Software:Nemo (file manager)
From HandWiki
Short description: File manager
 Screenshot of Nemo v4.0.6 | |
| Developer(s) | Linux Mint |
|---|---|
| Initial release | September 2012 |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Unix-like |
| Platform | Cinnamon |
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Type | File manager |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
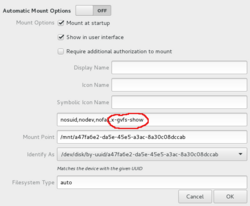
Whether Nemo shows a mount or not, is determined by the option
x-gvfs-show for the gvfs-udisks2-volume-monitor process.[1] Screenshot of GNOME Disks.Nemo is a free and open-source software and official file manager of the Cinnamon desktop environment. It is a fork of GNOME Files (formerly named Nautilus).
History
Nemo version 1.0.0 was released in July 2012 along with version 1.6 of the Cinnamon,[2][better source needed] reaching version 1.1.2 in November 2012.[3] It started as a fork of the GNOME file manager Nautilus v3.4[4][5][6][better source needed] after the developers of the operating system Linux Mint considered that "Nautilus 3.6 is a catastrophe".[7][8][9] Developer Gwendal Le Bihan named the project "nemo" after Jules Verne's famous character Captain Nemo, who is the captain of the Nautilus.[9]
Features
Nemo v1.0.0 had the following features as described by the developers:[9]
- Uses GVfs and GIO
- All the features Nautilus 3.4 had and which are missing in Nautilus 3.6 (all desktop icons, compact view, etc.)
- Open in terminal (integral part of Nemo)
- Open as root (integral part of Nemo)
- File operations progress information (when copying or moving files, one can see the percentage and information about the operation on the window title and so also in the window list)
- Proper GTK bookmarks management
- Full navigation options (back, forward, up, refresh)
- Ability to toggle between the path entry and the path breadcrumb widgets
- Many more configuration options
- Ability to SSH into remote servers
- Native support for FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and MTP (Media Transfer Protocol)
See also
References
- ↑ "udisks2/what-is-shown.txt". https://git.gnome.org/browse/gvfs/tree/monitor/udisks2/what-is-shown.txt..
- ↑ NEMO: THE LINUX MINT TEAM FORKS NAUTILUS, Web UPD8, Aug 2012
- ↑ "Cinnamon 1.6.7, Nemo 1.1.2". November 14, 2012. http://cinnamon.linuxmint.com/?p=252.
- ↑ Linux Mint developers work on GNOME file manager fork, Zdnet, Aug 2012
- ↑ NEMO FILE MANAGER FOR UBUNTU OR LINUX MINT VIA PPA, Technology Linux & Windows, Dec 2012
- ↑ Linux Mint Team Forks Nautilus, Brings Out Nemo, Muktware, 2012
- ↑ Linux Mint Explain Nautilus Fork, Call New Version a "Catastrophe", OMG Ubuntu, Sep 2012
- ↑ Linux Mint founder calls Nautilus 3.6 "a catastrophe", H Online, Sep 2012
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 "Introducing Nemo". September 4, 2012. http://cinnamon.linuxmint.com/?p=198.
External links
- Introducing Nemo (2012)
- Install Nemo File Manager in Ubuntu (2012)
 |


