Chemistry:Dibenzothiophene
From HandWiki
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dibenzo[b,d]thiophene | |
| Other names
Diphenylene sulfide, DBT
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8S | |
| Molar mass | 184.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless crystals |
| Density | 1.252 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 97 to 100 °C (207 to 212 °F; 370 to 373 K) (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 332 to 333 °C (630 to 631 °F; 605 to 606 K) |
| insol. | |
| Solubility in other solvents | benzene and related |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable, toxic |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H302, H311, H315, H331, H332, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P361, P362, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Thiophene Anthracene Benzothiophene Dibenzofuran |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
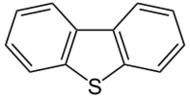
Dibenzothiophene (DBT, diphenylene sulfide) is the organosulfur compound consisting of two benzene rings fused to a central thiophene ring. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to anthracene. This tricyclic heterocycle, and especially its disubstituted derivative 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene are problematic impurities in petroleum.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of biphenyl with sulfur dichloride in the presence of aluminium chloride.[2]
Reduction with lithium results in scission of one C-S bond. With butyllithium, this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4-position. S-oxidation with peroxides gives the sulfoxide.[3]
References
- ↑ Ho, Teh C. (2004). "Deep HDS of Diesel Fuel: Chemistry and Catalysis". Catalysis Today 98 (1–2): 3–18. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2004.07.048.
- ↑ Klemm, L. H.; Karchesy, Joseph J. (1978). "The Insertion and Extrusion of Heterosulfur Bridges. VIII. Dibenzothiophene from Biphenyl and Derivatives". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 15 (4): 561–563. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570150407.
- ↑ Waldecker, Bernd; Kafuta, Kevin; Alcarazo, Manuel (2019). "Preparation of 5-(Triisopropylalkynyl) dibenzo[b,d]thiophenium triflate". Organic Syntheses 96: 258–276. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.096.0258.
 |

