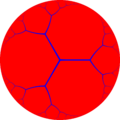
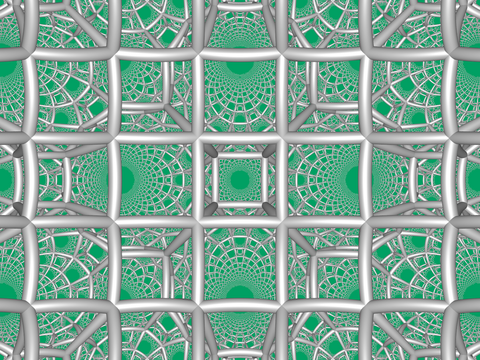
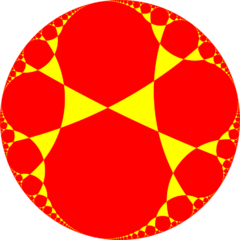
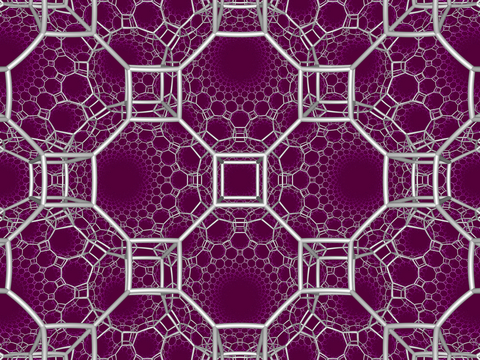
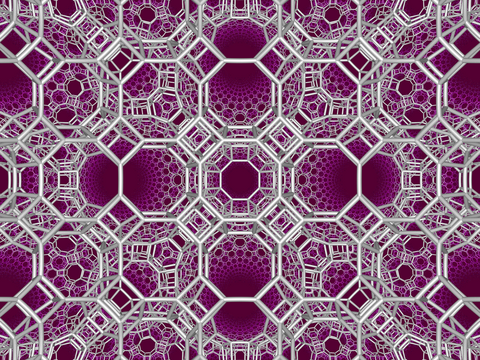
Square tiling honeycomb
| Square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | Hyperbolic regular honeycomb Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | {4,4,3} r{4,4,4} {41,1,1} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | {4,4} |
| Faces | square {4} |
| Edge figure | triangle {3} |
| Vertex figure | 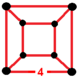 cube, {4,3} |
| Dual | Order-4 octahedral honeycomb |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{N}_3 }[/math], [43] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{M}_3 }[/math], [41,1,1] |
| Properties | Regular |
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the square tiling honeycomb is one of 11 paracompact regular honeycombs. It is called paracompact because it has infinite cells, whose vertices exist on horospheres and converge to a single ideal point at infinity. Given by Schläfli symbol {4,4,3}, it has three square tilings, {4,4}, around each edge, and six square tilings around each vertex, in a cubic {4,3} vertex figure.[1]
A geometric honeycomb is a space-filling of polyhedral or higher-dimensional cells, so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical tiling or tessellation in any number of dimensions.
Honeycombs are usually constructed in ordinary Euclidean ("flat") space, like the convex uniform honeycombs. They may also be constructed in non-Euclidean spaces, such as hyperbolic uniform honeycombs. Any finite uniform polytope can be projected to its circumsphere to form a uniform honeycomb in spherical space.
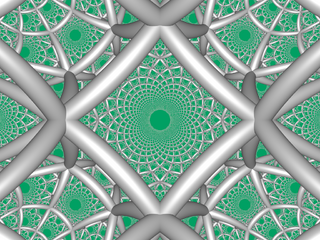
Rectified order-4 square tiling
It is also seen as a rectified order-4 square tiling honeycomb, r{4,4,4}:
| {4,4,4} | r{4,4,4} = {4,4,3} |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination = Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
 |
|
Symmetry
The square tiling honeycomb has three reflective symmetry constructions:
as a regular honeycomb, a half symmetry construction
↔
, and lastly a construction with three types (colors) of checkered square tilings
↔
. It also contains an index 6 subgroup [4,4,3*] ↔ [41,1,1], and a radial subgroup [4,(4,3)*] of index 48, with a right dihedral-angled octahedral fundamental domain, and four pairs of ultraparallel mirrors:
. This honeycomb contains
that tile 2-hypercycle surfaces, which are similar to the paracompact order-3 apeirogonal tiling
:
Related polytopes and honeycombs
The square tiling honeycomb is a regular hyperbolic honeycomb in 3-space. It is one of eleven regular paracompact honeycombs.
There are fifteen uniform honeycombs in the [4,4,3] Coxeter group family, including this regular form, and its dual, the order-4 octahedral honeycomb, {3,4,4}.
The square tiling honeycomb is part of the order-4 square tiling honeycomb family, as it can be seen as a rectified order-4 square tiling honeycomb.
It is related to the 24-cell, {3,4,3}, which also has a cubic vertex figure. It is also part of a sequence of honeycombs with square tiling cells:
Rectified square tiling honeycomb
| Rectified square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb Semiregular honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | r{4,4,3} or t1{4,4,3} 2r{3,41,1} r{41,1,1} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | {4,3} r{4,4} |
| Faces | square {4} |
| Vertex figure | 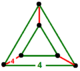 triangular prism |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{O}_3 }[/math], [3,41,1] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{M}_3 }[/math], [41,1,1] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive |
The rectified square tiling honeycomb, t1{4,4,3},
has cube and square tiling facets, with a triangular prism vertex figure.
It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic uniform triapeirogonal tiling, r{∞,3}, with triangle and apeirogonal faces.
Truncated square tiling honeycomb
| Truncated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | t{4,4,3} or t0,1{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | {4,3} t{4,4} |
| Faces | square {4} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure | 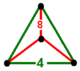 triangular pyramid |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{N}_3 }[/math], [43] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{M}_3 }[/math], [41,1,1] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The truncated square tiling honeycomb, t{4,4,3},
has cube and truncated square tiling facets, with a triangular pyramid vertex figure. It is the same as the cantitruncated order-4 square tiling honeycomb, tr{4,4,4},
.
Bitruncated square tiling honeycomb
| Bitruncated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | 2t{4,4,3} or t1,2{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | t{4,3} t{4,4} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure | 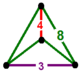 digonal disphenoid |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The bitruncated square tiling honeycomb, 2t{4,4,3},
has truncated cube and truncated square tiling facets, with a digonal disphenoid vertex figure.
Cantellated square tiling honeycomb
| Cantellated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | rr{4,4,3} or t0,2{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | r{4,3} rr{4,4}40px {}x{3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} |
| Vertex figure | 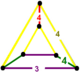 isosceles triangular prism |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The cantellated square tiling honeycomb, rr{4,4,3},
has cuboctahedron, square tiling, and triangular prism facets, with an isosceles triangular prism vertex figure.
Cantitruncated square tiling honeycomb
| Cantitruncated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | tr{4,4,3} or t0,1,2{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | t{4,3} tr{4,4}40px {}x{3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure | 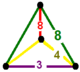 isosceles triangular pyramid |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The cantitruncated square tiling honeycomb, tr{4,4,3},
has truncated cube, truncated square tiling, and triangular prism facets, with an isosceles triangular pyramid vertex figure.
Runcinated square tiling honeycomb
| Runcinated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,3{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | {3,4} {4,4}40px {}x{4} 40px {}x{3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} |
| Vertex figure | 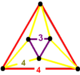 irregular triangular antiprism |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The runcinated square tiling honeycomb, t0,3{4,4,3},
has octahedron, triangular prism, cube, and square tiling facets, with an irregular triangular antiprism vertex figure.
Runcitruncated square tiling honeycomb
| Runcitruncated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | t0,1,3{4,4,3} s2,3{3,4,4} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | rr{4,3} t{4,4}40px {}x{3} 40px {}x{8} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure | 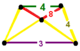 isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The runcitruncated square tiling honeycomb, t0,1,3{4,4,3},
has rhombicuboctahedron, octagonal prism, triangular prism and truncated square tiling facets, with an isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid vertex figure.
Runcicantellated square tiling honeycomb
The runcicantellated square tiling honeycomb is the same as the runcitruncated order-4 octahedral honeycomb.
Omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb
| Omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,1,2,3{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | tr{4,4} {}x{6} 40px {}x{8} 40px tr{4,3} |
| Faces | square {4} hexagon {6} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure | 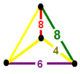 irregular tetrahedron |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{R}_3 }[/math], [4,4,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb, t0,1,2,3{4,4,3},
has truncated square tiling, truncated cuboctahedron, hexagonal prism, and octagonal prism facets, with an irregular tetrahedron vertex figure.
Omnisnub square tiling honeycomb
| Omnisnub square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | h(t0,1,2,3{4,4,3}) |
| Coxeter diagram | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | sr{4,4} sr{2,3} 40px sr{2,4} 40px sr{4,3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} |
| Vertex figure | irregular tetrahedron |
| Coxeter group | [4,4,3]+ |
| Properties | Non-uniform, vertex-transitive |
The alternated omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb (or omnisnub square tiling honeycomb), h(t0,1,2,3{4,4,3}),
has snub square tiling, snub cube, triangular antiprism, square antiprism, and tetrahedron cells, with an irregular tetrahedron vertex figure.
Alternated square tiling honeycomb
| Alternated square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb Semiregular honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | h{4,4,3} hr{4,4,4} {(4,3,3,4)} h{41,1,1} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | {4,4} {4,3} |
| Faces | square {4} |
| Vertex figure | cuboctahedron |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{O}_3 }[/math], [3,41,1] [4,1+,4,4] ↔ [∞,4,4,∞] [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{BR}_3 }[/math], [(4,4,3,3)] [1+,41,1,1] ↔ [∞[6]] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, quasiregular |
The alternated square tiling honeycomb, h{4,4,3},
is a quasiregular paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It has cube and square tiling facets in a cuboctahedron vertex figure.
Cantic square tiling honeycomb
| Cantic square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | h2{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | t{4,4} r{4,3} 40px t{4,3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure |  rectangular pyramid |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{O}_3 }[/math], [3,41,1] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The cantic square tiling honeycomb, h2{4,4,3},
is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It has truncated square tiling, truncated cube, and cuboctahedron facets, with a rectangular pyramid vertex figure.
Runcic square tiling honeycomb
| Runcic square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | h3{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | {4,4} r{4,3} 40px {3,4} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} |
| Vertex figure | 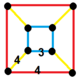 square frustum |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{O}_3 }[/math], [3,41,1] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The runcic square tiling honeycomb, h3{4,4,3},
is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It has square tiling, rhombicuboctahedron, and octahedron facets in a square frustum vertex figure.
Runcicantic square tiling honeycomb
| Runcicantic square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | h2,3{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | t{4,4} tr{4,3} 40px t{3,4} |
| Faces | square {4} hexagon {6} octagon {8} |
| Vertex figure | 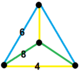 mirrored sphenoid |
| Coxeter groups | [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{O}_3 }[/math], [3,41,1] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The runcicantic square tiling honeycomb, h2,3{4,4,3},
↔
, is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It has truncated square tiling, truncated cuboctahedron, and truncated octahedron facets in a mirrored sphenoid vertex figure.
Alternated rectified square tiling honeycomb
| Alternated rectified square tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | hr{4,4,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination ↔ Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
|
| Cells | |
| Faces | |
| Vertex figure | triangular prism |
| Coxeter groups | [4,1+,4,3] = [∞,3,3,∞] |
| Properties | Nonsimplectic, vertex-transitive |
The alternated rectified square tiling honeycomb is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space.
See also
- Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
- Regular tessellations of hyperbolic 3-space
- Paracompact uniform honeycombs
References
- ↑ Coxeter The Beauty of Geometry, 1999, Chapter 10, Table III
- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. ISBN:0-486-61480-8. (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
- The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays (1999), Dover Publications, LCCN 99-35678, ISBN:0-486-40919-8 (Chapter 10, Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space) Table III
- Jeffrey R. Weeks The Shape of Space, 2nd edition ISBN:0-8247-0709-5 (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I, II)
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966
- N.W. Johnson: Geometries and Transformations, (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups
- Norman W. Johnson and Asia Ivic Weiss Quadratic Integers and Coxeter Groups PDF Can. J. Math. Vol. 51 (6), 1999 pp. 1307–1336
 |