Chemistry:Methylglucoside
From HandWiki
Revision as of 14:14, 27 November 2020 by imported>QCDvac (url)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
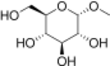
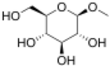
Methyl D-glucopyranoside
| |||
| Other names
1-O-Methyl-D-glucopyranose
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H14O6 | |||
| Molar mass | 194.183 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.46 g/cm3 (α)[1] | ||
| Melting point | 168 °C (334 °F; 441 K) (α)[1] | ||
| 108 g/100 mL[1] | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methylglucoside is a monosaccharide derived from glucose. It can be prepared in the laboratory by the acid-catalyzed reaction of glucose with methanol.[2]
It is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a variety of products including emollients, emulsifiers, humectants, moisturizers, thickening agents, plasticizers, surfactants, varnishes, and resins. The formation of methyl glycoside indicates that the structure of glucose is not open chain[1][3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5997
- ↑ B. Helferich and W. Schäfer (1926). "α-METHYL d-GLUCOSIDE". Organic Syntheses 6: 64. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv1p0364.
- ↑ "Methyl Glucoside Derivatives". Lubrizol. http://www.lubrizol.com/PersonalCare/Products/MethylGlucosideDerivatives/default.html. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
 |