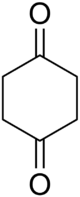
Chemistry:1,4-Cyclohexanedione
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclohexane-1,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 774152 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 101292 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 112.128 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 77 to 78.5 °C (170.6 to 173.3 °F; 350.1 to 351.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 130 to 133 °C (266 to 271 °F; 403 to 406 K) (20 mm.)[<span title="What the heck is "20 mm."??? Is this a pressure in millimetres of mercury (mmHg)? Units of measurement should not be abbreviated (here "mmHg" or "mmH2O" or "mmWho-knows-what" is abbreviated as "mm.")! The unit of measurement of pressure is not milimetre! Also, "mm." could be abbreviated version of millimetres of water (mmH2O) or millimetres of who knows what. The readers have no power to read the writer's mind! Explain this jargon for an average mortal human being. (August 2023)">clarification needed] |
| Very | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol. Insoluble in diethyl ether. |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 132 °C (270 °F; 405 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1,4-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH
2)
4(CO)
2. This white solid is one of the three isomeric cyclohexanediones. This particular diketone is used as a building block in the synthesis of more complex molecules.
Preparation
1,4-Cyclohexanedione is prepared in two steps from diesters of succinic acid. Specifically under basic conditions, the diethyl succinate condenses to give the cyclohexenediol derivative diethylsuccinoylsuccinate. This intermediate can be hydrolysed and decarboxylated to afford the desired dione.[2]
This dione condenses with malononitrile to give an intermediate that can be dehydrogenated to tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ).[3]
References
- ↑ MSDS for 1,4-Cyclohexanedione
- ↑ Nielsen, Arnold T.; Carpenter, Wayne R. (1965). "1,4-Cyclohexanedione". Organic Syntheses 45: 25. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.045.0025.
- ↑ Strittmatter, Harald; Hildbrand, Stefan; Pollak, Peter (2007). "Malonic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_063.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
 |

