Chemistry:Amiphenazole
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
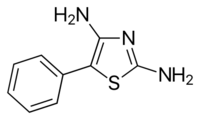
| Formula | C9H9N3S |
| Molar mass | 191.25 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Amiphenazole (Daptazile) is a respiratory stimulant traditionally used as an antidote for barbiturate or opiate overdose, usually in combination with bemegride,[1][2] as well as poisoning from other sedative drugs[3][4] and treatment of respiratory failure from other causes.[5] It was considered particularly useful as it could counteract the sedation and respiratory depression produced by morphine but with less effect on analgesia.[6][7] It is still rarely used in medicine in some countries, although it has largely been replaced by more effective respiratory stimulants such as doxapram and specific opioid antagonists such as naloxone.[8][9]
References
- ↑ "Barbiturate poisoning treated with amiphenazole and bemegride". British Medical Journal 2 (5001): 1099–101. November 1956. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5001.1099. PMID 13364395.
- ↑ "Massive doses of bemegride and amiphenazole in treatment of barbiturate poisoning". British Medical Journal 1 (5073): 757–8. March 1958. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5073.757. PMID 13510792.
- ↑ "Treatment of acute primidone poisoning with bemegride and amiphenazole". British Medical Journal 2 (5042): 451–2. August 1957. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5042.451. PMID 13446511.
- ↑ "Treatment of glutethimide poisoning with bemegride and amiphenazole". Lancet 272 (6965): 407–9. February 1957. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(57)90466-x. PMID 13407028.
- ↑ "Use of amiphenazole in respiratory failure". British Medical Journal 1 (5273): 223–6. January 1962. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5273.223. PMID 14465883.
- ↑ "Further experience with amiphenazole and morphine in intractable pain". British Medical Journal 1 (4959): 142–4. January 1956. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.4959.142. PMID 13276651.
- ↑ "Amiphenazole and morphine in production of analgesia". British Medical Journal 2 (5092): 366–8. August 1958. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5092.366. PMID 13560868.
- ↑ "Antagonists of morphine-induced respiratory depression. A study in postoperative patients". Anaesthesia 35 (1): 17–21. January 1980. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb03714.x. PMID 6994518.
- ↑ "The cognitive and psychomotor effects of opioid drugs in cancer pain management". Cancer Surveys 21: 67–84. 1994. PMID 8565000.
 |

