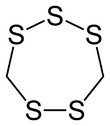
Chemistry:Lenthionine
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2,3,5,6-Pentathiepane | |||
| Other names
1,2,3,5,6-Pentathiacycloheptane
1,4-Dicarbacycloheptasulfane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4S5 | |||
| Molar mass | 188.35 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.549 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 60.5 °C (140.9 °F; 333.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 287 °C (549 °F; 560 K)[1] | ||
| 532.7 mg/L[1] | |||
| log P | 4.238[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Lenthionine is a cyclic organosulfur compound found in shiitake mushrooms, onions, and garlic, and it is partly responsible for their flavor.[2] The mechanism of its formation is unclear, but it likely involves the enzyme C–S lyase.[citation needed]
Preparation
Lenthionine has been isolated from mushrooms by submerging them in water and allowing them to set overnight. The mushrooms were then centrifuged, and dissolved in chloroform, which was later evaporated to form a yellow oil layer. Chromatography was then used to isolate the lenthionine.[3]
Lenthionine has been prepared in situ bubbling hydrogen sulfide gas through a solution of sulfur and sodium sulfide until the pH reached 8. Then, the solution had a large amount of dichloromethane added, and it was stirred at room temperature until an organic layer formed, which contained the lenthionine.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Showing metabocard for Lenthionine (HMDB0031258)". March 23, 2022. https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0031258.
- ↑ Block, Eric; Deorazio, Russell (1994). "Chemistry in a salad bowl: Comparative organosulfur chemistry of garlic, onion and shiitake mushrooms". Pure Appl. Chem. 66 (10–11): 2205–2206. doi:10.1351/pac199466102205. http://www.iupac.org/publications/pac/1994/pdf/6610x2205.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Morita, Katsura; Kobayashi, Shigeru (1967). "Isolation, Structure, and Synthesis of Lenthionine and Its Analogs." (in en). Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 15 (7): 988–993. doi:10.1248/cpb.15.988. ISSN 0009-2363. PMID 5625860. http://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/cpb1958/15/7/15_7_988/_article.
 |