Chemistry:Saracatinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
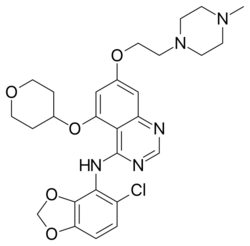
| Formula | C27H32ClN5O5 |
| Molar mass | 542.03 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Saracatinib (AZD-0530) is an experimental drug being developed by AstraZeneca. It acts as a dual kinase inhibitor, with selective actions as a Src inhibitor and a Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor.[1][2]
It was originally under development for the treatment of cancer, but while it appeared promising in animal studies and was well tolerated in humans, it failed to show sufficient efficacy in cancer patients and was ultimately not developed further for this application. However, saracatinib has subsequently been researched for other applications such as Alzheimer's disease. AZD0530 is an inhibitor of Src and Abl family kinases1. It has been developed as treatment for malignancies because these kinases play a role in tumor invasion and proliferation. However, the Src family kinases (SFKs) are highly expressed in brain and have major effects on synaptic plasticity2. Moreover, the investigators have recently shown that a specific SFK, namely Fyn, is aberrantly activated by specific conformations of the Amyloid Beta (Aß) peptide from Alzheimer's disease (AD). Genetic deletion of Fyn rescues AD deficits in preclinical models. This clinical trial will test the potential benefit of AZD0530 for Alzheimer's disease modification.[3][4][5][6] and schizophrenia.[7] It has furthermore been described that Saracatinib impairs maintenance of human T-cells Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by targeting the LCK tyrosine kinase in cells displaying high level of lipid rafts.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "N-(5-chloro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-7-[2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]-5- (tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yloxy)quinazolin-4-amine, a novel, highly selective, orally available, dual-specific c-Src/Abl kinase inhibitor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 49 (22): 6465–88. November 2006. doi:10.1021/jm060434q. PMID 17064066.
- ↑ "Novel dual Src/Abl inhibitors for hematologic and solid malignancies". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 19 (8): 931–45. August 2010. doi:10.1517/13543784.2010.499898. PMID 20557276.
- ↑ "A phase II study of saracatinib (AZD0530), a Src inhibitor, administered orally daily to patients with advanced thymic malignancies". Lung Cancer 89 (1): 57–60. July 2015. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.04.008. PMID 26009269.
- ↑ "Phase II study of saracatinib (AZD0530) in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer". Investigational New Drugs 33 (4): 977–84. August 2015. doi:10.1007/s10637-015-0257-z. PMID 26062928.
- ↑ "Fyn inhibition rescues established memory and synapse loss in Alzheimer mice". Annals of Neurology 77 (6): 953–71. June 2015. doi:10.1002/ana.24394. PMID 25707991.
- ↑ "A phase Ib multiple ascending dose study of the safety, tolerability, and central nervous system availability of AZD0530 (saracatinib) in Alzheimer's disease". Alzheimer's Research & Therapy 7 (1): 35. 2015. doi:10.1186/s13195-015-0119-0. PMID 25874001.
- ↑ "MICA: SRC inhibitors as potential antipsychotics: human testing with psilocybin.". Imperial College London. 27 July 2015. http://gtr.rcuk.ac.uk/project/7912459A-4CED-49BB-A529-3E2588E162A1.
- ↑ "Saracatinib impairs maintenance of human T-ALL by targeting the LCK tyrosine kinase in cells displaying high level of lipid rafts". Leukemia 32 (9): 2062–2065. September 2018. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0081-5. PMID 29535432.
 |

