Biology:Baptanodon
| Baptanodon | |
|---|---|
| |
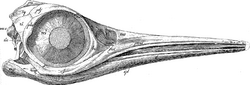
| Holotype skull of B. natans | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Ichthyosauria |
| Family: | †Ophthalmosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Ophthalmosaurinae |
| Genus: | †Baptanodon Marsh, 1880 |
| Type species | |
| †Baptanodon natans Marsh, 1880
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Baptanodon is an ichthyosaur of the Late Jurassic period (160-156 million years ago), named for its supposed lack of teeth (although teeth of this genus have since been discovered).[1] It had a graceful 3.5 m (11 ft) long dolphin-shaped body, and its jaws were well adapted for catching squid.[2] Major fossil finds of this genus have been recorded in North America. The type species, Sauranodon natans, was originally included under Sauranodon in 1879,[3] but this name was preoccupied.
Discovery and species
Baptanodon is a replacement name for Sauranodon applied to ichthyosaur material in 1879[3] and was moved to its own genus Baptanodon in 1880 when Sauranodon was found to be preoccupied.[4] Baptanodon was considered a junior synonym of Ophthalmosaurus by Maisch & Matzke (2000).[5] However, cladistic analyses published in the 2010s indicate that Baptanodon is not congeneric with Ophthalmosaurus icenicus.[6][7][8]
Classification
The cladogram below follows Fischer et al. 2012.[7]
| Thunnosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Palaeobiology
Fossils of Baptanodon have been found in the Oxfordian-age Sundance Formation of Wyoming, which also has yielded fossils of the cryptoclidids Tatenectes and Pantosaurus, and the pliosaurid Megalneusaurus.[4][10]
See also
- List of ichthyosaurs
- Timeline of ichthyosaur research
References
- ↑ Gilmore, C. W. (1902). "Discovery of teeth in Baptanodon, an ichthyosaurian from the Jurassic of Wyoming". Science 16 (414): 913–914. doi:10.1126/science.16.414.913. PMID 17756122. Bibcode: 1902Sci....16..913G. https://archive.org/details/jstor-1628588/page/n1/mode/2up.
- ↑ Massare, J.A.; Wahl, W.R.; Ross, M.; Connely, M.V. (2014). "Palaeoecology of the marine reptiles of the Redwater Shale Member of the Sundance Formation (Jurassic) of central Wyoming, USA". Geological Magazine 151 (1): 167–182. doi:10.1017/S0016756813000472.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 O. C. Marsh. 1879. A new order of extinct reptiles (Sauranodonta), from the Jurassic Formation of the Rocky Mountains. The American Journal of Science and Arts, series 3
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Marsh, O. C., 1880, Note on Sauranodon: American Journal of Science, 3rd series, v. 19, n. 4, p. 491.
- ↑ Maisch MW, Matzke AT. 2000. The Ichthyosauria. Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde, Serie B (Geologie und Paläontologie) 298: 1-159.
- ↑ Patrick S. Druckenmiller; Erin E. Maxwell (2010). "A new Lower Cretaceous (lower Albian) ichthyosaur genus from the Clearwater Formation, Alberta, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (8): 1037–1053. doi:10.1139/E10-028. Bibcode: 2010CaJES..47.1037D.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Valentin Fischer (2012). "New Ophthalmosaurid Ichthyosaurs from the European Lower Cretaceous Demonstrate Extensive Ichthyosaur Survival across the Jurassic–Cretaceous Boundary". PLOS ONE 7 (1): e29234. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029234. PMID 22235274. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...729234F.
- ↑ Ilaria Paparella; Erin E. Maxwell; Angelo Cipriani; Scilla Roncacè; Michael W. Caldwell (2017). "The first ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the Upper Jurassic of the Umbrian–Marchean Apennines (Marche, Central Italy)". Geological Magazine. 154 (4): 837–858. doi:10.1017/S0016756816000455.
- ↑ Arkhangel’sky, M. S., 1998, On the Ichthyosaurian Genus Platypterygius: Palaeontological Journal, v. 32, n. 6, p. 611-615.
- ↑ Marsh, O. C., 1895, The Reptilia of the Baptanodon Beds: American Journal of Science, 3rd series, v. 34., n. 299, p. 405-406.
Wikidata ☰ Q55604865 entry
 |

