Chemistry:Chromone
From HandWiki
Revision as of 08:51, 21 September 2021 by imported>Importwiki (fixing)
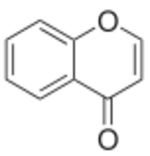
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chromen-4-one
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
4-Chromone; 1,4-Benzopyrone; 4H-Chromen-4-one; Benzo-gamma-pyrone; 1-Benzopyran-4-one; 4H-Benzo(b)pyran-4-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.145 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | -2.0 (of conjugate acid) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Chromone (or 1,4-benzopyrone) is a derivative of benzopyran with a substituted keto group on the pyran ring. It is an isomer of coumarin.
Derivatives of chromone are collectively known as chromones. Most, though not all, chromones are also phenylpropanoids.
Examples
- 6,7-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydrochromone has been isolated from Sarcolobus globosus.
- Eucryphin, a chromone rhamnoside, can be isolated from the bark of Eucryphia cordifolia.[1]
- Cromolyn (disodium cromoglicate) was found to inhibit antigen challenge as well as stress induced symptoms.[2] Cromoglicate is used as a mast cell stabilizer in allergic rhinitis, asthma and allergic conjunctivitis.
- Nedocromil sodium was found to have a somewhat longer half-life than cromolyn; however, production was discontinued in the US in 2008.
- Xanthone with a second aromatic ring.
See also
- Coumarin – a structural isomer
- Furanochromones
References
- ↑ Eucryphin, a new chromone rhamnoside from the bark of Eucryphia cordifolia. R. Tschesche, S. Delhvi, S. Sepulveda and E. Breitmaier, Phytochemistry, Volume 18, Issue 5, 1979, pages 867–869, doi:10.1016/0031-9422(79)80032-1
- ↑ HOWELL, J.B. & ALTOUNYAN, R.E. (1967). A double-blind trial of disodium cromoglycate in the treatment of allergic bronchial asthma. Lancet, 2, 539–542. Abstract
External links
- CID 10286 from PubChem – "4-chromone"
- Chromones at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Synthesis at organic-chemistry.org
 |

