Astronomy:V701 Coronae Australis
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox (celestial coordinates) | |
|---|---|
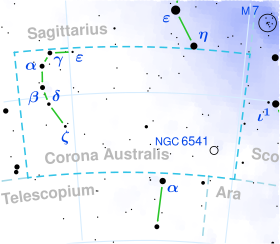
| Constellation | Corona Australis |
| Right ascension | 19h 03m 17.69619s[1] |
| Declination | −38° 15′ 11.3335″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.69 to 5.73[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F2 III/IV[3] or F0 IIIn[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.32[5] |
| Variable type | δ Scuti[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 4±7.4[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +12.794[1] mas/yr Dec.: +14.271[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 15.2952 ± 0.0559[1] mas |
| Distance | 213.2 ± 0.8 ly (65.4 ± 0.2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +1.55[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.83+0.07−0.06[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.85±0.14[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 17.5+0.2−0.1[1] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.75±0.12[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,046±240[11] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.21[12] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 265[13] km/s |
| Age | 1.25[11] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
V701 Coronae Australis (HD 176723; HR 7197; 40 G. Coronae Australis), or simply V701 CrA, is a solitary,[15] yellowish-white hued variable star located in the southern constellation Corona Australis. It has an average apparent magnitude of 5.72,[16] making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 213 light-years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements,[1] and it is currently receding with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 4 km/s.[6] At its current distance, V701 CrA's brightness is diminished by a quarter of a magnitude due to extinction[17] and it has an absolute magnitude of +1.55.[7]
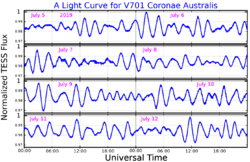
The object was first suspected to be variable in 1990. The variations matched that of δ Scuti variables.[19] Three years later, it was confirmed to be variable and was given the variable star designation V701 Coronae Australis.[20] It ranges from magnitude 5.69 to 5.73[2] within 3.25 hours.[21]
V701 CrA has a stellar classification of F2 III/IV,[3] indicating that it is an evolved F-type star with the blended luminosity class of a subgiant and giant star. It has also been given a class of F0 IIIn,[4] indicating broad or nebulous absorption lines due to rapid rotation. It has 1.83 times the mass of the Sun[8] and a slightly enlarged radius of 2.85 R☉.[9] It radiates 17.5 times the luminosity of the Sun[1] from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 7,046 K.[11] The star spins rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 265 km/s,[13] which causes it to have an equatorial bulge that is 26% larger than the poles.[22] It is metal deficient with an iron abundance 62% that of the Sun ([Fe/H] = −0.21)[12] and it is estimated to be 1.25 billion years old.[11] V701 CrA was considered to be a chemically peculiar star and was given a class of FpSr. Its peculiarity is now considered to be doubtful.[23]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Samus’, N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (January 2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. ISSN 1063-7729. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Houk, N. (1982). Michigan Catalogue of Two-dimensional Spectral Types for the HD stars. Declinations −40° to −26°. 3. Bibcode: 1982mcts.book.....H.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Evans, D. S.; Laing, J. D.; Menzies, A.; Stoy, R. H. (1964). "Fundamental data for southern stars (fifth list)". Royal Greenwich Observatory Bulletins 85: 207–224. Bibcode: 1964RGOB...85..207E.
- ↑ Johnson, H. L.; Mitchell, R. I.; Iriarte, B.; Wisniewski, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL Photometry of the Bright Stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory 4: 99–110. Bibcode: 1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Holmberg, J.; Nordström, B.; Andersen, J. (6 August 2007). "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the Solar neighbourhood II". Astronomy & Astrophysics 475 (2): 519–537. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077221. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2007A&A...475..519H.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331–346. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. ISSN 1063-7737. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Nordström, B.; Mayor, M.; Andersen, J.; Holmberg, J.; Pont, F.; Jørgensen, B. R.; Olsen, E. H.; Udry, S. et al. (16 April 2004). "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the Solar neighbourhood". Astronomy & Astrophysics 418 (3): 989–1019. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20035959. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2004A&A...418..989N.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kervella, P.; Thévenin, F.; Di Folco, E.; Ségransan, D. (October 2004). "The angular sizes of dwarf stars and subgiants". Astronomy & Astrophysics 426 (1): 297–307. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20035930. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2004A&A...426..297K.
- ↑ Allende Prieto, C.; Lambert, D. L. (December 1999). "Fundamental parameters of nearby stars from the comparison with evolutionary calculations: masses, radii and effective temperatures". Astronomy and Astrophysics 352: 555–562. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 1999A&A...352..555A.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (12 May 2015). "The Ages of Early-type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal 804 (2): 146. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804..146D.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Casagrande, L.; Schönrich, R.; Asplund, M.; Cassisi, S.; Ramírez, I.; Meléndez, J.; Bensby, T.; Feltzing, S. (26 May 2011). "New constraints on the chemical evolution of the solar neighbourhood and Galactic disc(s): Improved astrophysical parameters for the Geneva-Copenhagen Survey⋆". Astronomy & Astrophysics 530: A138. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201016276. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2011A&A...530A.138C.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Huang, Su-Shu (September 1953). "A Statistical Study of the Rotation of the Stars.". The Astrophysical Journal 118: 285. doi:10.1086/145751. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 1953ApJ...118..285H.
- ↑ "V* V701 Coronae Australis". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=V%2A+V701+Coronae+Australis.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (11 September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P. et al. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 355: L27–L30. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ↑ Gontcharov, George A.; Mosenkov, Aleksandr V. (28 September 2017). "Verifying reddening and extinction for Gaia DR1 TGAS main sequence stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 472 (4): 3805–3820. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx2219. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2017MNRAS.472.3805G.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ Lampens, P.; Rufener, F. (April 1990). "Study of delta Scuti stars in the Geneva photometric system. I. New photometric data and period analysis for nine stars.". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 83: 145–182. ISSN 0365-0138. Bibcode: 1990A&AS...83..145L.
- ↑ Kazarovets, E. V.; Samus, N. N.; Goranskij, V. P. (February 1993). "The 71st Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3840: 1. ISSN 0374-0676. Bibcode: 1993IBVS.3840....1K.
- ↑ Rodriguez, E.; Lopez de Coca, P.; Rolland, A.; Garrido, R.; Costa, V. (July 1994). "δ Scuti stars: a new revised list". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 106: 21–28. ISSN 0365-0138. Bibcode: 1994A&AS..106...21R.
- ↑ van Belle, Gerard T. (14 March 2012). "Interferometric observations of rapidly rotating stars". The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review 20 (1): 51. doi:10.1007/s00159-012-0051-2. ISSN 0935-4956. Bibcode: 2012A&ARv..20...51V.
- ↑ Renson, P.; Manfroid, J. (19 March 2009). "Catalogue of Ap, HgMn and Am stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 498 (3): 961–966. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810788. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2009A&A...498..961R.
<ref> tag with name "Gould1879" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
 |