Higher-order schedules – completion of one schedule is reinforced according to a second schedule; e.g. in FR2 (FI10 secs), two successive fixed interval schedules require completion before a response is reinforced.
Superimposed schedules
The psychology term superimposed schedules of reinforcement refers to a structure of rewards where two or more simple schedules of reinforcement operate simultaneously. Reinforcers can be positive, negative, or both. An example is a person who comes home after a long day at work. The behavior of opening the front door is rewarded by a big kiss on the lips by the person's spouse and a rip in the pants from the family dog jumping enthusiastically. Another example of superimposed schedules of reinforcement is a pigeon in an experimental cage pecking at a button. The pecks deliver a hopper of grain every 20th peck, and access to water after every 200 pecks.
Superimposed schedules of reinforcement are a type of compound schedule that evolved from the initial work on simple schedules of reinforcement by B.F. Skinner and his colleagues (Skinner and Ferster, 1957). They demonstrated that reinforcers could be delivered on schedules, and further that organisms behaved differently under different schedules. Rather than a reinforcer, such as food or water, being delivered every time as a consequence of some behavior, a reinforcer could be delivered after more than one instance of the behavior. For example, a pigeon may be required to peck a button switch ten times before food appears. This is a "ratio schedule". Also, a reinforcer could be delivered after an interval of time passed following a target behavior. An example is a rat that is given a food pellet immediately following the first response that occurs after two minutes has elapsed since the last lever press. This is called an "interval schedule".
In addition, ratio schedules can deliver reinforcement following fixed or variable number of behaviors by the individual organism. Likewise, interval schedules can deliver reinforcement following fixed or variable intervals of time following a single response by the organism. Individual behaviors tend to generate response rates that differ based upon how the reinforcement schedule is created. Much subsequent research in many labs examined the effects on behaviors of scheduling reinforcers.
If an organism is offered the opportunity to choose between or among two or more simple schedules of reinforcement at the same time, the reinforcement structure is called a "concurrent schedule of reinforcement". Brechner (1974, 1977) introduced the concept of superimposed schedules of reinforcement in an attempt to create a laboratory analogy of social traps, such as when humans overharvest their fisheries or tear down their rainforests. Brechner created a situation where simple reinforcement schedules were superimposed upon each other. In other words, a single response or group of responses by an organism led to multiple consequences. Concurrent schedules of reinforcement can be thought of as "or" schedules, and superimposed schedules of reinforcement can be thought of as "and" schedules. Brechner and Linder (1981) and Brechner (1987) expanded the concept to describe how superimposed schedules and the social trap analogy could be used to analyze the way energy flows through systems.
Superimposed schedules of reinforcement have many real-world applications in addition to generating social traps. Many different human individual and social situations can be created by superimposing simple reinforcement schedules. For example, a human being could have simultaneous tobacco and alcohol addictions. Even more complex situations can be created or simulated by superimposing two or more concurrent schedules. For example, a high school senior could have a choice between going to Stanford University or UCLA, and at the same time have the choice of going into the Army or the Air Force, and simultaneously the choice of taking a job with an internet company or a job with a software company. That is a reinforcement structure of three superimposed concurrent schedules of reinforcement.
Superimposed schedules of reinforcement can create the three classic conflict situations (approach–approach conflict, approach–avoidance conflict, and avoidance–avoidance conflict) described by Kurt Lewin (1935) and can operationalize other Lewinian situations analyzed by his force field analysis. Other examples of the use of superimposed schedules of reinforcement as an analytical tool are its application to the contingencies of rent control (Brechner, 2003) and problem of toxic waste dumping in the Los Angeles County storm drain system (Brechner, 2010).
Concurrent schedules
In operant conditioning, concurrent schedules of reinforcement are schedules of reinforcement that are simultaneously available to an animal subject or human participant, so that the subject or participant can respond on either schedule. For example, in a two-alternative forced choice task, a pigeon in a Skinner box is faced with two pecking keys; pecking responses can be made on either, and food reinforcement might follow a peck on either. The schedules of reinforcement arranged for pecks on the two keys can be different. They may be independent, or they may be linked so that behavior on one key affects the likelihood of reinforcement on the other.
It is not necessary for responses on the two schedules to be physically distinct. In an alternate way of arranging concurrent schedules, introduced by Findley in 1958, both schedules are arranged on a single key or other response device, and the subject can respond on a second key to change between the schedules. In such a "Findley concurrent" procedure, a stimulus (e.g., the color of the main key) signals which schedule is in effect.
Concurrent schedules often induce rapid alternation between the keys. To prevent this, a "changeover delay" is commonly introduced: each schedule is inactivated for a brief period after the subject switches to it.
When both the concurrent schedules are variable intervals, a quantitative relationship known as the matching law is found between relative response rates in the two schedules and the relative reinforcement rates they deliver; this was first observed by R.J. Herrnstein in 1961. Matching law is a rule for instrumental behavior which states that the relative rate of responding on a particular response alternative equals the relative rate of reinforcement for that response (rate of behavior = rate of reinforcement). Animals and humans have a tendency to prefer choice in schedules.[25]
Shaping
Shaping is the reinforcement of successive approximations to a desired instrumental response. In training a rat to press a lever, for example, simply turning toward the lever is reinforced at first. Then, only turning and stepping toward it is reinforced. Eventually the rat will be reinforced for pressing the lever. The successful attainment of one behavior starts the shaping process for the next. As training progresses, the response becomes progressively more like the desired behavior, with each subsequent behavior becoming a closer approximation of the final behavior.[26]
The intervention of shaping is used in many training situations, and also for individuals with autism as well as other developmental disabilities. When shaping is combined with other evidence-based practices such as Functional Communication Training (FCT),[27] it can yield positive outcomes for human behavior. Shaping typically uses continuous reinforcement, but the response can later be shifted to an intermittent reinforcement schedule.
Shaping is also used for food refusal.[28] Food refusal is when an individual has a partial or total aversion to food items. This can be as minimal as being a picky eater to so severe that it can affect an individual's health. Shaping has been used to have a high success rate for food acceptance.[29]
Chaining
Chaining involves linking discrete behaviors together in a series, such that the consequence of each behavior is both the reinforcement for the previous behavior, and the antecedent stimulus for the next behavior. There are many ways to teach chaining, such as forward chaining (starting from the first behavior in the chain), backwards chaining (starting from the last behavior) and total task chaining (teaching each behavior in the chain simultaneously). People's morning routines are a typical chain, with a series of behaviors (e.g. showering, drying off, getting dressed) occurring in sequence as a well learned habit.
Challenging behaviors seen in individuals with autism and other related disabilities have successfully managed and maintained in studies using a scheduled of chained reinforcements.[30] Functional communication training is an intervention that often uses chained schedules of reinforcement to effectively promote the appropriate and desired functional communication response.[31]
Mathematical models
There has been research on building a mathematical model of reinforcement. This model is known as MPR, which is short for mathematical principles of reinforcement. Peter Killeen has made key discoveries in the field with his research on pigeons.[32]
Applications
Reinforcement and punishment are ubiquitous in human social interactions, and a great many applications of operant principles have been suggested and implemented. Following are a few examples.
Addiction and dependence
Positive and negative reinforcement play central roles in the development and maintenance of addiction and drug dependence. An addictive drug is intrinsically rewarding; that is, it functions as a primary positive reinforcer of drug use. The brain's reward system assigns it incentive salience (i.e., it is "wanted" or "desired"),[33][34][35] so as an addiction develops, deprivation of the drug leads to craving. In addition, stimuli associated with drug use – e.g., the sight of a syringe, and the location of use – become associated with the intense reinforcement induced by the drug.[33][34][35] These previously neutral stimuli acquire several properties: their appearance can induce craving, and they can become conditioned positive reinforcers of continued use.[33][34][35] Thus, if an addicted individual encounters one of these drug cues, a craving for the associated drug may reappear. For example, anti-drug agencies previously used posters with images of drug paraphernalia as an attempt to show the dangers of drug use. However, such posters are no longer used because of the effects of incentive salience in causing relapse upon sight of the stimuli illustrated in the posters.
In drug dependent individuals, negative reinforcement occurs when a drug is self-administered in order to alleviate or "escape" the symptoms of physical dependence (e.g., tremors and sweating) and/or psychological dependence (e.g., anhedonia, restlessness, irritability, and anxiety) that arise during the state of drug withdrawal.[33]
Animal training
Animal trainers and pet owners were applying the principles and practices of operant conditioning long before these ideas were named and studied, and animal training still provides one of the clearest and most convincing examples of operant control. Of the concepts and procedures described in this article, a few of the most salient are: availability of immediate reinforcement (e.g. the ever-present bag of dog yummies); contingency, assuring that reinforcement follows the desired behavior and not something else; the use of secondary reinforcement, as in sounding a clicker immediately after a desired response; shaping, as in gradually getting a dog to jump higher and higher; intermittent reinforcement, reducing the frequency of those yummies to induce persistent behavior without satiation; chaining, where a complex behavior is gradually put together.[36]
Child behavior – parent management training
Providing positive reinforcement for appropriate child behaviors is a major focus of parent management training. Typically, parents learn to reward appropriate behavior through social rewards (such as praise, smiles, and hugs) as well as concrete rewards (such as stickers or points towards a larger reward as part of an incentive system created collaboratively with the child).[37] In addition, parents learn to select simple behaviors as an initial focus and reward each of the small steps that their child achieves towards reaching a larger goal (this concept is called "successive approximations").[37][38] They may also use indirect rewards such through progress charts. Providing positive reinforcement in the classroom can be beneficial to student success. When applying positive reinforcement to students, it's crucial to make it individualized to that student's needs. This way, the student understands why they are receiving the praise, they can accept it, and eventually learn to continue the action that was earned by positive reinforcement. For example, using rewards or extra recess time might apply to some students more, whereas others might accept the enforcement by receiving stickers or check marks indicating praise.
Economics
Both psychologists and economists have become interested in applying operant concepts and findings to the behavior of humans in the marketplace. An example is the analysis of consumer demand, as indexed by the amount of a commodity that is purchased. In economics, the degree to which price influences consumption is called "the price elasticity of demand." Certain commodities are more elastic than others; for example, a change in price of certain foods may have a large effect on the amount bought, while gasoline and other essentials may be less affected by price changes. In terms of operant analysis, such effects may be interpreted in terms of motivations of consumers and the relative value of the commodities as reinforcers.[39]
Gambling – variable ratio scheduling
As stated earlier in this article, a variable ratio schedule yields reinforcement after the emission of an unpredictable number of responses. This schedule typically generates rapid, persistent responding. Slot machines pay off on a variable ratio schedule, and they produce just this sort of persistent lever-pulling behavior in gamblers. Because the machines are programmed to pay out less money than they take in, the persistent slot-machine user invariably loses in the long run. Slots machines, and thus variable ratio reinforcement, have often been blamed as a factor underlying gambling addiction.[40]
Managing behavior in organizations
An alternative to traditional pay for performance incentive schemes that is rooted in reinforcement theory, known as the O.B. Mod Approach, has been proposed as a practical approach to managing the performance-related behaviors of an organization's members. . O.B. Mod. and its "reinforce-for-performance" basis has been shown empirically to yield performance improvements in both manufacturing and service organizations, though improvements varied by type of reinforcer in both contexts.[41]
Nudge theory
Nudge theory (or nudge) is a concept in behavioral science, political theory and economics which argues that positive reinforcement and indirect suggestions to try to achieve non-forced compliance can influence the motives, incentives and decision making of groups and individuals, at least as effectively – if not more effectively – than direct instruction, legislation, or enforcement.
Praise
The concept of praise as a means of behavioral reinforcement in humans is rooted in B.F. Skinner's model of operant conditioning. Through this lens, praise has been viewed as a means of positive reinforcement, wherein an observed behavior is made more likely to occur by contingently praising said behavior.[42] Hundreds of studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of praise in promoting positive behaviors, notably in the study of teacher and parent use of praise on child in promoting improved behavior and academic performance,[43][44] but also in the study of work performance.[45] Praise has also been demonstrated to reinforce positive behaviors in non-praised adjacent individuals (such as a classmate of the praise recipient) through vicarious reinforcement.[46] Praise may be more or less effective in changing behavior depending on its form, content and delivery. In order for praise to effect positive behavior change, it must be contingent on the positive behavior (i.e., only administered after the targeted behavior is enacted), must specify the particulars of the behavior that is to be reinforced, and must be delivered sincerely and credibly.[47]
Acknowledging the effect of praise as a positive reinforcement strategy, numerous behavioral and cognitive behavioral interventions have incorporated the use of praise in their protocols.[48][49] The strategic use of praise is recognized as an evidence-based practice in both classroom management[48] and parenting training interventions,[44] though praise is often subsumed in intervention research into a larger category of positive reinforcement, which includes strategies such as strategic attention and behavioral rewards.
Manipulation
Braiker identified the following ways that manipulators control their victims:[50]
- Positive reinforcement: includes praise, superficial charm, superficial sympathy (crocodile tears), excessive apologizing, money, approval, gifts, attention, facial expressions such as a forced laugh or smile, and public recognition.
- Negative reinforcement: may involve removing one from a negative situation
- Intermittent or partial reinforcement: Partial or intermittent negative reinforcement can create an effective climate of fear and doubt. Partial or intermittent positive reinforcement can encourage the victim to persist – for example in most forms of gambling, the gambler is likely to win now and again but still lose money overall.
- Punishment: includes nagging, yelling, the silent treatment, intimidation, threats, swearing, emotional blackmail, the guilt trip, sulking, crying, and playing the victim.
- Traumatic one-trial learning: using verbal abuse, explosive anger, or other intimidating behavior to establish dominance or superiority; even one incident of such behavior can condition or train victims to avoid upsetting, confronting or contradicting the manipulator.
Traumatic bonding
Traumatic bonding occurs as the result of ongoing cycles of abuse in which the intermittent reinforcement of reward and punishment creates powerful emotional bonds that are resistant to change.[51][52]
The other source indicated that [53] 'The necessary conditions for traumatic bonding are that one person must dominate the other and that the level of abuse chronically spikes and then subsides. The relationship is characterized by periods of permissive, compassionate, and even affectionate behavior from the dominant person, punctuated by intermittent episodes of intense abuse. To maintain the upper hand, the victimizer manipulates the behavior of the victim and limits the victim's options so as to perpetuate the power imbalance. Any threat to the balance of dominance and submission may be met with an escalating cycle of punishment ranging from seething intimidation to intensely violent outbursts. The victimizer also isolates the victim from other sources of support, which reduces the likelihood of detection and intervention, impairs the victim's ability to receive countervailing self-referent feedback, and strengthens the sense of unilateral dependency ... The traumatic effects of these abusive relationships may include the impairment of the victim's capacity for accurate self-appraisal, leading to a sense of personal inadequacy and a subordinate sense of dependence upon the dominating person. Victims also may encounter a variety of unpleasant social and legal consequences of their emotional and behavioral affiliation with someone who perpetrated aggressive acts, even if they themselves were the recipients of the aggression.
Video games
Most video games are designed around some type of compulsion loop, adding a type of positive reinforcement through a variable rate schedule to keep the player playing the game, though this can also lead to video game addiction.[54]
As part of a trend in the monetization of video games in the 2010s, some games offered "loot boxes" as rewards or purchasable by real-world funds that offered a random selection of in-game items, distributed by rarity. The practice has been tied to the same methods that slot machines and other gambling devices dole out rewards, as it follows a variable rate schedule. While the general perception that loot boxes are a form of gambling, the practice is only classified as such in a few countries as gambling and otherwise legal. However, methods to use those items as virtual currency for online gambling or trading for real-world money has created a skin gambling market that is under legal evaluation.[55]
Workplace culture of fear
Ashforth discussed potentially destructive sides of leadership and identified what he referred to as petty tyrants: leaders who exercise a tyrannical style of management, resulting in a climate of fear in the workplace.[56] Partial or intermittent negative reinforcement can create an effective climate of fear and doubt.[50] When employees get the sense that bullies are tolerated, a climate of fear may be the result.[57]
Individual differences in sensitivity to reward, punishment, and motivation have been studied under the premises of reinforcement sensitivity theory and have also been applied to workplace performance.
Criticisms
The standard definition of behavioral reinforcement has been criticized as circular, since it appears to argue that response strength is increased by reinforcement, and defines reinforcement as something that increases response strength (i.e., response strength is increased by things that increase response strength). However, the correct usage[58] of reinforcement is that something is a reinforcer because of its effect on behavior, and not the other way around. It becomes circular if one says that a particular stimulus strengthens behavior because it is a reinforcer, and does not explain why a stimulus is producing that effect on the behavior. Other definitions have been proposed, such as F.D. Sheffield's "consummatory behavior contingent on a response", but these are not broadly used in psychology.[59]
Increasingly, understanding of the role reinforcers play is moving away from a "strengthening" effect to a "signalling" effect.[60] That is, the view that reinforcers increase responding because they signal the behaviors that are likely to result in reinforcement. While in most practical applications, the effect of any given reinforcer will be the same regardless of whether the reinforcer is signalling or strengthening, this approach helps to explain a number of behavioral phenomena including patterns of responding on intermittent reinforcement schedules (fixed interval scallops) and the differential outcomes effect.[61]
See also
References
- ↑ Definition of reinforcement from the American Psychological Association Retrieved on January 30th, 2024
- ↑ "Neuronal Reward and Decision Signals: From Theories to Data". Physiological Reviews 95 (3): 853–951. July 2015. doi:10.1152/physrev.00023.2014. PMID 26109341. "Rewards in operant conditioning are positive reinforcers. ... Operant behavior gives a good definition for rewards. Anything that makes an individual come back for more is a positive reinforcer and therefore a reward. Although it provides a good definition, positive reinforcement is only one of several reward functions. ... Rewards are attractive. They are motivating and make us exert an effort. ... Rewards induce approach behavior, also called appetitive or preparatory behavior, and consummatory behavior. ... Thus any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward. ... Intrinsic rewards are activities that are pleasurable on their own and are undertaken for their own sake, without being the means for getting extrinsic rewards. ... Intrinsic rewards are genuine rewards in their own right, as they induce learning, approach, and pleasure, like perfectioning, playing, and enjoying the piano. Although they can serve to condition higher order rewards, they are not conditioned, higher order rewards, as attaining their reward properties does not require pairing with an unconditioned reward.".
- ↑ "Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders". Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2009. pp. 364–375. ISBN 9780071481274.
- ↑ Nestler EJ (December 2013). "Cellular basis of memory for addiction". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 15 (4): 431–443. PMID 24459410. "Despite the importance of numerous psychosocial factors, at its core, drug addiction involves a biological process: the ability of repeated exposure to a drug of abuse to induce changes in a vulnerable brain that drive the compulsive seeking and taking of drugs, and loss of control over drug use, that define a state of addiction. ... A large body of literature has demonstrated that such ΔFosB induction in D1-type [nucleus accumbens] neurons increases an animal's sensitivity to drug as well as natural rewards and promotes drug self-administration, presumably through a process of positive reinforcement ... Another ΔFosB target is cFos: as ΔFosB accumulates with repeated drug exposure it represses c-Fos and contributes to the molecular switch whereby ΔFosB is selectively induced in the chronic drug-treated state.41. ... Moreover, there is increasing evidence that, despite a range of genetic risks for addiction across the population, exposure to sufficiently high doses of a drug for long periods of time can transform someone who has relatively lower genetic loading into an addict.".
- ↑ "Glossary of Terms". Department of Neuroscience. http://neuroscience.mssm.edu/nestler/glossary.html. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ↑ "Neurobiologic Advances from the Brain Disease Model of Addiction". New England Journal of Medicine 374 (4): 363–371. January 2016. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1511480. PMID 26816013. "Substance-use disorder: A diagnostic term in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) referring to recurrent use of alcohol or other drugs that causes clinically and functionally significant impairment, such as health problems, disability, and failure to meet major responsibilities at work, school, or home. Depending on the level of severity, this disorder is classified as mild, moderate, or severe.
Addiction: A term used to indicate the most severe, chronic stage of substance-use disorder, in which there is a substantial loss of self-control, as indicated by compulsive drug taking despite the desire to stop taking the drug. In the DSM-5, the term addiction is synonymous with the classification of severe substance-use disorder.". - ↑ "Some Experiments on Animal Intelligence". Science 7 (181): 818–24. June 1898. doi:10.1126/science.7.181.818. PMID 17769765. Bibcode: 1898Sci.....7..818T. https://zenodo.org/record/1448297.
- ↑ Skinner, B. F. "The Behavior of Organisms: An Experimental Analysis", 1938 New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts
- ↑ Walden Two. Toronto: The Macmillan Company. 1948. https://archive.org/details/waldentwo1948skin.
- ↑ Honig, Werner (1966). Operant Behavior: Areas of Research and Application. New York: Meredith Publishing Company. p. 381. http://psycnet.apa.org/record/1966-35017-000.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.0 11.1 Flora, Stephen (2004). The Power of Reinforcement. Albany: State University of New York Press.
- ↑ Stajkovic, Alex (2019). Management and Leadership, What Can MBD Do in My Workday?. First Research Paradigms Applied
- ↑ Learning Processes: Instrumental Conditioning. Toronto: The Macmillan Company. 1969.
- ↑ Well-Being in the Workplace and its Relationship to Business Outcomes: A Review of the Gallup Studies. Washington D.C.: American Psychological Association. 2002. http://media.gallup.com/documents/whitePaper--Well-BeingInTheWorkplace.pdf.
- ↑ Skinner, B.F. (1974). About Behaviorism
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 Miltenberger, R. G. "Behavioral Modification: Principles and Procedures". Thomson/Wadsworth, 2008.
- ↑ "Use of noncontingent reinforcement in the treatment of challenging behavior. A review and clinical guide". Behavior Modification 22 (4): 529–47. October 1998. doi:10.1177/01454455980224005. PMID 9755650.
- ↑ "Use of fluorescent probes for describing the process of encapsulation by hypotonic dialysis". The Use of Resealed Erythrocytes as Carriers and Bioreactors. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 326. 1992. pp. 73–80. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-3030-5_9. ISBN 978-1-4613-6321-7.
- ↑ Baer, Donald M.; Wolf, Montrose M.. "The entry into natural communities of reinforcement". Control of human behavior. 2. Glenview, IL: Scott Foresman. pp. 319–24.
- ↑ "Toward a technology of generalization: The identification of natural contingencies of reinforcement". The Behavior Analyst 9 (1): 19–26. 1986. doi:10.1007/bf03391926. PMID 22478644.
- ↑ "Differential reinforcement as treatment for behavior disorders: procedural and functional variations". Research in Developmental Disabilities 13 (4): 393–417. 1992. doi:10.1016/0891-4222(92)90013-v. PMID 1509180.
- ↑ "Within Session FR Pausing.". The Behavior Analyst Today 8 (2): 175–86. 2007. doi:10.1037/h0100611.
- ↑ McSweeney, Frances K.; Murphy, Eric S.; Kowal, Benjamin P. (2001). "Dynamic changes in reinforcer value: Some misconceptions and why you should care.". The Behavior Analyst Today 2 (4): 341–349. doi:10.1037/h0099952.
- ↑ Experimental Analysis of Behavior. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 1991. ISBN 9781483291260. https://books.google.com/books?id=uVYJAwAAQBAJ.
- ↑ "On Choice, Preference, and Preference For Choice.". The Behavior Analyst Today 7 (2): 234–48. 2006. doi:10.1037/h0100083. PMID 23372459.
- ↑ "Chapter 7: Learning". Psychology (2nd ed.). New York: Worth Publishers. 2011. pp. 284–85. ISBN 978-1-4292-3719-2. https://archive.org/details/psychology0000scha/page/284.
- ↑ Ghaemmaghami, Mahshid; Hanley, Gregory P.; Jessel, Joshua; Landa, Robin (2018-05-14). "Shaping complex functional communication responses". Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 51 (3): 502–520. doi:10.1002/jaba.468. ISSN 0021-8855. PMID 29761485. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jaba.468.
- ↑ Tarbox and Lanagan Bermudez, Jonathan and Taira (2017). Treating Feeding Challenges in Autism. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 1–6. ISBN 978-0-12-813563-1.
- ↑ Turner, Virginia R (2020). "Response Shaping to Improve Food Acceptance for Children with Autism: Effects of Small and Large Food Sets". Research in Developmental Disabilities 98: 103574. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2020.103574. PMID 31982827.
- ↑ "CORRIGENDUM to "Further Evaluations of Functional Communication Training and Chained Schedules of Reinforcement to Treat Multiple Functions of Challenging Behavior"". Behavior Modification 46 (1): 254. 2020-07-24. doi:10.1177/0145445520945810. ISSN 0145-4455. PMID 32706269.
- ↑ Falcomata, Terry S.; Roane, Henry S.; Muething, Colin S.; Stephenson, Kasey M.; Ing, Anna D. (2012-02-09). "Functional Communication Training and Chained Schedules of Reinforcement to Treat Challenging Behavior Maintained by Terminations of Activity Interruptions". Behavior Modification 36 (5): 630–649. doi:10.1177/0145445511433821. ISSN 0145-4455. PMID 22327267. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0145445511433821.
- ↑ Killeen, Peter R. (4 February 2010). "Mathematical principles of reinforcement". Behavioral and Brain Sciences 17 (1): 105–135. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00033628. http://cogprints.org/591/1/199802001.html.
- ↑ Jump up to: 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 "Reinforcement principles for addiction medicine; from recreational drug use to psychiatric disorder". Neuroscience for Addiction Medicine: From Prevention to Rehabilitation - Constructs and Drugs. Progress in Brain Research. 223. 2016. pp. 63–76. doi:10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.07.005. ISBN 9780444635457. "Abused substances (ranging from alcohol to psychostimulants) are initially ingested at regular occasions according to their positive reinforcing properties. Importantly, repeated exposure to rewarding substances sets off a chain of secondary reinforcing events, whereby cues and contexts associated with drug use may themselves become reinforcing and thereby contribute to the continued use and possible abuse of the substance(s) of choice. ...
An important dimension of reinforcement highly relevant to the addiction process (and particularly relapse) is secondary reinforcement (Stewart, 1992). Secondary reinforcers (in many cases also considered conditioned reinforcers) likely drive the majority of reinforcement processes in humans. In the specific case of drug [addiction], cues and contexts that are intimately and repeatedly associated with drug use will often themselves become reinforcing ... A fundamental piece of Robinson and Berridge's incentive-sensitization theory of addiction posits that the incentive value or attractive nature of such secondary reinforcement processes, in addition to the primary reinforcers themselves, may persist and even become sensitized over time in league with the development of drug addiction (Robinson and Berridge, 1993). ...
Negative reinforcement is a special condition associated with a strengthening of behavioral responses that terminate some ongoing (presumably aversive) stimulus. In this case we can define a negative reinforcer as a motivational stimulus that strengthens such an “escape” response. Historically, in relation to drug addiction, this phenomenon has been consistently observed in humans whereby drugs of abuse are self-administered to quench a motivational need in the state of withdrawal (Wikler, 1952)." - ↑ Jump up to: 34.0 34.1 34.2 "From prediction error to incentive salience: mesolimbic computation of reward motivation". The European Journal of Neuroscience 35 (7): 1124–43. April 2012. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.07990.x. PMID 22487042. "When a Pavlovian CS+ is attributed with incentive salience it not only triggers ‘wanting' for its UCS, but often the cue itself becomes highly attractive – even to an irrational degree. This cue attraction is another signature feature of incentive salience. The CS becomes hard not to look at (Wiers & Stacy, 2006; Hickey et al., 2010a; Piech et al., 2010; Anderson et al., 2011). The CS even takes on some incentive properties similar to its UCS. An attractive CS often elicits behavioral motivated approach, and sometimes an individual may even attempt to ‘consume' the CS somewhat as its UCS (e.g., eat, drink, smoke, have sex with, take as drug). ‘Wanting' of a CS can turn also turn the formerly neutral stimulus into an instrumental conditioned reinforcer, so that an individual will work to obtain the cue (however, there exist alternative psychological mechanisms for conditioned reinforcement too).".
- ↑ Jump up to: 35.0 35.1 35.2 "Pleasure systems in the brain". Neuron 86 (3): 646–64. May 2015. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.018. PMID 25950633. "An important goal in future for addiction neuroscience is to understand how intense motivation becomes narrowly focused on a particular target. Addiction has been suggested to be partly due to excessive incentive salience produced by sensitized or hyper-reactive dopamine systems that produce intense ‘wanting' (Robinson and Berridge, 1993). But why one target becomes more ‘wanted' than all others has not been fully explained. In addicts or agonist-stimulated patients, the repetition of dopamine-stimulation of incentive salience becomes attributed to particular individualized pursuits, such as taking the addictive drug or the particular compulsions. In Pavlovian reward situations, some cues for reward become more ‘wanted' more than others as powerful motivational magnets, in ways that differ across individuals (Robinson et al., 2014b; Saunders and Robinson, 2013). ... However, hedonic effects might well change over time. As a drug was taken repeatedly, mesolimbic dopaminergic sensitization could consequently occur in susceptible individuals to amplify ‘wanting' (Leyton and Vezina, 2013; Lodge and Grace, 2011; Wolf and Ferrario, 2010), even if opioid hedonic mechanisms underwent down-regulation due to continual drug stimulation, producing ‘liking' tolerance. Incentive-sensitization would produce addiction, by selectively magnifying cue-triggered ‘wanting' to take the drug again, and so powerfully cause motivation even if the drug became less pleasant (Robinson and Berridge, 1993).".
- ↑ Carrots and sticks: principles of animal training. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2007. ISBN 978-0-521-68691-4.
- ↑ Jump up to: 37.0 37.1 Kazdin AE (2010). Problem-solving skills training and parent management training for oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (2nd ed.), 211–226. New York: Guilford Press.
- ↑ Forgatch MS, Patterson GR (2010). Parent management training — Oregon model: An intervention for antisocial behavior in children and adolescents. Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (2nd ed.), 159–78. New York: Guilford Press.
- ↑ Domjan, M. (2009). The Principles of Learning and Behavior. Wadsworth Publishing Company. 6th Edition. pages 244–249.
- ↑ "Impulsivity, intelligence, and discriminating reinforcement contingencies in a fixed-ratio 3 schedule". The Spanish Journal of Psychology 15 (3): 922–9. November 2012. doi:10.5209/rev_sjop.2012.v15.n3.39384. PMID 23156902.
- ↑ "Reinforce for performance: The need to go beyond pay and even rewards". Academy of Management Executive 13 (2): 49–57. 1999. doi:10.5465/AME.1999.1899548. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/managementfacpub/169.
- ↑ Kazdin, Alan (1978). History of behavior modification: Experimental foundations of contemporary research. Baltimore: University Park Press. ISBN 9780839112051. https://archive.org/details/historyofbehavio0000kazd.
- ↑ "Superior vena cava syndrome: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment". American Journal of Critical Care 1 (1): 54–64. 1992. doi:10.4037/ajcc1992.1.1.54. PMID 1307879.
- ↑ Jump up to: 44.0 44.1 "Identifying common elements of evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children's disruptive behavior problems". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 47 (5): 505–14. May 2008. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e31816765c2. PMID 18356768.
- ↑ "Task clarification, performance feedback, and social praise: Procedures for improving the customer service of bank tellers". Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 21 (1): 65–71. 1988. doi:10.1901/jaba.1988.21-65. PMID 16795713.
- ↑ "Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the external auditory canal". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 106 (2): 214–5. 1992. doi:10.1177/019459989210600211. PMID 1310808.
- ↑ Brophy, Jere (1981). "On praising effectively". The Elementary School Journal 81 (5): 269–278. doi:10.1086/461229.
- ↑ Jump up to: 48.0 48.1 Simonsen, Brandi; Fairbanks, Sarah; Briesch, Amy; Myers, Diane; Sugai, George (2008). "Evidence-based Practices in Classroom Management: Considerations for Research to Practice". Education and Treatment of Children 31 (1): 351–380. doi:10.1353/etc.0.0007.
- ↑ Weisz, John R.; Kazdin, Alan E. (2010). Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents. Guilford Press. ISBN 9781606235256. https://books.google.com/books?id=QLzBv53CU2UC.
- ↑ Jump up to: 50.0 50.1 Braiker, Harriet B. (2004). Who's Pulling Your Strings ? How to Break The Cycle of Manipulation. ISBN 0-07-144672-9.
- ↑ Dutton; Painter (1981). "Traumatic Bonding: The development of emotional attachments in battered women and other relationships of intermittent abuse". Victimology (7).
- ↑ Chrissie Sanderson. Counselling Survivors of Domestic Abuse. Jessica Kingsley Publishers; 15 June 2008. ISBN:978-1-84642-811-1. p. 84.
- ↑ "Traumatic Bonding | Encyclopedia.com". http://www.encyclopedia.com/social-sciences/applied-and-social-sciences-magazines/traumatic-bonding.
- ↑ Hopson, John (27 April 2001). "Behavioral Game Design". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/feature/131494/behavioral_game_design.php.
- ↑ Hood, Vic (October 12, 2017). "Are loot boxes gambling?". Eurogamer. http://www.eurogamer.net/articles/2017-10-11-are-loot-boxes-gambling.
- ↑ Ashforth, Blake (1994). "Petty tyranny in organizations". Human Relations 47 (7): 755–778. doi:10.1177/001872679404700701.
- ↑ "Organisational Effects of Workplace Bullying". Bullying and Harassment in the Workplace: Developments in Theory, Research, and Practice (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. 2010. ISBN 978-1-4398-0489-6.
- ↑ Skinner for the classroom : selected papers. Champaign, Ill.: Research Press. 1982. ISBN 978-0-87822-261-2. https://archive.org/details/skinnerforclassr00skin.
- ↑ Vaccarino, Franco J.; Schiff, Bernard B.; Glickman, Stephen E. (1989). Contemporary learning theories. Hillsdale, N.J.: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. ISBN 978-0-89859-915-2.
- ↑ "Reinforcement: food signals the time and location of future food". Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior 96 (1): 63–86. July 2011. doi:10.1901/jeab.2011.96-63. PMID 21765546.
- ↑ McCormack, Jessica; Arnold-Saritepe, Angela; Elliffe, Douglas (June 2017). "The differential outcomes effect in children with autism". Behavioral Interventions 32 (4): 357–369. doi:10.1002/bin.1489.
Further reading
- Brechner KC (1974). An experimental analysis of social traps (PhD thesis). Arizona State University.
- "An experimental analysis of social traps". Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 13 (6): 552–64. 1977. doi:10.1016/0022-1031(77)90054-3.
- Social Traps, Individual Traps, and Theory in Social Psychology. Bulletin No. 870001. Pasadena, CA: Time River Laboratory. 1987.
- "Superimposed schedules applied to rent control.". Economic and Game Theory. 28 February 2003. http://www.dklevine.com/bin/workshops-php/discuss/discuss.php3?showID=396467000000000285.
- "A social trap analysis of energy distribution systems". Advances in Environmental Psychology. 3. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum & Associates. 1981.
- Chance, Paul (2003). Learning and Behavior (5th ed.). Toronto: Thomson-Wadsworth.
- "Some weaknesses of a response-strength account of reinforcer effects". European Journal of Behavior Analysis 21 (2): 1–16. 2019. doi:10.1080/15021149.2019.1685247.
- "The etymology of basic concepts in the experimental analysis of behavior". Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior 82 (3): 311–6. November 2004. doi:10.1901/jeab.2004.82-311. PMID 15693525.
- Schedules of reinforcement. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts. 1957. ISBN 0-13-792309-0. https://archive.org/details/schedulesofreinf0000fers.
- A dynamic theory of personality: Selected papers. New York: McGraw-Hill. 1935. ISBN 9781447497134. https://books.google.com/books?id=qDl9CgAAQBAJ.
- The behavior of organisms. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts. 1938. ISBN 9780996453905. https://books.google.com/books?id=S9WNCwAAQBAJ.
- "A case history in scientific method". American Psychologist 11 (5): 221–33. 1956. doi:10.1037/h0047662.
- "Fixed and variable schedules of response-independent reinforcement". Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior 11 (4): 405–14. July 1968. doi:10.1901/jeab.1968.11-405. PMID 5672249.
- "Glossary of reinforcement terms". University of Iowa. http://www.psychology.uiowa.edu/Faculty/wasserman/Glossary/reinforcement.html.
- "Well-Being in the Workplace and its Relationship to Business Outcomes: A Review of the Gallup Studies.". Flourishing: The Positive Person and the Good Life. Washington D.C.: American Psychological Association. 2002. pp. 205–224.
External links
et:Sarrus
 |