Chemistry:Momordenol
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
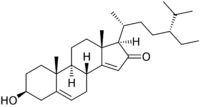
3β-Hydroxystigmasta-5,14-dien-16-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3bR,7S,9aR,9bS,11aR)-1-[(2R,5R)-5-Ethyl-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-7-hydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-1,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-dodecahydro-2H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H46O2 | |
| Molar mass | 426.685 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Momordenol (3β-hydroxy-stigmasta-5,14-dien-16-one) is a natural chemical compound, a sterol found in the fresh fruit of the bitter melon (Momordica charantia).[1]
The compound is soluble in ethyl acetate and methanol but not in pure chloroform or petrol. It crystallizes as fine needles that melt at 160–161 °C. It was isolated in 1997 by S. Begum and others.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Begum, Sabira; Ahmed, Mansoor; Siddiqui, Bina S.; Khan, Abdullah; Saify, Zafar S.; Arif, Mohammed (1997). "Triterpenes, A sterol and a monocyclic alcohol from Momordica charantia". Phytochemistry 44 (7): 1313–1320. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(96)00615-2. Bibcode: 1997PChem..44.1313B.
 |

