Chemistry:Acetozone
From HandWiki
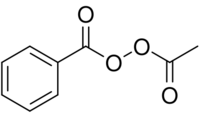
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetic benzoic peroxyanhydride | |
| Other names
Acetyl benzoyl peroxide; Benzoyl acetyl peroxide; Benzozone; Acetyl benzenecarboperoxoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 180.159 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid[1] |
| Melting point | 36–37 °C (97–99 °F; 309–310 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 130 °C (266 °F; 403 K)[2] (19 mmHg) |
| Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, ether, and oils[2] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Acetozone is an organic peroxide that is a strong oxidant.[1]
In the early 20th century, it found use as a surgical antiseptic[3] and for the treatment of typhoid fever.[4]
It has also been used as a bleaching agent for flour.[2][5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Acetozone". Oxford Dictionaries. https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/acetozone.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Merck Index (12th ed.). p. 15. 78.
- ↑ Gore-Gillon, G; Hewlett, R. T (1917). "Acetozone As a General Surgical Antiseptic". British Medical Journal 2 (2955): 209–10. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.2955.209. PMID 20768694.
- ↑ Humiston, RAY (1906). "Acetozone in Typhoid Fever". JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association (20): 1651. doi:10.1001/jama.1906.25210200047002. https://zenodo.org/record/1423362.
- ↑ "Acetyl benzoyl peroxide". Hazardous Substance Fact Sheets. New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. http://www.nj.gov/health/eoh/rtkweb/documents/fs/0011.pdf.
 |

