Chemistry:Glucosone
From HandWiki
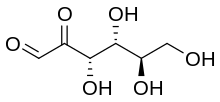 Skeletal formula of d-Glucosone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
d-arabino-Hexos-2-ulose[1]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3S,4R,5R)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxy-2-oxohexanal | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| MeSH | glucosone |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O6 | |
| Molar mass | 178.140 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Short description: Reactive carbonyl compound
Glucosone is a reactive carbonyl compound that can be produced by an Amadori rearrangement of a derivative of glucose. It is a dicarbonyl intermediate of the Maillard reaction whose production is higher under oxidative versus non-oxidative conditions.[2]
References
- ↑ McNaught, Alan D. (1996). "Nomenclature of Carbohydrates". International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry and International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (Great Britain) 68 (10): 1929. https://publications.iupac.org/pac/1996/pdf/6810x1919.pdf. Retrieved December 22, 2023.
- ↑ Nemet, I; Strauch, CM; Monnier, VM (2011). "Favored and disfavored pathways of protein crosslinking by glucose: glucose lysine dimer (GLUCOLD) and crossline versus glucosepane". Amino Acids 40 (1): 167–81. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0631-2. PMID 20607325.
 |

