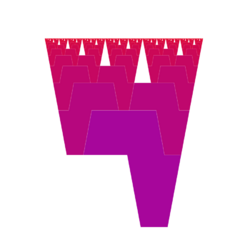
Africa (fractal)
Africa is a fractal made of a set of octagons that have some resemblance to the shape of Africa.[1][2][3] The number of octagons of different sizes in the fractal is related to the Fibonacci sequence: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, .... The height of the largest octagon of the fractal is φ times longer than that of the second octagon; where φ is the golden ratio.[4][5][6]
Definition
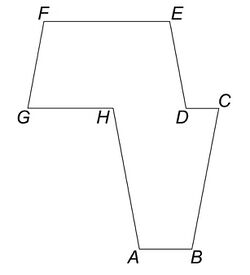
The original version of the fractal was defined by the octagon with the following vertices:[7]
|
[math]\displaystyle{ A=(a_1,a_2)=\left(0,0\right) }[/math] |
[math]\displaystyle{ B=(b_1,b_2)=\left(2,0\right) }[/math] |
|
[math]\displaystyle{ C=(c_1,c_2)=\left(3,\frac{16}{3}\right) }[/math] |
[math]\displaystyle{ D=(d_1,d_2)=\left(4-\sqrt{5}, \frac{16}{3}\right) }[/math] |
|
[math]\displaystyle{ E=(e_1,e_2)=\left(\frac{9-3\sqrt{5}}{2},\frac{8\sqrt{5}+8}{3}\right) }[/math] |
[math]\displaystyle{ F=(f_1,f_2)=\left(\frac{-3+\sqrt{5}}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{5}-3}{2-\sqrt{5}},\frac{8\sqrt{5}+8}{3}\right) }[/math] |
|
[math]\displaystyle{ G=(g_1,g_2)=\left(-1-\frac{\sqrt{5}-3}{2-\sqrt{5}},\frac{16}{3}\right) }[/math] |
[math]\displaystyle{ H=(h_1,h_2)=\left(-1,\frac{16}{3}\right) }[/math] |
The following relations are obvious and necessary based on the shape of fractal:
[math]\displaystyle{ c_1-b_1=a_1-h_1 }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ d_1-e_1=f_1-g_1 }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ c_2-b_2=h_2-a_2 }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ e_2-d_2=f_2-g_2 }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{b_1-a_1}{c_1-d_1}=\frac{c_1-b_1}{d_1-e_1}=\frac{c_2-b_2}{e_2-d_2}= \frac{1+\sqrt5}{2}=\varphi }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{2(h_1-g_1)}{\varphi}+\frac{b_1-a_1}{\varphi^2}=e_1-f_1 }[/math]
where φ is the golden ratio. The fractal is made up of a countable number of copies of the octagon and its lateral inversion. The octagon has some resemblance to the shape of Africa:
Tessellation
The shape of the fractal can form the following tessellations:[8]
Properties
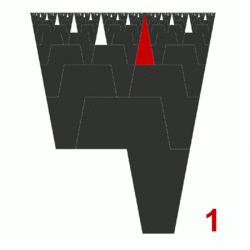
In the fractal, the number of octagons of each size (in order of size) is the Fibonacci sequence from the second term: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, .... The number of isosceles triangles of each size (in order of size) is the Fibonacci sequence from the first term: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, ....[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bellos, Alex (February 24, 2015). "Catch of the day: mathematician nets weird, complex fish". The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/science/alexs-adventures-in-numberland/2015/feb/24/catch-of-the-day-mathematician-nets-weird-complex-fish.
- ↑ Ouellette, Jennifer (February 28, 2015). "Physics Week in Review: February 28, 2015". Scientific American. https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/cocktail-party-physics/physics-week-in-review-february-28-2015/.
- ↑ Chung, Stephy (September 18, 2015). "Next da Vinci? Math genius using formulas to create fantastical works of art". CNN. http://www.cnn.com/2015/09/17/arts/math-art/.
- ↑ "Fractal Africa". The De Morgan Forum – London Mathematical Society. September 21, 2016. http://education.lms.ac.uk/2016/08/hamid-naderi-yeganeh-fractal-africa/.
- ↑ "Importing Things From the Real World Into the Territory of Mathematics!". HuffPost (blog). http://www.huffingtonpost.com/hamid-naderi-yeganeh/importing-things-from-the_b_8111912.html.
- ↑ Antonick, Gary (10 August 2015). "John Conway’s Wizard Puzzle". The New York Times. https://wordplay.blogs.nytimes.com/2015/08/10/feiveson-1/.
- ↑ Alexandre Borovik (2016-08-25). "Hamid Naderi Yeganeh: Fractal Africa" (in en). https://demorgangazette.wordpress.com/2016/08/25/hamid-naderi-yeganeh-fractal-africa/.
- ↑ Hamid Naderi Yeganeh, Africa-Fractal, http://archive.org/details/Africa-Fractal, retrieved 2022-06-23