Astronomy:Eta Phoenicis
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation Phoenix
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
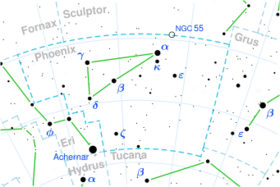
| Constellation | Phoenix |
| Right ascension | 00h 43m 21.23841s[1] |
| Declination | −57° 27′ 47.0073″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.36[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0IV[2] |
| U−B color index | -0.02[3] |
| B−V color index | +0.00[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +7.70[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -5.07[1] mas/yr Dec.: +16.51[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 13.24 ± 0.34[1] mas |
| Distance | 246 ± 6 ly (76 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | -0.03[2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.93[5] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 120[5] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.85[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 9,822[6] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.00[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 124[5] km/s |
| Other designations | |
CCDM J00434-5728A, FK5 23, GC 866, HIP 3405, HR 191, HD 4150, SAO 232162, WDS J00434-5728A | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Eta Phoenicis (η Phe) is a class A0IV[2] (white subgiant) star in the constellation Phoenix. Its apparent magnitude is 4.36[2] and it is approximately 246 light years away based on parallax.[1]
Eta Phoenicis has two reported companions; in addition to a distant secondary, B, at magnitude 11.5 and separation 20", the primary has a reported companion Ab with an estimated separation of 6.8 AU, a period slightly longer than 10 years, a magnitude of 8.5, and a spectral type around G5V.[8][9] The primary is surrounded by an orbiting debris disk.[10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mallama, A. (2014). "Sloan Magnitudes for the Brightest Stars". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers 42 (2): 443. Bibcode: 2014JAVSO..42..443M.Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 537: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015). "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal 804 (2): 146. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804..146D. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2012). "Dependence of kinematics on the age of stars in the solar neighborhood". Astronomy Letters 38 (12): 771–782. doi:10.1134/S1063773712120031. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..771G. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466. doi:10.1086/323920. Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ Marion, L.; Absil, O.; Ertel, S.; Le Bouquin, J.-B.; Augereau, J.-C.; Blind, N.; Defrère, D.; Lebreton, J. et al. (2014). "Searching for faint companions with VLTI/PIONIER". Astronomy & Astrophysics 570: A127. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201424780. Bibcode: 2014A&A...570A.127M.
- ↑ Marion, L. et al. (October 2014), "Searching for faint companions with VLTI/PIONIER. II. 92 main sequence stars from the Exozodi survey", Astronomy & Astrophysics 570: 12, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201424780, A127, Bibcode: 2014A&A...570A.127M.
 |