Chemistry:Dichlorodifluoroethane
From HandWiki
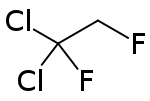
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dichlorodifluoroethane
| |
| Other names
R-132, HCFC 132
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UN number | 3082 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2Cl2F2 | |
| Molar mass | 134.93 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting point | −106.5 °C (−159.7 °F; 166.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 45.1 °C (113.2 °F; 318.2 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Inhalation |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H331 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P301+316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P304+340, P316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P330, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Dichlorodifluoroethane (also known as 1,1-dichloro-1,2-difluoroethane or R-132) is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon with the chemical formula C
2H
3F
2Cl
2). It is a volatile derivative ethane. It appears as a colourless, odorless non-flammable liquid.[2] The use of Dichlorodifluoroethane is restricted by the US EPA through the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 which intend to phase-out the use of substances that deplete the ozone layer, HCFC-132 is cited as an ozone depleting substance, it is considered as a class II substance by the EPA.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "System of Registries | US EPA". https://sor.epa.gov/sor_internet/registry/substreg/searchandretrieve/substancesearch/search.do?details=displayDetails&selectedSubstanceId=80343#HealthAndOther. Retrieved Sep 26, 2022.
- ↑ "1,1-Dichloro-1,2-difluoroethane". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/33239. Retrieved Sep 26, 2022.
- ↑ "System of Registries | US EPA". https://sor.epa.gov/sor_internet/registry/substreg/searchandretrieve/searchbylist/search.do?search=&searchCriteria.substanceList=174&searchCriteria.substanceType=-1. Retrieved Sep 26, 2022.

