Chemistry:3-Bromopyridine
From HandWiki
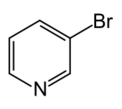
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Bromopyridine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 105880 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H4BrN | |||
| Molar mass | 157.998 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.640 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −27 | ||
| Boiling point | 173 °C (343 °F; 446 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H226, H301, H302, H311, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+310, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P361 | |||
| Flash point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
3-Chloropyridine 2-Bromopyridine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
3-Bromopyridine is an isomer of bromopyridine with the formula C5H4BrN. It is a colorless liquid that is mainly used as a building block in organic synthesis.[1][2]
It participates as a substrate in many reactions associated with aryl halides, e.g., the Heck reaction[3] and Buchwald-Hartwig coupling.[4]
References
- ↑ Li, Wenjie; Nelson, Dorian P.; Jensen, Mark S.; Hoerrner, R. Scott; Cai, Dongwei; Larsen, Robert D. (2005). "Synthesis of 3-Pyridylboronic Acid and ITS Pinacol Ester. Application of 3-Pyridylboronic Acid in Suzuki Coupling to Prepare 3-Pyridin-3-Ylquinoline". Organic Syntheses 81: 89. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.081.0089.
- ↑ Shimizu, Shinkichi; Watanabe, Nanao; Kataoka, Toshiaki; Shoji, Takayuki; Abe, Nobuyuki; Morishita, Sinji; Ichimura, Hisao (2007). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399.
- ↑ Heck, Richard F. (1979). "Palladium-catalyzed reactions of organic halides with olefins". Accounts of Chemical Research 12 (4): 146–151. doi:10.1021/ar50136a006.
- ↑ Zhang, Hui; Cai, Qian; Ma, Dawei (2005). "Amino Acid Promoted CuI-Catalyzed C−N Bond Formation between Aryl Halides and Amines or N-Containing Heterocycles". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 70 (13): 5164–5173. doi:10.1021/jo0504464. PMID 15960520.
 |