Chemistry:Malononitrile
From HandWiki
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Malononitrile[2]
| |||
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanedinitrile[2] | |||
| Other names
Malonodinitrile, Cyanoacetonitrile, Dicyanomethane, Malonic dinitrile[1]
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 773697 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1303 | |||
| MeSH | dicyanmethane | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2647 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H2N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 66.063 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless or white solid[1] | ||
| Density | 1.049 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 32 °C; 89 °F; 305 K | ||
| Boiling point | 220.1 °C; 428.1 °F; 493.2 K | ||
| 13% (20 °C)[1] | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
110.29 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S |
130.96 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
187.7 to 188.1 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−1,654.0 to −1,654.4 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  
| ||
| GHS Signal word | DANGER | ||
| H301, H311, H331, H410 | |||
| P261, P273, P280, P301+310, P311 | |||
| Flash point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
| ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 3 ppm (8 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanenitriles
|
| ||
Related compounds
|
DBNPA | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
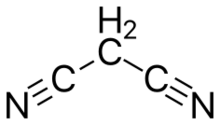
Malononitrile is an organic compound nitrile with the formula CH2(CN)2. It is a colorless or white solid. It can be prepared by dehydration of cyanoacetamide.[3]
Malononitrile is relatively acidic, with a pKa of 11 in water.[4] This allows it to be used in the Knoevenagel condensation, for example in the preparation of CS gas:

Malononitrile is a suitable starting material for the Gewald reaction, where the nitrile condenses with a ketone or aldehyde in the presence of elemental sulfur and a base to produce a 2-aminothiophene.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0378". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0378.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 902. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Surrey, Alexander (1945). "Malononitrile". Organic Syntheses 25: 63–64. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.025.0063.
- ↑ Evans pKa table
- ↑ Sabnis, R.W.; Rangnekar, D.W.; Sonawane, N.D. (1999). "2-Aminothiophenes By The Gewald Reaction". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 36 (2): 333–345. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570360203. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=10040669. Retrieved 2007-07-18.
External links