Biology:Multicrustacea
| Multicrustacea | |
|---|---|

| |
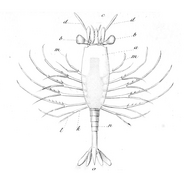
| From left to right and from top to bottom: Grapsus grapsus (a crab), Homarus gammarus (a lobster), Procambarus clarkii (a crayfish), Lysmata amboinensis (a shrimp), Euphausia superba (a krill), Hemilepistus reaumuri (a woodlouse), Calanoida (a copepod), and Lepas anatifera (a barnacle) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Clade: | Pancrustacea |
| Superclass: | Multicrustacea Regier, Shultz, Zwick, Hussey, Ball, Wetzer, Martin & Cunningham, 2010 |
| Classes | |
| |
The clade[1][2][3][4] Multicrustacea constitutes the largest superclass of crustaceans, containing approximately four-fifths of all described crustacean species, including crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, barnacles, copepods, amphipods, mantis shrimp and others. The largest branch of multicrustacea is the class Malacostraca (see below).
Classification
Superclass Multicrustacea Regier, Shultz, Zwick, Hussey, Ball, Wetzer, Martin & Cunningham, 2010 [5]
- †Family Priscansermarinidae Newman, 2004
- Class Copepoda Milne-Edwards, 1840 - Copepods [lower-alpha 1]
- Infra-class Neocopepoda Huys & Boxshall, 1991
- Super-order Gymnoplea Giesbrecht, 1882
- Order Calanoida Sars GO, 1903
- Super-order Podoplea Giesbrecht, 1882
- Order Cyclopoida Burmeister, 1834
- Order Gelyelloida Huys, 1988
- Order Harpacticoida G. O. Sars, 1903
- Order Misophrioida Gurney, 1933
- Order Monstrilloida Sars, 1901
- Order Mormonilloida Boxshall,1979
- Order Polyarthra Lang, 1944 (=Canuelloida Khodami, Vaun MacArthur, Blanco-Bercial & Martinez Arbizu, 2017 )
- Order Siphonostomatoida Thorell, 1859
- Super-order Gymnoplea Giesbrecht, 1882
- Infra-class Progymnoplea Lang, 1948
- Order Platycopioida Fosshagen, 1985
- Infra-class Neocopepoda Huys & Boxshall, 1991
- Class Thecostraca Gruvel, 1905[7][lower-alpha 1]
- Subclass Ascothoracida Lacaze-Duthiers, 1880
- Order Dendrogastrida Grygier, 1987
- Order Laurida Grygier, 1987
- Subclass Cirripedia Burmeister, 1834
- Infraclass Acrothoracica Gruvel, 1905
- Order Cryptophialida Kolbasov, Newman & Hoeg, 2009
- Order Lithoglyptida Kolbasov, Newman & Hoeg, 2009
- Infraclass Rhizocephala Müller, 1862
- Infraclass Thoracica Darwin, 1854
- Superorder Phosphatothoracica Gale, 2019
- Order Iblomorpha Buckeridge & Newman, 2006
- †Order Eolepadomorpha Chan et al., 2021
- Superorder Thoracicalcarea Gale, 2015
- Order Balanomorpha Pilsbry, 1916
- Order Calanticomorpha Chan et al., 2021
- Order Pollicipedomorpha Chan et al., 2021
- Order Scalpellomorpha Buckeridge & Newman, 2006
- Order Verrucomorpha Pilsbry, 1916
- †Order Archaeolepadomorpha Chan et al., 2021
- †Order Brachylepadomorpha Withers, 1923
- Superorder Phosphatothoracica Gale, 2019
- Infraclass Acrothoracica Gruvel, 1905
- Subclass Facetotecta Grygier, 1985
- Subclass Ascothoracida Lacaze-Duthiers, 1880
- Class Tantulocarida Boxshall & Lincoln, 1983
- Family Basipodellidae Boxshall & Lincoln, 1983
- Family Cumoniscidae Nierstrasz & Brender à Brandis, 1923 (=Deoterthridae Boxshall & Lincoln, 1987)
- Family Doryphallophoridae Huys, 1991
- Family Microdajidae Boxshall & Lincoln, 1987
- Family Onceroxenidae Huys, 1991
- Class Malacostraca Latreille, 1802
- Subclass Eumalacostraca Grobben, 1892
- Superorder Eucarida Calman, 1904
- Order Decapoda Latreille, 1802 - crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns (includes former order Order Amphionidacea Williamson, 1973)
- Order Euphausiacea Dana, 1852 - krill
- Superorder Peracarida Calman, 1904
- Order Amphipoda Latreille, 1816 - amphipodes, gammares
- Order Bochusacea Gutu & Iliffe, 1998
- Order Cumacea Krøyer, 1846 - cumaceae
- Order Ingolfiellida Hansen, 1903
- Order Isopoda Latreille, 1817 - isopods (including clover)
- Order Lophogastrida Sars, 1870 - lophogastrides
- Order Mictacea Bowman, Garner, Hessler, Iliffe & Sanders, 1985 - mictacés
- Order Mysida Haworth, 1825 - mysidacés
- †Order Pygocephalomorpha
- Order Spelaeogriphacea Gordon, 1957 - spelaeogriphaceae
- Order Stygiomysida Tchindonova, 1981 - stygiomysides
- Order Tanaidacea Dana, 1849 - tanaidaceae
- Order Thermosbaenacea Monod, 1927 - thermosbaenaceae
- Superorder Syncarida Packard, 1879
- Order Anaspidacea Calman, 1904
- Order Bathynellacea Chappuis, 1915
- †Order Palaeocaridacea Brooks, 1962
- Superorder Eucarida Calman, 1904
- Subclass Hoplocarida Calman, 1904
- Order Stomatopoda Latreille, 1817 - shrimps-mantes
- Subclass Phyllocarida Packard, 1879
- †Order Archaeostraca Claus, 1888
- †Order Canadaspidida Novozhilov, 1960
- †Order Hoplostraca Schram, 1973
- †Order Hymenostraca Rolfe, 1969
- Order Leptostraca Claus, 1880
- †Genus Nothozoe Barrande, 1872
- Subclass Eumalacostraca Grobben, 1892
- Incertae sedis
- Order Cyclida
Notes:
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Class Hexanauplia Oakley, Wolfe, Lindgren & Zaharof, 2013 was proposed for copepods and thecopods, but not supported by subsequent studies.[6]
Fossil record
The earliest fossils representative of Multicrustacea are from the Cambrian.[8] However, the more specific timeline is uncertain. Some Cambrian fossils of uncertain taxonomic placement, such as those of Priscansermarinus, are nonetheless likely to be members of Multicrustacea.[citation needed]
Image gallery
Anew Lepas anatifera (Lepadiformes)
Balth Chthamalus stellatus (Sessilia)
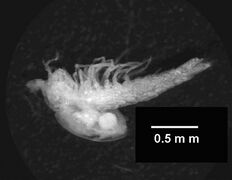
Amphionides reynaudii , the unique Amphionidacea known.
Crab Cancer bellianus (Eucarida)
Antarctic Krill Euphausia superba (Euphausiacea)
Atylus swammerdami (Amphipoda)
Diastylis bradyi (Cumacea)
Bathynomus doederleinii (Isopoda)
Mictocaris halope (Mictacea)
Tanaissus lilljeborgi (Tanaidacea)
Tethysbaena ophelicola (Thermosbaenacea)
Koonunga cursor (Anaspidacea)
Taxonomic references
- World Register of Marine Species : taxon Multicrustacea Regier Shultz Zwick Hussey, Ball, Wetzer, Martin & Cunningham, 2010 ( + class list + orders list)
- Tree of Life Web Project : Multicrustacea
- Animal Diversity Web : Multicrustacea[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- Catalog of Life : Multicrustacea
- IUCN : taxon Multicrustacea
Notes and references
- ↑ World Register of Marine Species, accessed 13 April 2016
- ↑ J. C. Regier; J. W. Shultz; R. E. Kambic (22 February 2005). "Pancrustacean phylogeny: hexapods are terrestrial crustaceans and maxillopods are not monophyletic". Proceedings of the Royal Society B 272 (1561): 395–401. doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2917. PMID 15734694.
- ↑ Jerome C. Regier; Jeffrey W. Shultz; Andreas Zwick; April Hussey; Bernard Ball; Regina Wetzer; Joel W. Martin; Clifford W. Cunningham (25 February 2010). "Arthropod relationships revealed by phylogenomic analysis of nuclear protein-coding sequences". Nature 463 (7284): 1079–1083. doi:10.1038/nature08742. PMID 20147900. Bibcode: 2010Natur.463.1079R.
- ↑ Bjoern M. von Reumont; Ronald A. Jenner; Matthew A. Wills; Emiliano Dell'Ampio; Günther Pass; Ingo Ebersberger; Benjamin Meyer; Stefan Koenemann et al. (March 2012). "Pancrustacean phylogeny in the light of new phylogenomic data: support for Remipedia as the possible sister group of Hexapoda". Molecular Biology and Evolution 29 (3): 1031–1045. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr270. PMID 22049065.
- ↑ Todd H. Oakley; Joanna M. Wolfe; Annie R. Lindgren; Alexander K. Zaharoff (January 2013). "Phylotranscriptomics to bring the understudied into the fold: monophyletic ostracoda, fossil placement, and pancrustacean phylogeny". Molecular Biology and Evolution 30 (1): 215–233. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss216. PMID 22977117.
- ↑ WoRMS. "Multicrustacea". http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=845959.
- ↑ WoRMS. "Hexanauplia". http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=889925.
- ↑ "World Register of Marine Species, Class Thecostraca". http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=22388.
- ↑ Collette, Joseph H.; Hagadorn, James W. (2010). "Early evolution of phyllocarid arthropods: phylogeny and systematics of Cambrian–Devonian archaeostracans". Journal of Paleontology 84 (5): 795–820. doi:10.1666/09-092.1. Bibcode: 2010JPal...84..795C.
Wikidata ☰ Q11937877 entry
 |